SEO For 2013 & Beyond: SEO Made Simple For Beginners (2013)
Chapter 1. UNDERSTANDING SEARCH ENGINES
Search engines have special software robots, often called crawlers, whose main job is to locate and build a list of words they find in the websites they go through. The crawlers usually start from popular web pages and heavily used servers, and follow all the links there to spread all over the web.
See the following image (Figure 1.1), created after the illustration in HowStuffWorks1.1.
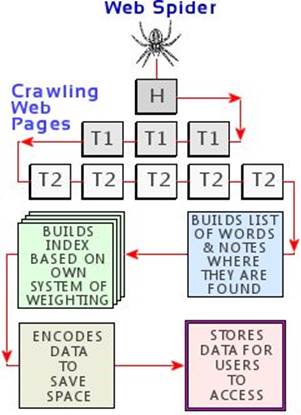
Figure 1.1
When search engine crawlers like Google’s Googlebot visits a webpage, they usually record 2 sets of vital information from the page:
1. Individual words within the page and how frequent are their occurrences, and
2. Where the words are located in the page HTML.
Words that occur in the title tag, other meta tags, and in other special places in the page convey their relative importance in that page. They are noted by the crawler and the concerned page is later considered for listing following a search query for one or more of those relevant words.
Remember that in order to have your website’s pages crawled, they must be ‘found’. This means that at least one page in your website must be linked from another web page that has already been crawled and therefore ‘known’ to the search engine.
How Search Engines Rank Pages
In the above diagram (Figure 1.1) notice that at the time of crawling a webpage, a web spider such as Googlebot builds a list of important words appearing in the webpage (excepting ‘a’, ‘an’, ‘the’), their frequency of appearance, and the places where they occur.
When the same word or more precisely the same group of words appears in the title and sub-titles of the page, in the meta description tag, and also in the body text of the page, the crawling spider may likely consider that group of words as important and relevant for that page.
Following the same procedure, the spider builds an index of relevant words for the webpage based on its own ‘system of weighting’.
In a similar way, the indexing is done for other pages in the website and for all the billions of webpages that are crawled by the search engine spiders.
Finally, the spider encodes the indexed data and stores them securely in another place. This entire cycle of events by the search engine spider goes on non-stop every single moment of every single day.
All search engines have their proprietary, closely-guarded set of rules that determine how much ‘weight’ to give to a webpage with respect to its relevance for a certain word or a group of words. This set of rules is popularly called an algorithm. The algorithm is changed by the search engine owner as and when it feels necessary to do.
When a surfer looks for information for a search term, the search engine immediately dips into the huge mass of encoded storage data, and then fetches the webpages considered the most relevant for the search term in the list of results.
In actuality, the relevance of a webpage vis-à-vis a search term is not dependent on the word indexing only as explained above.
There are other crucial factors that play much bigger roles, like the structure of the website, relevance and spread of contents, quality of incoming links, internal linking, site speed, and so on.
Find out what Google has to say about its algorithms that rank relevant results higher1.2.
What Happens When Search Engine Algorithm Changes
As evident, the listing of relevant webpages in the search results for a particular search term is completely controlled by the algorithm of the respective search engine. Therefore, if there is a change in the algorithm either by design or accident (mainly by design), the list of search results may also change as well.
Usually, the change in algorithm occurs when the search engine wants to update the indexing process. This is necessary for the search engines because they will want to have the most relevant search results presented to the user every time he does a search for his chosen search term.
A simple explanation for an algorithm change can be that when the search engine tests the results for each probable search term it has in its massive repository and finds that there is scope for improvement in the final results in terms of a new set of parameters, it may tweak the algorithm to reflect that.
If you look at the Google Algorithm Change History maintained by Moz1.3, there already have been 7 major changes in 2013 so far after roughly 38 changes in the previous year, 2012.
The recently started MozCast1.4 is what it says a weather report showing turbulence in the Google algorithm. The hotter and stormier the weather the more Google's rankings changed.
From the viewpoint of a small website owner, the change in search engine algorithm is too tech-heavy and distracting to spend time on and be bothered about.
What Is Search Engine Optimization
Search engine optimization, or SEO, its acronym, is the aggregate of all actions that you do to your website as a whole and to all the pages within the site seeking to improve the ranking of the pages in your website in the search engine results.
In practical terms, SEO is a marketing exercise that complements your other marketing efforts with 2 clear objectives:
1. How to bring in visitors to your site from the search engine results, and
2. How to convert the visitors who come to your site
If you have a product or service to sell in your website, you are likely to employ one or more of several marketing methods like, ads, banners, sponsoring events, free offers, etc. However, look closely and you’ll find that the role of all of these marketing methods ends after bringing the visitors to your website.
In sharp contrast, the role of SEO is not only to bring visitors from the search results, but continue thereafter to retain and convert them as well.
In this larger role for SEO, there is a paramount need for creating quality and relevant website contents, since it is the contents that attract and retain the visitors in a website.
If the visitors spend more time in a website it is a signal that the contents in the site are liked by them. And when that happens, there is greater chance of converting the visitors to take some kind of action.
Coming to the core of SEO, the issue is how important and relevant a webpage is with respect to a particular set of words, called ‘keywords’, in the eyes of search engines.
To give an example, if the homepage of your website is considered important by Google for the keywords (or key-phrase) ‘online video’, then it has a good chance to rank among the top 10 search results for that search term.
Should that occur…there could be a huge surge in traffic to the homepage, giving you the opportunity to boost your web business.
It is evident that SEO encompasses a wide range of activities, all of which have to work in tandem for the best results. At the very least some important SEO actions are as under:
1. Keyword research
2. Planning site structure
3. Website designing
4. Content development
5. Link building
6. Traffic monitoring
7. Avoiding technical glitches
As against the above, there are some techniques that seek to artificially inflate the relevance of web pages in the eyes of search engines so as to attain higher rankings in the search results. These are known as spamdexing or Black Hat SEO.
3 such common techniques are:
1. Keyword Stuffing
2. Article Spinning
3. Link Farming
The point to note is that spamdexing never serves any good purpose in the long term. They really don’t work nowadays. In fact, search engines like Google are sophisticated enough to locate such attempts in a short time. When that happens, the concerned website is punished to oblivion.
Knowing Google
Google, as we all know, is the largest search engine on the planet. Many of us use Google to search the information we want. For quite some time, it has maintained vice-like grip on search market share, owning as much as two-thirds of the total daily searches in many countries.
At this point, let me briefly refer to a study1.5 by Betsy Sparrow of Columbia University on the use of the Internet. She found that:
Since the advent of search engines…. our brains rely on the Internet for memory. We remember less through knowing information itself than by knowing where the information can be found.
This means that we are relying more and more on the search engines for different information. Imagine therefore what a huge influx of users there will be to the various search engines!!
With that knowledge let’s now understand how Google matters in SEO.
Google in fact is a big marketing company, and its biggest asset is the world’s largest search engine. The Total Google’s revenues1.6 in the 2013 first quarter is a little over $12.9 billion, and nearly 92% ($11.9 billion) of that comes from selling ads. Now this is very important.
As a search engine owner, Google is kind of paranoid about providing the best search experience to the users so that they come back often to use Google. And this in turn increases its revenue from advertising.
As part of its quest for better earnings Google changes the algorithm frequently, maintains an army of human evaluators to check out websites, and does not hesitate to take on big companies who it feels has done wrong things for better rankings.
Main Points to Consider
From the above it can be said that while Google does care about their product which is pretty obvious, what it doesn’t care about is your website and your business.
This may sound harsh, but this is the reality.
In other words, your business may be the best of its type, but as long as it doesn’t fit into Google’s ways of doing things, your website hardly matters to them.
The web is huge, and considering that most traffic originate from the search results, as a small business owner the best roadmap for you will be to do things that work.
Here are some main points to consider and adhere to:
1. Stick to proven SEO techniques.
2. There is no shortcut to SEO.
3. SEO is sum-total of long-drawn & continuous efforts.
4. SEO seeks to level the field between the mightiest & the weakest.
5. Don’t try unethical means; they don’t succeed.
6. Don’t pay heed to every expert view.
7. Find out real SEO experts and follow their views as they do many tests & interact frequently.
I have italicized the first and the third points, because in my view they are crucial for achieving success from SEO for your web business.