Exam Ref 70-696 Managing Enterprise Devices and Apps (2014)
Chapter 7. Provision and manage mobile devices
Mobile devices, whether laptops, tablets, or smartphones, make up an increasing percentage of the devices used to perform work-related activities in organizations. Mobile device management (MDM) enables the organization to manage those devices. You can perform MDM through Microsoft Exchange Server by using Configuration Manager, through Microsoft Intune, or through a combination of Exchange and Microsoft Intune.
Objectives in this chapter:
![]() Objective 7.1: Integrate Configuration Manager with the Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync Connector.
Objective 7.1: Integrate Configuration Manager with the Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync Connector.
![]() Objective 7.2: Manage devices with Microsoft Intune.
Objective 7.2: Manage devices with Microsoft Intune.
![]() Objective 7.3: Manage connection profiles by using Configuration Manager.
Objective 7.3: Manage connection profiles by using Configuration Manager.
Objective 7.1: Integrate Configuration Manager with the Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync Connector
In many organizations, mobile devices already connect to a Microsoft Exchange deployment by using ActiveSync. Although it’s possible to apply mobile device policies directly through Exchange to apply configuration settings to these devices, this requires Exchange administrators to perform MDM tasks. Configuration Manager provides the option of configuring a connector between a Configuration Manager deployment and Microsoft Exchange so that MDM policies set in Configuration Manager are applied through the mobile device’s ActiveSync connection to Exchange Server.
This section covers the following topics:
![]() Exchange Server connector
Exchange Server connector
![]() Connector settings
Connector settings
![]() Connector configuration
Connector configuration
Exchange Server connector
In many organizations, mobile devices connect to an organization’s infrastructure through Microsoft Exchange. Users of mobile devices that are running the iOS, Android, Windows Phone, and Windows Mobile operating systems already synchronize their email messages. The Exchange Server connector for System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager enables you to manage mobile devices remotely that connect to an Exchange Server deployment, without requiring Configuration Manager to enroll these devices directly.
The Exchange Server connector enables you to manage mobile devices by using the Configuration Manager console instead of Exchange ActiveSync mailbox policies. You can use the Exchange Server connector with an on-premises deployment of Exchange and a cloud-based Exchange deployment.
The Exchange Server connector enables you to perform the following mobile device–management tasks:
![]() Discovery Enables Configuration Manager to discover any mobile device that has registered with the Exchange Server environment.
Discovery Enables Configuration Manager to discover any mobile device that has registered with the Exchange Server environment.
![]() Hardware inventory Enables Configuration Manager to perform hardware inventory only based on the information that it receives from Exchange. This is not as comprehensive as a hardware inventory that is available to mobile devices that you manage through the Intune connector for Configuration Manager.
Hardware inventory Enables Configuration Manager to perform hardware inventory only based on the information that it receives from Exchange. This is not as comprehensive as a hardware inventory that is available to mobile devices that you manage through the Intune connector for Configuration Manager.
![]() Settings management Enables you to override default Exchange ActiveSync mailbox policy settings with settings that you configure through the Exchange Server connector for Configuration Manager.
Settings management Enables you to override default Exchange ActiveSync mailbox policy settings with settings that you configure through the Exchange Server connector for Configuration Manager.
![]() Quarantine and block from Exchange Server Enables you to block a mobile device from the Exchange Server organization and from Configuration Manager.
Quarantine and block from Exchange Server Enables you to block a mobile device from the Exchange Server organization and from Configuration Manager.
![]() Remote wipe Enables Exchange Server administrators, the device user, and Configuration Manager administrators to wipe devices remotely.
Remote wipe Enables Exchange Server administrators, the device user, and Configuration Manager administrators to wipe devices remotely.
![]() Reporting Enables basic mobile device–management reports but does not provide all the reports that are available when you manage the device by using the Intune connector for Configuration Manager.
Reporting Enables basic mobile device–management reports but does not provide all the reports that are available when you manage the device by using the Intune connector for Configuration Manager.
When you configure the Exchange Server connector, you determine whether Configuration Manager or Exchange ActiveSync mailbox policies are responsible for managing specific settings, including the following groups:
![]() General
General
![]() Password
Password
![]() Email Management
Email Management
![]() Security
Security
![]() Applications
Applications
The important thing to remember is that after you configure any setting in a group, Configuration Manager is responsible for managing all of that group’s settings. If you do not configure any settings in a group, the applicable Exchange ActiveSync policy remains in effect. When planning to use the Exchange Server connector, remember that responsibility for managing mobile devices will shift from the Exchange administrators to the Configuration Manager administrators.
General settings
The General Settings group of policies, shown in Figure 7-1, enables you to configure the following settings:
![]() Internet Sharing From Mobile Devices Whether the device allows tethering
Internet Sharing From Mobile Devices Whether the device allows tethering
![]() Computer Synchronization Whether the device can be synchronized with a computer
Computer Synchronization Whether the device can be synchronized with a computer
![]() Allow mobile devices that cannot be provisioned Whether mobile devices that cannot be managed completely by Exchange can make connection
Allow mobile devices that cannot be provisioned Whether mobile devices that cannot be managed completely by Exchange can make connection
![]() Refresh Interval (Hours) How often the mobile device policy is refreshed
Refresh Interval (Hours) How often the mobile device policy is refreshed
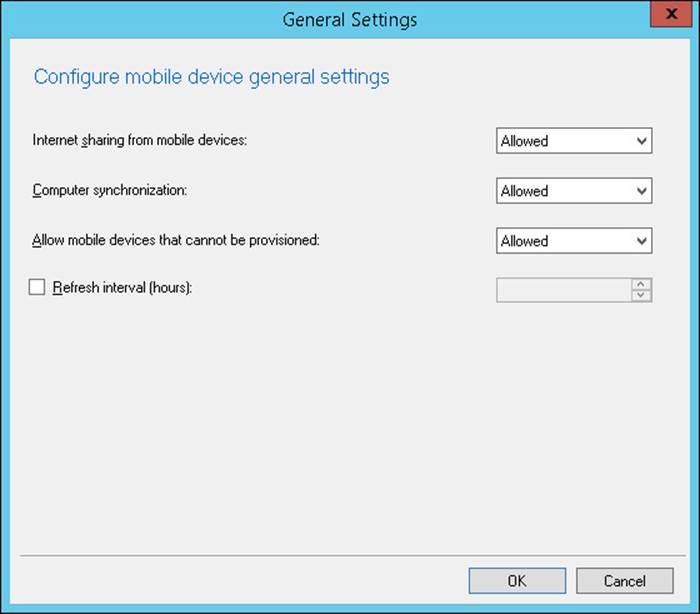
FIGURE 7-1 General Settings
Password settings
The Password Settings group, shown in Figure 7-2, enables you to configure the following settings:
![]() Require Password Settings On Mobile Devices Whether to require a password to unlock the mobile device
Require Password Settings On Mobile Devices Whether to require a password to unlock the mobile device
![]() Minimum Password Length (Characters) Minimum required password length
Minimum Password Length (Characters) Minimum required password length
![]() Password Expiration In Days Maximum password age
Password Expiration In Days Maximum password age
![]() Number Of Passwords Remembered How many unique passwords are stored before one can be reused
Number Of Passwords Remembered How many unique passwords are stored before one can be reused
![]() Number Of Failed Logon Attempts Before Device Is Wiped Number of incorrect password entries that can be made before the device wipes
Number Of Failed Logon Attempts Before Device Is Wiped Number of incorrect password entries that can be made before the device wipes
![]() Idle Time In Minutes Before Mobile Device Is Locked Number of minutes of inactivity before the device locks
Idle Time In Minutes Before Mobile Device Is Locked Number of minutes of inactivity before the device locks
![]() Password Complexity Whether complex passwords are required
Password Complexity Whether complex passwords are required
![]() Minimum Number Of Complex Characters Number of character types required in a complex password (uppercase/lowercase/symbol/number)
Minimum Number Of Complex Characters Number of character types required in a complex password (uppercase/lowercase/symbol/number)
![]() Allow Simple Password Whether to allow a simple password
Allow Simple Password Whether to allow a simple password
![]() Allow Password Recovery Whether to allow passwords to be recovered by administrators
Allow Password Recovery Whether to allow passwords to be recovered by administrators
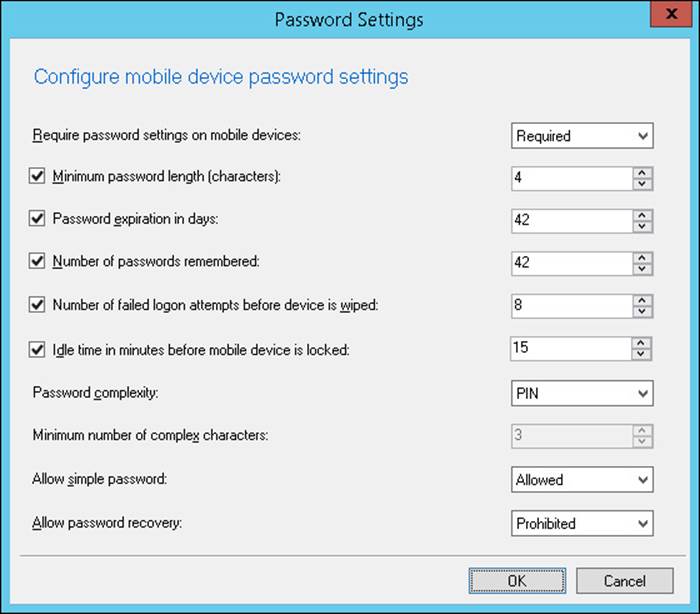
FIGURE 7-2 Password Settings
Email management
The Email Management Settings group, shown in Figure 7-3, enables you to configure the following settings:
![]() POP And IMAP Email Whether to allow POP and IMAP protocol email
POP And IMAP Email Whether to allow POP and IMAP protocol email
![]() Maximum Time To Keep Email How long email will be stored
Maximum Time To Keep Email How long email will be stored
![]() Maximum Time To Keep Calendar Entries How long calendar entries can be stored
Maximum Time To Keep Calendar Entries How long calendar entries can be stored
![]() Direct Push When Roaming Whether to allow Direct Push when the mobile device is on a roaming network
Direct Push When Roaming Whether to allow Direct Push when the mobile device is on a roaming network
![]() Allowed Message Formats Whether to allow HTML and/or plaintext messaging formats
Allowed Message Formats Whether to allow HTML and/or plaintext messaging formats
![]() Size Limit In Kilobytes (KB) For Plain Text Email (Automatically Downloaded) Maximum size of plaintext messages that will be automatically downloaded
Size Limit In Kilobytes (KB) For Plain Text Email (Automatically Downloaded) Maximum size of plaintext messages that will be automatically downloaded
![]() Size Limit In KB For HTML Email (Automatically Downloaded) Maximum size for HTML format messages that will be downloaded
Size Limit In KB For HTML Email (Automatically Downloaded) Maximum size for HTML format messages that will be downloaded
![]() Email Attachments Whether to allow email attachments to be downloaded
Email Attachments Whether to allow email attachments to be downloaded
![]() Size Limit In KB For Email Attachments (Automatically Downloaded) Maximum size for automatically downloaded email attachments
Size Limit In KB For Email Attachments (Automatically Downloaded) Maximum size for automatically downloaded email attachments
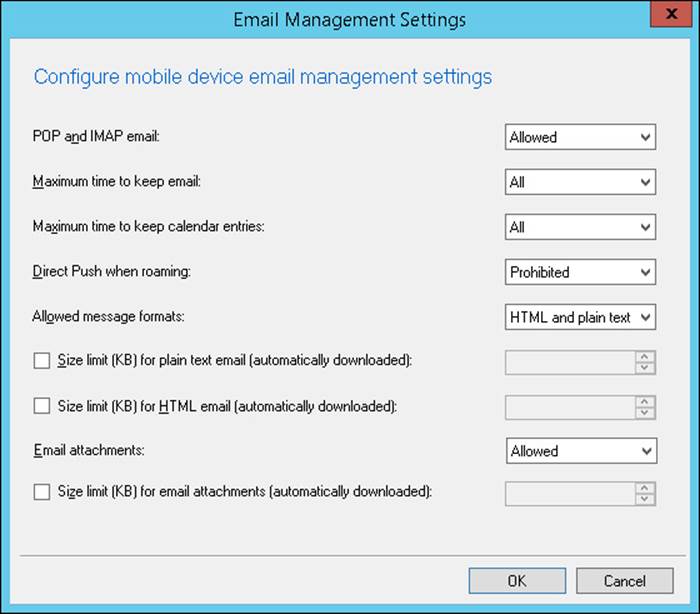
FIGURE 7-3 Email Management Settings
Security
The Security Settings group, shown in Figure 7-4, enables you to configure the following settings:
![]() Remote Desktop Whether the device supports Remote Desktop
Remote Desktop Whether the device supports Remote Desktop
![]() Removable Storage Whether the device supports removable storage
Removable Storage Whether the device supports removable storage
![]() Camera Whether the device’s camera can be used
Camera Whether the device’s camera can be used
![]() Bluetooth Whether Bluetooth functionality can be used
Bluetooth Whether Bluetooth functionality can be used
![]() Wireless Network Connections Whether to allow connections to a wireless network
Wireless Network Connections Whether to allow connections to a wireless network
![]() Infrared Whether to allow infrared connections
Infrared Whether to allow infrared connections
![]() Browser Whether to allow use of the mobile device’s browser
Browser Whether to allow use of the mobile device’s browser
![]() Storage Card Encryption Whether to enforce encryption on any storage card
Storage Card Encryption Whether to enforce encryption on any storage card
![]() File Encryption On Mobile Device Whether to require encryption on the mobile device itself
File Encryption On Mobile Device Whether to require encryption on the mobile device itself
![]() Short Message Service (SMS) And Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) Messaging Whether to allow SMS/MMS functionality on the device
Short Message Service (SMS) And Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS) Messaging Whether to allow SMS/MMS functionality on the device
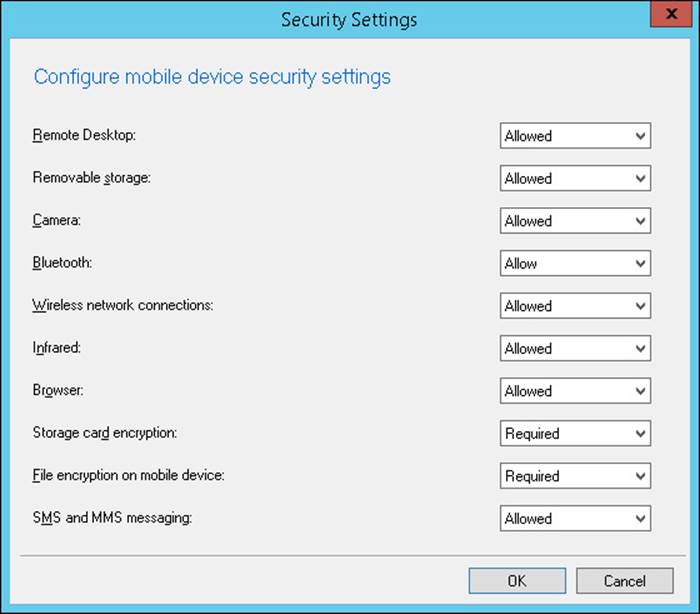
FIGURE 7-4 Security Settings
Applications
The Applications Settings group, shown in Figure 7-5, enables you to configure the following settings:
![]() Unsigned File Installation Whether to allow the installation of unsigned files
Unsigned File Installation Whether to allow the installation of unsigned files
![]() Unsigned Applications Whether to allow the installation of unsigned applications
Unsigned Applications Whether to allow the installation of unsigned applications
![]() Block The Following Applications In ROM A list of specifically blocked applications
Block The Following Applications In ROM A list of specifically blocked applications
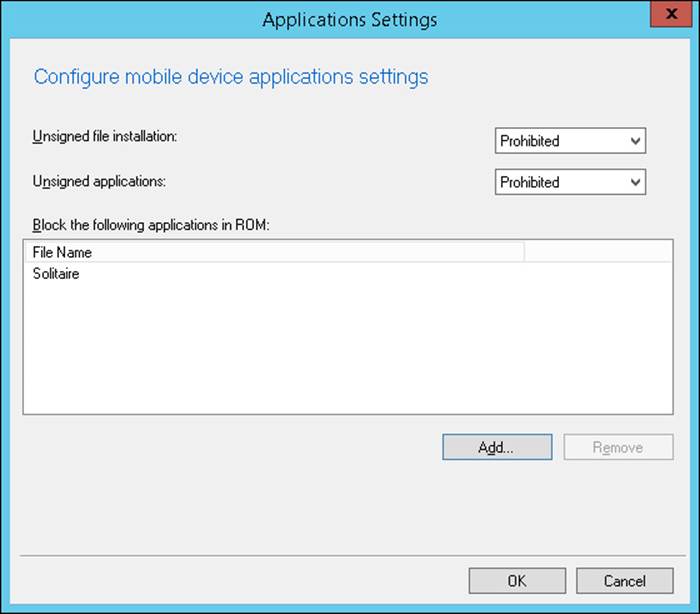
FIGURE 7-5 Applications Settings
Connector configuration
You should configure the account that you want to use when you set up an Exchange Server connector to be a member of the following Exchange management roles:
![]() Recipient Management
Recipient Management
![]() View Only Organization Management
View Only Organization Management
![]() Server Management
Server Management
The Exchange Server connector enables you to manage any device that supports Exchange ActiveSync, although not all devices that use Exchange ActiveSync support all Exchange ActiveSync management functionality. The Exchange Server connector does not install a client on the mobile device that you are managing. This means that using the Exchange Server connector provides only a subset of the functionality available for mobile device management when compared to managing the same devices through the Configuration Manager Intune connector.
When you configure the Exchange Server connector, you specify the address of a Client Access server as shown in Figure 7-6. When configuring the address of the client access server, specify one that is in the same Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) site as the Configuration Manager site system server.
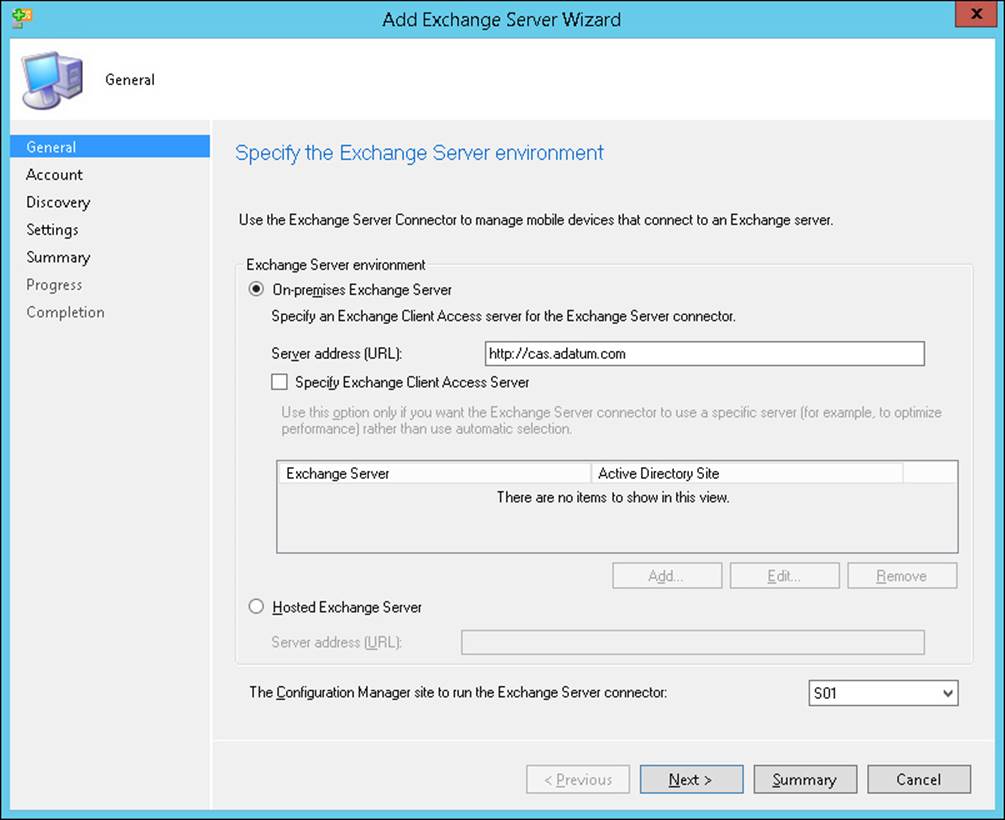
FIGURE 7-6 Add Exchange Server Wizard
The Exchange Server connector connects through the client access server to configure the default Exchange ActiveSync mailbox policy on the mailbox server. Even though the mailbox server is used to interact with the policy, the policy itself is stored within Active Directory Domain Services.
The first time a mobile device connects to the client access server, it retrieves the policy. Every subsequent time that the device connects to the client access server, it checks to see whether there are updates to the policy. If the policy has been updated, the mobile device downloads and applies the new policy.
More Info: Configuration Manager and Activesync
You can learn more about Configuration Manager and ActiveSync at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/gg682001.aspx.
More Info: Mobile Device Management
You can learn more about the Microsoft mobile device management strategy by watching the session from TechED New Zealand in 2014 at http://channel9.msdn.com/events/TechEd/NewZealand/2014/PCIT305.
 Exam Tip
Exam Tip
Remember which type of Exchange Server you specify when creating the connection between Configuration Manager and Exchange.
 Thought experiment: ActiveSync MDM at Fabrikam
Thought experiment: ActiveSync MDM at Fabrikam
You are responsible for MDM at Fabrikam, a manufacturer of surveillance drones. You have configured the Configuration Manager ActiveSync connector for Exchange and will be managing MDM policies from Configuration Manager. You will be implementing policies as required. Because of the secure nature of Fabrikam’s facilities, you need to ensure that the cameras on any mobile phones brought into the facilities are disabled. In addition, because several Fabrikam executives travel extensively overseas, you want to ensure that Direct Push functionality is disabled when their mobile phones are connected to roaming networks. With this in mind, answer the following questions:
1. Which settings group would you configure to ensure that mobile device cameras cannot be used on mobile devices managed at Fabrikam?
2. Which settings group would you configure to block Direct Push notifications when a mobile device is connected to a roaming network?
Objective summary
![]() The Exchange Server connector enables you to configure mobile device policies applied through ActiveSync to devices that connect to an Exchange deployment.
The Exchange Server connector enables you to configure mobile device policies applied through ActiveSync to devices that connect to an Exchange deployment.
![]() After you configure one setting in a settings group, all settings in that group will be managed through Configuration Manager rather than through Exchange.
After you configure one setting in a settings group, all settings in that group will be managed through Configuration Manager rather than through Exchange.
![]() When configuring the Exchange Server connector on the Configuration Manager server, specify the address of the client access server.
When configuring the Exchange Server connector on the Configuration Manager server, specify the address of the client access server.
![]() The Exchange Server connector enables you to perform Discovery, Hardware Inventory, Settings Management, Remote Wipe, Reporting, and Quarantine And Block from Exchange Server.
The Exchange Server connector enables you to perform Discovery, Hardware Inventory, Settings Management, Remote Wipe, Reporting, and Quarantine And Block from Exchange Server.
Objective review
Answer the following questions to test your knowledge of the information in this objective. You can find the answers to these questions and explanations of why each answer choice is correct or incorrect in the “Answers” section at the end of the chapter.
1. You are configuring the Configuration Manager Exchange Server connector. Your organization has an Exchange Server 2010 deployment. Each Exchange Server role is located on a separate server. Which of the following server addresses should you specify when creating the connector?
A. The address of the Hub Transport server
B. The address of the mailbox server
C. The address of the client access server
D. The address of the Edge Transport server
2. Which of the following Exchange Server ActiveSync connector settings would you configure to ensure that a person must change her mobile device password every five weeks?
A. Minimum Password Length
B. Password Expiration In Days
C. Number Of Passwords Remembered
D. Number Of Failed Logon Attempts Before The Device Is Wiped
3. Which of the following Exchange Server ActiveSync connector settings would you configure to ensure that a person cannot use one of his 20 previously used passwords the next time he has to change his mobile device password?
A. Number Of Failed Logon Attempts Before The Device Is Wiped
B. Number Of Passwords Remembered
C. Password Expiration In Days
D. Minimum Password Length
4. You work at a secure facility. You want to ensure that people cannot unlock a stolen mobile device by randomly attempting to guess the password. Which of the following Exchange Server ActiveSync connector settings would you configure to ensure that the device is wiped if such an attempt is made?
A. Password Expiration In Days
B. Minimum Password Length
C. Number Of Failed Logon Attempts Before The Device Is Wiped
D. Number Of Passwords Remembered
Objective 7.2: Manage devices with Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune (formerly Windows Intune) is a cloud-based management service. You can use it to manage enrolled mobile devices through a web portal. You can also configure a connector between Intune and an on-premises Configuration Manager deployment. When you do this, Intune functions as a conduit through which Configuration Manager policies are applied.
This section covers the following topics:
![]() Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune
![]() Integrating Microsoft Intune with Configuration Manager
Integrating Microsoft Intune with Configuration Manager
![]() Device enrollment
Device enrollment
Microsoft Intune
Microsoft Intune is a cloud-based management service that enables you to manage client computers and mobile devices. You can use Intune to perform the following tasks:
![]() Deploy and manage software updates
Deploy and manage software updates
![]() Deploy and manage applications
Deploy and manage applications
![]() Inventory hardware and software
Inventory hardware and software
![]() Manage endpoint protection
Manage endpoint protection
![]() Perform remote assistance
Perform remote assistance
![]() Manage mobile devices
Manage mobile devices
![]() Manage software licensing
Manage software licensing
![]() Configure Windows Firewall policy
Configure Windows Firewall policy
You can use Intune to perform management tasks on computers that rarely connect to an organizational network. You can also use Intune to perform management tasks on a device that is not joined to an Active Directory domain. Intune also enables you to manage software deployment for computers that are running Windows, Android, and Apple iOS operating systems.
You do not need a Configuration Manager deployment to use Intune, but you can integrate Intune into a Configuration Manager deployment. Using Configuration Manager with Intune enables you to manage all of your organization’s devices, both mobile devices and traditional computers, using a single console.
Intune supports management of clients on the following operating systems:
![]() Windows 8.1 (x86, x64), Windows 8 (x86, x64), Windows 7, and Windows Vista
Windows 8.1 (x86, x64), Windows 8 (x86, x64), Windows 7, and Windows Vista
![]() Windows RT 8.1 and Windows RT
Windows RT 8.1 and Windows RT
![]() Windows Phone 8 and Windows Phone 8.1
Windows Phone 8 and Windows Phone 8.1
![]() Apple iOS 6, iOS 7, and iOS 8
Apple iOS 6, iOS 7, and iOS 8
![]() Android 4
Android 4
More Info: Set Up Intune
You can learn more about setting up Intune at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn646960.aspx.
Application deployment with Microsoft Intune
Each operating system Intune manages has different requirements according to what is needed to perform application deployment.
To deploy applications directly to mobile devices that are running Windows RT, you must obtain sideloading keys, and you must have a code-signing certificate to sign the applications. The Windows RT or Windows Phone 8 device must trust this code-signing certificate. In addition, you can use deep linking to deploy an application from the appropriate Windows App store directly to mobile devices that are running the Windows RT, Windows RT 8.1, Windows Phone 8, or Windows Phone 8.1 operating systems.
You can use Intune to deploy applications to iOS devices by deep linking to the Apple Store or by sideloading apps, which means you are installing them by using direct access to the source files. To deploy applications to iOS devices, you must obtain the appropriate mobile device management certificates from Apple. You can use a similar process for devices running the Android operating system.
More Info: Intune Application Deployment
You can learn more about Intune application deployment at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn646955.aspx.
Integrating Microsoft Intune with Configuration Manager
To configure the connector between Intune and System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager or System Center 2012 Configuration Manager with SP1, you must create the connector and deploy the Intune connector site system role.
Prior to configuring the Intune connector, you should ensure that you perform the following tasks:
![]() Sign up for an Intune organizational account. Before you can configure the connector, you must have Intune administrator credentials for the organizationname.onmicrosoft. com domain. Do not use the account that you used to sign up for Intune (the Outlook.com, Hotmail.com, orlive.com Microsoft account) to configure the connector.
Sign up for an Intune organizational account. Before you can configure the connector, you must have Intune administrator credentials for the organizationname.onmicrosoft. com domain. Do not use the account that you used to sign up for Intune (the Outlook.com, Hotmail.com, orlive.com Microsoft account) to configure the connector.
![]() Add a public company domain to Intune. You should have a public company domain for which you can create Domain Name System (DNS) resource records, and you must configure this domain within Intune. This isn’t a requirement, but it is highly recommended.
Add a public company domain to Intune. You should have a public company domain for which you can create Domain Name System (DNS) resource records, and you must configure this domain within Intune. This isn’t a requirement, but it is highly recommended.
![]() If you have a public domain name that you will be using with Intune, configure user account, or user principal name (UPN), suffixes. You must configure user accounts with UPNs for the public company domain.
If you have a public domain name that you will be using with Intune, configure user account, or user principal name (UPN), suffixes. You must configure user accounts with UPNs for the public company domain.
![]() Configure directory synchronization. You must configure Active Directory synchronization between your on-premises Active Directory and the Microsoft Azure Active Directory that you are using with the Intune organizationname.onmicrosoft.com domain.
Configure directory synchronization. You must configure Active Directory synchronization between your on-premises Active Directory and the Microsoft Azure Active Directory that you are using with the Intune organizationname.onmicrosoft.com domain.
![]() Create a DNS alias. Create a canonical name (CNAME) record in DNS that maps enterpriseenrollment.organizationname.com (where organizationname.com is your organization’s DNS suffix) to manage.microsoft.com.
Create a DNS alias. Create a canonical name (CNAME) record in DNS that maps enterpriseenrollment.organizationname.com (where organizationname.com is your organization’s DNS suffix) to manage.microsoft.com.
![]() Obtain relevant certificates or keys. Depending on the mobile devices that you will be managing through Intune, you need the certificates or keys that are listed in the following table.
Obtain relevant certificates or keys. Depending on the mobile devices that you will be managing through Intune, you need the certificates or keys that are listed in the following table.
Depending on the mobile device operating system, you will need certificates or keys to enroll mobile devices through the Intune with Configuration Manager connector. Table 7-1 details those specifications.
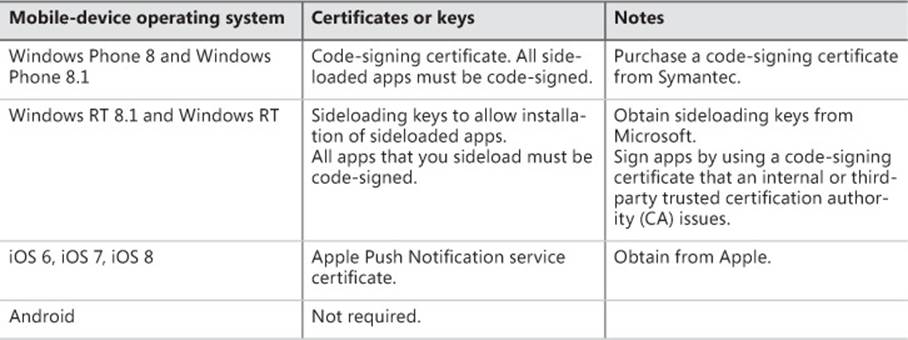
TABLE 7-1 Mobile device operating system requirements
To create the Intune connector, you must perform the following procedure:
1. In the Administration workspace, expand the Hierarchy Configuration folder and then click Microsoft Intune Subscriptions.
2. On the ribbon, click Add Microsoft Intune Subscription.
3. On the Introduction page, click Next.
4. On the Subscription page, sign in by using an account configured as an administrator for your Intune organization. Select the Allow The Configuration Manager Console To Manage This Subscription check box.
5. Review the privacy links.
6. On the General page, specify the following settings:
![]() Collection: Specify which user collection contains users who will enroll their mobile devices.
Collection: Specify which user collection contains users who will enroll their mobile devices.
![]() Company name: Specify your organization name.
Company name: Specify your organization name.
![]() URL to company privacy information: Provide privacy information (optional).
URL to company privacy information: Provide privacy information (optional).
![]() Color scheme for company portal: Change the color of the company portal if desired.
Color scheme for company portal: Change the color of the company portal if desired.
![]() Configuration Manager site code: Specify the primary site for mobile devices.
Configuration Manager site code: Specify the primary site for mobile devices.
7. On the Platforms page, choose the device types you want to manage and then review the platform requirements. For each device type that you select, you need to configure additional settings. You can configure these settings on a per-device basis when necessary.
When you enable Allow The Configuration Manager Console To Manage This Subscription, Configuration Manager takes control of the Intune subscription for mobile device management. You cannot undo this step. If you later decide that you do not want to manage Intune by using Configuration Manager, you must create a new Intune subscription.
To deploy the site system role for the Intune connector, perform the following procedure on a site system server that communicates with the Intune servers that manage.microsoft.com hosts:
1. In the Administration workspace, expand the Site Configuration folder and then click Servers And Site System Roles.
2. Select the site system server and then click Add Site System Roles on the ribbon.
3. On the System Role Selection page, select Microsoft Intune Connector and then click Next.
4. Complete the wizard.
More Info: Integrating Intune with Configuration Manager
You can learn more about integrating Intune with Configuration Manager at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj884158.aspx.
Device enrollment
Each mobile device operating system uses a different method to enable users to self-enroll their mobile devices, with the method sometimes different depending on whether you are using Intune as a standalone product or have configured integration with Configuration Manager. You can use the following method:
![]() Windows Phone 8 and Windows Phone 8.1 To enroll a Windows Phone 8 device, users select Company Apps or Workplace from their phones’ Settings screen. They then provide their domain credentials in the form of their UPN and password. The user is then prompted to install the company app or hub, which installs the company portal. The device collects inventory and applies management settings. Users then can access any available apps.
Windows Phone 8 and Windows Phone 8.1 To enroll a Windows Phone 8 device, users select Company Apps or Workplace from their phones’ Settings screen. They then provide their domain credentials in the form of their UPN and password. The user is then prompted to install the company app or hub, which installs the company portal. The device collects inventory and applies management settings. Users then can access any available apps.
![]() Windows RT 8.1 and Windows RT To enroll a Windows RT 8 device, go to the Workspace section of settings and provide the organizational credentials as shown in Figure 7-7. This enrolls the Windows RT device in Configuration Manager. If your organization has System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager, you also can download the Company Portal App from the Windows Store and then provide your user credentials.
Windows RT 8.1 and Windows RT To enroll a Windows RT 8 device, go to the Workspace section of settings and provide the organizational credentials as shown in Figure 7-7. This enrolls the Windows RT device in Configuration Manager. If your organization has System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager, you also can download the Company Portal App from the Windows Store and then provide your user credentials.
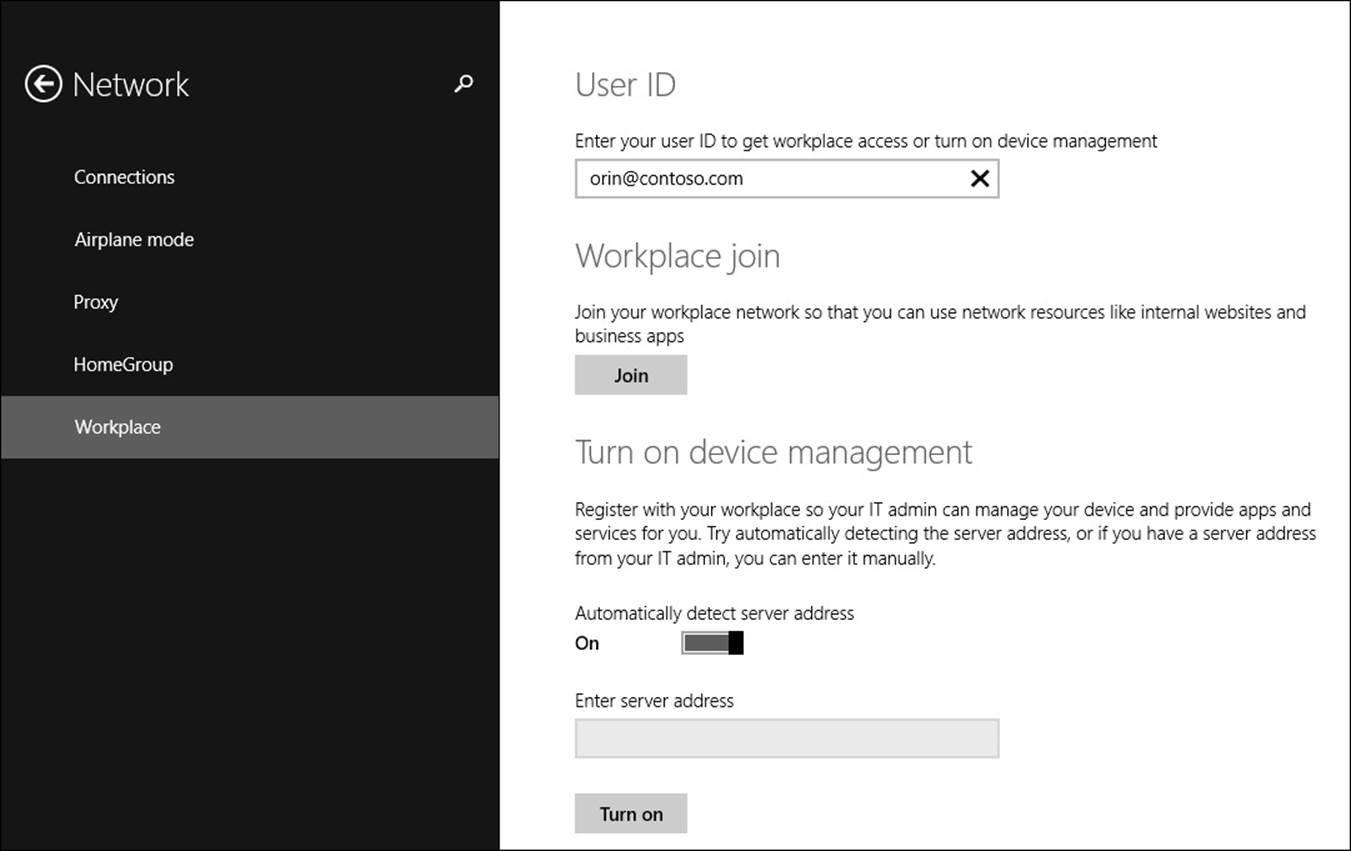
FIGURE 7-7 Workplace join
![]() iOS To enroll an iOS device, use the device’s browser to navigate to manage.microsoft.com and then provide credentials. If your organization has integrated System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager, you can obtain the Company Portal app through the Apple App Store.
iOS To enroll an iOS device, use the device’s browser to navigate to manage.microsoft.com and then provide credentials. If your organization has integrated System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager, you can obtain the Company Portal app through the Apple App Store.
![]() Android Users can enroll mobile devices that are running the Android operating system by acquiring the Company Portal App, without charge, from the Google Play store. They then can provide their credentials in the app to enroll in the Configuration Manager infrastructure. Only System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager supports this method.
Android Users can enroll mobile devices that are running the Android operating system by acquiring the Company Portal App, without charge, from the Google Play store. They then can provide their credentials in the app to enroll in the Configuration Manager infrastructure. Only System Center 2012 R2 Configuration Manager supports this method.
![]() Windows To enroll a computer running Windows 8.1, go to the Workplace settings control panel shown in Figure 7-8 and click Join. You’ll need to be signed on with an appropriate set of credentials. You also can download the Company Portal App from the Windows Store and then provide your user credentials.
Windows To enroll a computer running Windows 8.1, go to the Workplace settings control panel shown in Figure 7-8 and click Join. You’ll need to be signed on with an appropriate set of credentials. You also can download the Company Portal App from the Windows Store and then provide your user credentials.
FIGURE 7-8 Workplace join
More Info: Intune Enrollment
You can learn more about Intune enrollment at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-au/library/dn646957.aspx.
More Info: Integrating Intune with Configuration Manager
You can learn more about integrating Intune with Configuration Manager by watching the MMS 2013 session at http://channel9.msdn.com/events/MMS/2013/UD-B309.
 Exam Tip
Exam Tip
Remember that an Apple Push Notification Service certificate is required to manage devices running iOS. No such certificate is required to manage devices running Android.
 Thought experiment: Intune connector configuration at Tailspin Toys
Thought experiment: Intune connector configuration at Tailspin Toys
You are preparing to deploy an Intune connector between the Tailspin Toys Configuration Manager deployment and a recently activated Intune subscription.
1. With which hostname on the Internet must the site server on which you will deploy the Intune connector be able to communicate?
2. Which account should you specify when configuring the Intune connector on the Configuration Manager site server?
Objective summary
![]() You can use Intune to manage hardware inventory, software inventory, endpoint protection, remote assistance settings, software licensing, and firewall policy.
You can use Intune to manage hardware inventory, software inventory, endpoint protection, remote assistance settings, software licensing, and firewall policy.
![]() You can use Intune to deploy and manage software updates and applications.
You can use Intune to deploy and manage software updates and applications.
![]() You can use Intune separately from Configuration Manager, or you can integrate it with Configuration Manager.
You can use Intune separately from Configuration Manager, or you can integrate it with Configuration Manager.
![]() You can deploy apps to mobile devices by deep linking to the app in the appropriate vendor’s store.
You can deploy apps to mobile devices by deep linking to the app in the appropriate vendor’s store.
![]() You need to have an Apple Push Notification Service certificate from Apple if you want to manage and deploy applications to devices running the iOS operating system.
You need to have an Apple Push Notification Service certificate from Apple if you want to manage and deploy applications to devices running the iOS operating system.
![]() Devices running the Android operating system do not require special certificates to be managed through Intune.
Devices running the Android operating system do not require special certificates to be managed through Intune.
![]() You need to configure directory synchronization between Microsoft Azure Active Directory and on-premises Active Directory if you intend to integrate Intune with Configuration Manager.
You need to configure directory synchronization between Microsoft Azure Active Directory and on-premises Active Directory if you intend to integrate Intune with Configuration Manager.
![]() The site server that hosts the Intune connector must be able to communicate with manage.microsoft.com on the Internet.
The site server that hosts the Intune connector must be able to communicate with manage.microsoft.com on the Internet.
Objective review
Answer the following questions to test your knowledge of the information in this objective. You can find the answers to these questions and explanations of why each answer choice is correct or incorrect in the “Answers” section at the end of the chapter.
1. Which of the following device management tasks can you perform using Intune on a computer running Windows 8.1? (Choose all that apply.)
A. Operating system upgrade
B. BitLocker unlock
C. Application deployment
D. Hardware inventory
2. You work for adatum.com. You are preparing to integrate your on-premises Configuration Manager 2012 R2 deployment with a newly configured Intune subscription. Which of the following DNS configuration changes must you make?
A. Create a CNAME record named enterpriseenrollment.adatum.com that maps to manage.microsoft.com.
B. Create an MX record named enterpriseenrollment.adatum.com that maps to manage.microsoft.com.
C. Create an NS record named enterpriseenrollment.adatum.com that maps to manage.microsoft.com.
D. Create an SRV record named enterpriseenrollment.adatum.com that maps to manage.microsoft.com.
3. Which of the following are necessary if you want to deploy an in-house application by using Intune to 150 tablets running the Windows RT 8.1 operating system? (Choose two. Each correct answer forms part of a complete solution.)
A. Code-signing certificate trusted by the Windows RT 8.1 devices
B. Encryption certificate trusted by the Windows RT 8.1 devices
C. Sideloading keys
D. Activation keys
Objective 7.3: Manage connection profiles by using Configuration Manager
Connection profiles enable you to provision managed devices automatically with settings, including Wi-Fi access point authentication information, virtual private network (VPN) configuration, email account setup, and digital certificate provisioning.
This section covers the following topics:
![]() Remote connection profiles
Remote connection profiles
![]() VPN profiles
VPN profiles
![]() Certificate profiles
Certificate profiles
![]() Email profiles
Email profiles
![]() Wi-Fi profiles
Wi-Fi profiles
Remote connection profiles
You use remote connection profiles to configure Configuration Manager clients so that they can establish remote connections across the Internet to their work computers. This saves you from needing to provide instructions to end users on how they can perform these steps manually. For example, you can use remote connection profiles to configure a collection of desktop computers in the office so that it is possible for appropriately authenticated users on the Internet to establish remote desktop connection sessions. Through these sessions, these users would be able to interact with their office desktop computers directly, allowing access to files, shared folders, and resources such as printers.
You can configure remote connection profiles to:
![]() Force the use of a known Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway) server. Incoming connections will only be allowed if they are initiated from this address. You can configure RD Gateway servers with secure authentication policies so that connections from external clients are appropriately vetted before being forwarded to computers that can host remote desktop connection sessions on protected networks.
Force the use of a known Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway) server. Incoming connections will only be allowed if they are initiated from this address. You can configure RD Gateway servers with secure authentication policies so that connections from external clients are appropriately vetted before being forwarded to computers that can host remote desktop connection sessions on protected networks.
![]() Configure a collection of computers to allow inbound Remote Desktop connection sessions.
Configure a collection of computers to allow inbound Remote Desktop connection sessions.
![]() Limit inbound Remote Desktop connection sessions to users who are listed as primary users of a computer.
Limit inbound Remote Desktop connection sessions to users who are listed as primary users of a computer.
![]() Configure Windows Firewall with advanced security rules so that inbound connections are possible if the computer connects to a domain or private network.
Configure Windows Firewall with advanced security rules so that inbound connections are possible if the computer connects to a domain or private network.
Figure 7-9 shows the creation of a remote connection profile in which an RD Gateway server has been specified and settings allowing connections from primary users are enabled.
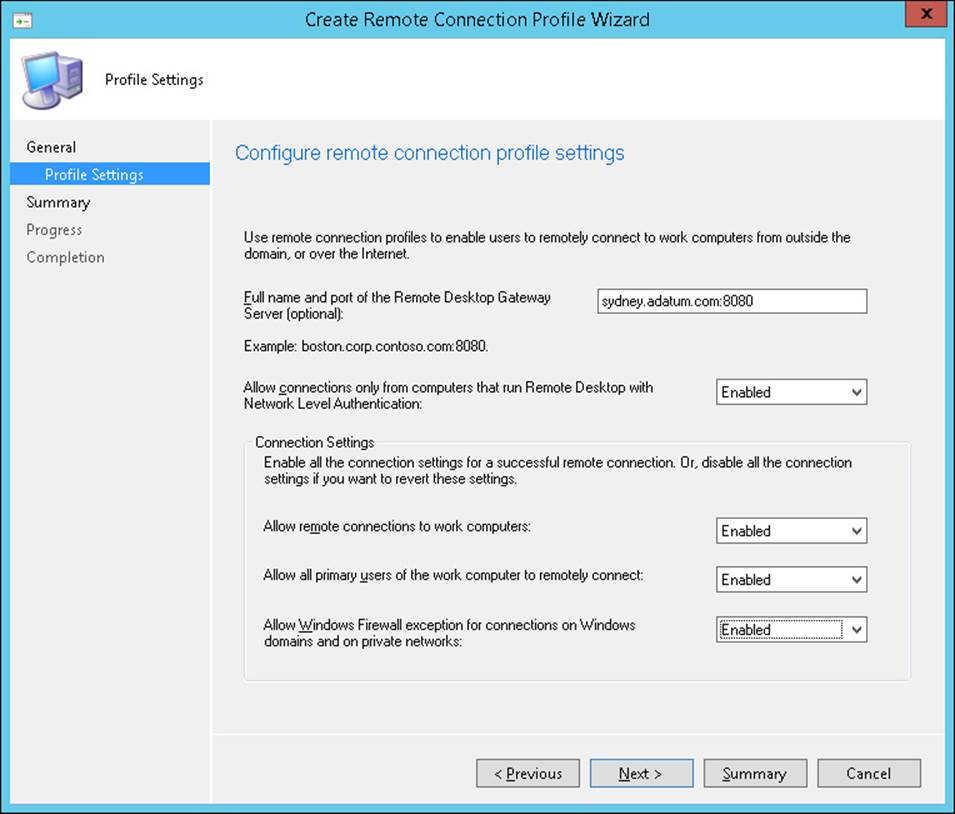
FIGURE 7-9 Create Remote Connection Profile Wizard
More Info: Remote Connection Profiles
You can learn more about remote connection profiles at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn261199.aspx.
VPN profiles
You can use VPN profiles to deploy VPN connection configuration information to Configuration Manager clients that are running Windows 8.1 and Windows RT 8.1 or to iPhone and iPad devices that are running iOS 5, iOS 6, and iOS 7. You can use VPN profiles to deploy VPN connections that use the following connection types:
![]() Cisco AnyConnect
Cisco AnyConnect
![]() Juniper Pulse
Juniper Pulse
![]() F5 Edge Client
F5 Edge Client
![]() Dell SonicWALL Mobile Connect
Dell SonicWALL Mobile Connect
![]() Check Point Mobile VPN
Check Point Mobile VPN
![]() Microsoft SSL (SSTP)
Microsoft SSL (SSTP)
![]() Microsoft Automatic
Microsoft Automatic
![]() IKEv2
IKEv2
![]() PPTP
PPTP
![]() L2TP
L2TP
The advantage of doing this is that by deploying the profiles to devices, end users will be able to make VPN connections without having to configure them themselves. Figure 7-10 shows the configuration of an IKEv2-based VPN profile.
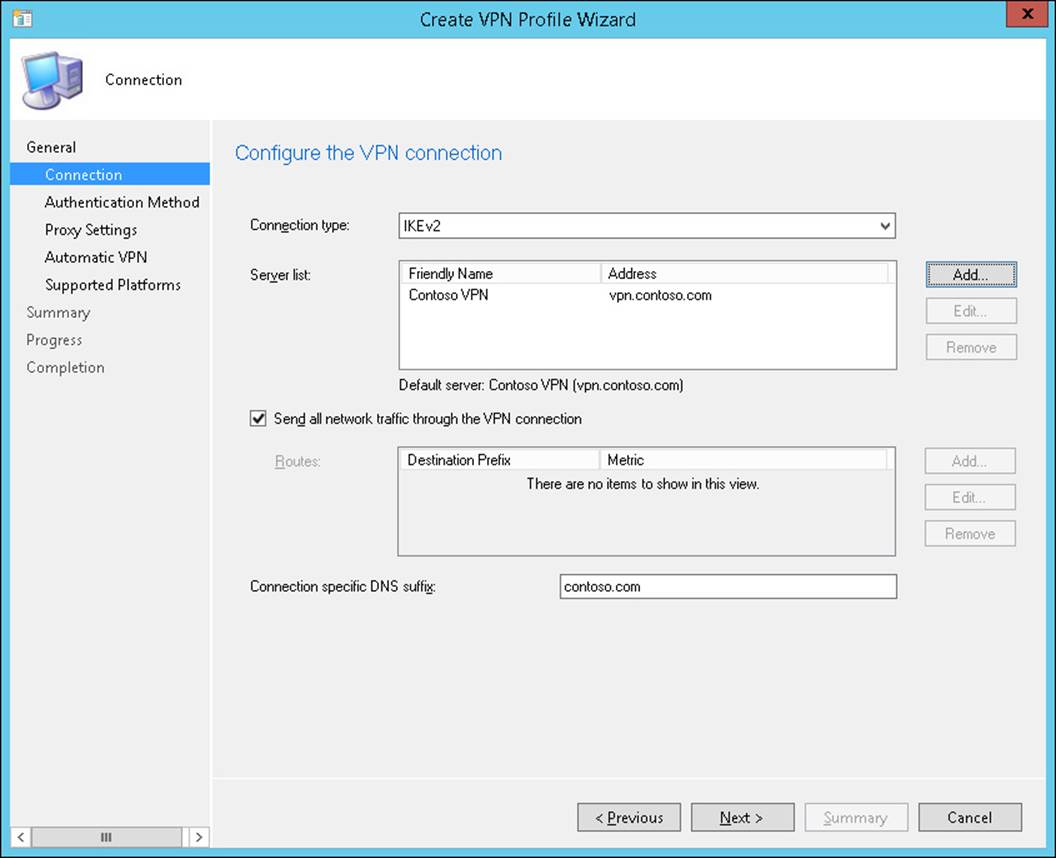
FIGURE 7-10 Create VPN Profile Wizard
More Info: VPN Profiles
You can learn more about VPN profiles at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn261217.aspx.
Certificate profiles
You can use certificate profiles to deploy certificates to Configuration Manager clients. Certificate profiles enable you to configure automatic certificate deployment to clients that cannot participate in the Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) autoenrollment process because they are not members of the organization’s AD DS. The Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, iOS, and Android operating systems support certificate profiles, which in turn support the following functionality:
![]() Certificate enrollment and renewal from enterprise or standalone certification authorities (CAs)
Certificate enrollment and renewal from enterprise or standalone certification authorities (CAs)
![]() Deployment of trusted CA certificates to compatible Configuration Manager clients
Deployment of trusted CA certificates to compatible Configuration Manager clients
![]() Monitoring of and reporting on installed certificates
Monitoring of and reporting on installed certificates
To use certificate profiles, you must deploy the certificate registration point on a site system server either in the central administration site or in a primary site. You cannot deploy this role in a secondary site.
Figure 7-11 shows the configuration of a certificate profile.
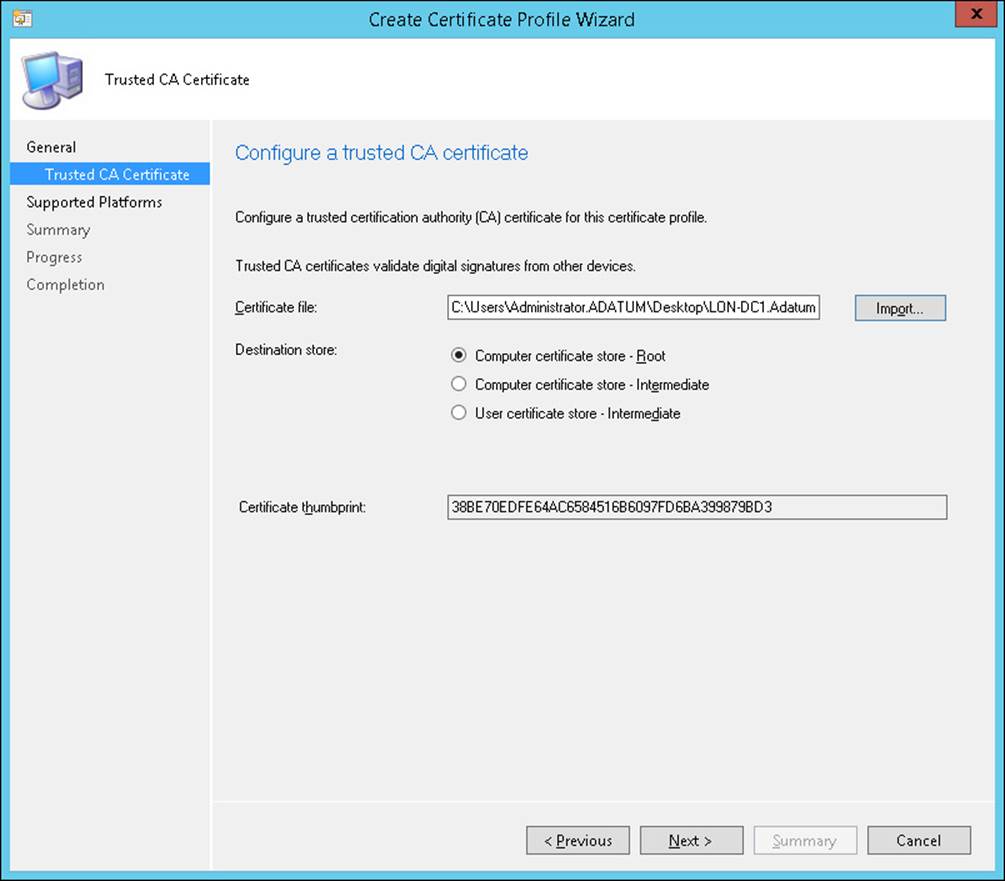
FIGURE 7-11 Create Certificate Profile Wizard
More Info: Certificate Profiles
You can learn more about certificate profiles at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn261202.aspx.
Email profiles
Email profiles are an optional feature in Configuration Manager 2012 R2. They enable you to provision managed devices running Windows Phone 8 and Windows Phone 8.1 or devices running iOS 5, iOS 6, iOS 7, and iOS 8 with profile information for organizational email accounts through Exchange ActiveSync. This minimizes the amount of effort required for a user to provision a connection to his organizational email account. In addition to email settings, an email profile configures synchronization settings for contacts, calendars, and tasks. Before it is possible to configure an email profile, it is necessary to install the Email Profiles Extension for Intune in the Configuration Manager site.
More Info: Email Profiles
You can learn more about email profiles at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-au/library/dn554226.aspx.
Wi-Fi profiles
You can use Wi-Fi profiles to deploy wireless network settings so that devices will connect automatically to preconfigured wireless networks without requiring the user to perform the operation manually. When you deploy Wi-Fi profiles, computers and mobile devices will connect to networks automatically without requiring direct user intervention.
You can use Wi-Fi profiles with devices running the following operating systems:
![]() Windows 8.1 (x86 and x64)
Windows 8.1 (x86 and x64)
![]() Windows RT 8.1
Windows RT 8.1
![]() iOS 5
iOS 5
![]() iOS 6
iOS 6
![]() iOS 7
iOS 7
![]() iOS 8
iOS 8
![]() Android
Android
Figure 7-12 shows a Wi-Fi profile for a wireless network with the SSID Contoso.
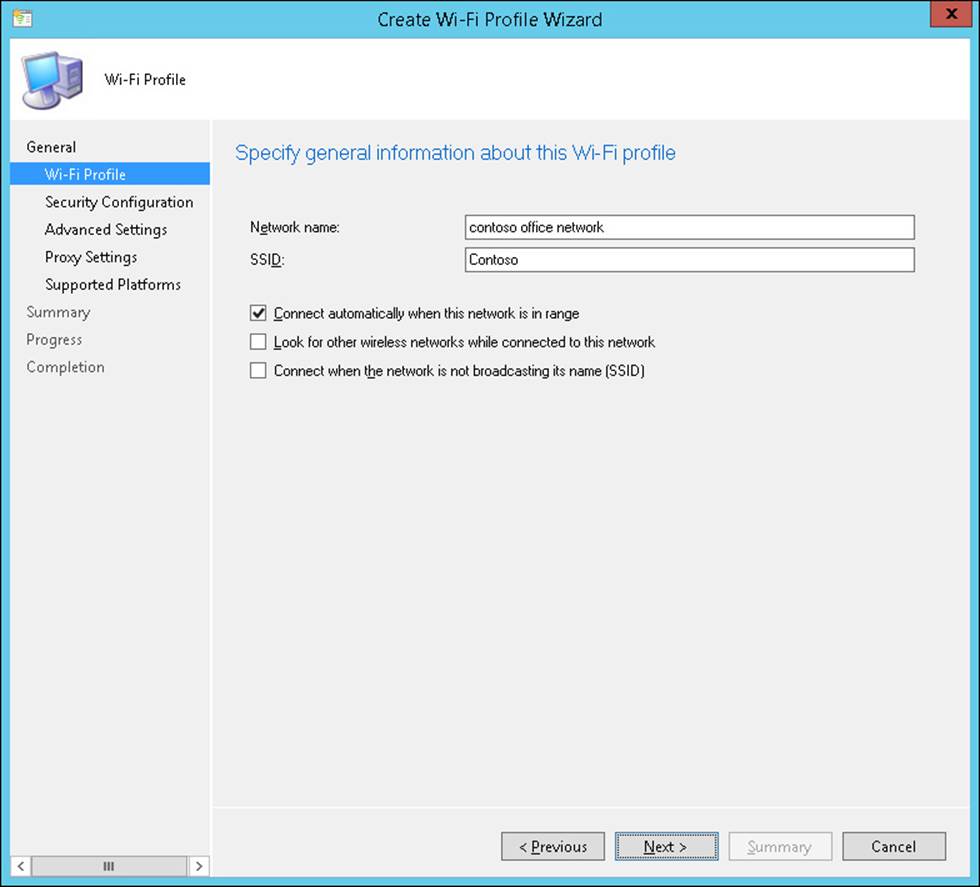
FIGURE 7-12 Create Wi-Fi Profile Wizard
More Info: Wi-Fi Profiles
You can learn more about Wi-Fi profiles at http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dn261221.aspx.
 Exam Tip
Exam Tip
Remember which items can be provisioned using profiles.
 Thought experiment: Managed iOS devices at Contoso
Thought experiment: Managed iOS devices at Contoso
You are using the MDM functionality of Configuration Manager and Intune to manage a large collection of iOS devices at Contoso. You want to ensure that the managed devices trust certificates issued by a standalone CA deployed on the Contoso perimeter network. You also want to ensure that users of managed iOS devices do not have to configure connections manually to the internal Contoso Wi-Fi network. With this information in mind, answer the following questions:
1. What steps can you take to ensure that managed iOS devices trust certificates issued by the standalone CA on the perimeter network?
2. What steps can you take to ensure that managed iOS devices can automatically connect to wireless networks?
Objective summary
![]() Remote connection profiles enable you to deploy Remote Desktop connection configuration information to managed computers, allowing remote access to those computers using a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) client.
Remote connection profiles enable you to deploy Remote Desktop connection configuration information to managed computers, allowing remote access to those computers using a Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) client.
![]() VPN profiles enable you to deploy VPN connection configuration information to managed devices.
VPN profiles enable you to deploy VPN connection configuration information to managed devices.
![]() Certificate profiles enable you to deploy certificates to managed devices.
Certificate profiles enable you to deploy certificates to managed devices.
![]() Email profiles enable you to deploy email, calendar, contacts, and tasks configuration information to managed devices.
Email profiles enable you to deploy email, calendar, contacts, and tasks configuration information to managed devices.
![]() Wi-Fi profiles enable you to deploy wireless network configuration information to managed devices.
Wi-Fi profiles enable you to deploy wireless network configuration information to managed devices.
Objective review
Answer the following questions to test your knowledge of the information in this objective. You can find the answers to these questions and explanations of why each answer choice is correct or incorrect in the “Answers” section at the end of the chapter.
1. You want to allow people to connect using Remote Desktop connection from their home computers, through an RD Gateway server deployed on your organization’s perimeter network, to their work desktop computers on your organization’s internal network. Which of the following profiles should you deploy to accomplish this goal?
A. Email profile
B. Certificate profile
C. VPN profile
D. Remote connection profile
2. You are testing a new device that uses a self-signed certificate to encrypt communication. You want to configure 30 Configuration Manager clients so that they trust this self-signed certificate. Which of the following profiles would you deploy to accomplish this goal?
A. Email profile
B. Certificate profile
C. VPN profile
D. Remote connection profile
3. You are switching your remote access service from an SSTP VPN to an IKEv2 VPN because this allows automatic reconnection without requiring user reauthentication. Which of the following profiles would you deploy to mobile computers so that they are updated with this new VPN connection information?
A. Remote connection profile
B. Certificate profile
C. VPN profile
D. Email profile
4. Which of the following can you use to configure nondomain-joined computers running the Windows 8.1 operating system with the appropriate settings that allow them to connect to your organization’s Exchange deployment?
A. Email profile
B. Certificate profile
C. VPN profile
D. Remote connection profile
Answers
Objective 7.1
Thought experiment
1. You would configure the Security Settings group to ensure that mobile device cameras cannot be used at Fabrikam.
2. You would configure the Email Management Settings group to block Direct Push notifications when a mobile device is connected to a roaming network.
Objective review
1. Correct Answer: C
A. Incorrect: When configuring the connector, you have to provide the address of the client access server.
B. Incorrect: When configuring the connector, you have to provide the address of the client access server.
C. Correct: When configuring the connector, you have to provide the address of the client access server.
D. Incorrect: When configuring the connector, you have to provide the address of the client access server.
2. Correct Answer: B
A. Incorrect: The Minimum Password Length setting configures minimum password length.
B. Correct: You would configure the Password Expiration In Days setting and set the value to 35 days if you wanted people to change their mobile device’s password every five weeks.
C. Incorrect: Use the Number Of Passwords Remembered setting to ensure that passwords cannot be reused.
D. Incorrect: Use the Number Of Failed Logon Attempts Before The Device Is Wiped setting to ensure that a device is wiped if a password is incorrectly entered a number of times in succession.
3. Correct Answer: B
A. Incorrect: Use the Number Of Failed Logon Attempts Before The Device Is Wiped setting to ensure that a device is wiped if a password is incorrectly entered a number of times in succession.
B. Correct: Use the Number Of Passwords Remembered setting to ensure that passwords cannot be reused.
C. Incorrect: The Password Expiration In Days setting determines how often a person must change her mobile device password.
D. Incorrect: The Minimum Password Length setting configures minimum password length.
4. Correct Answer: C
A. Incorrect: The Password Expiration In Days setting determines how often a person must change his mobile device password.
B. Incorrect: The Minimum Password Length setting configures minimum password length.
C. Correct: Use the Number Of Failed Logon Attempts Before The Device Is Wiped setting to ensure that a device is wiped if a password is incorrectly entered a number of times in succession.
D. Incorrect: Use the Number Of Passwords Remembered setting to ensure that passwords cannot be reused.
Objective 7.2
Thought experiment
1. The site server on which you deploy the Intune connector must be able to communicate with the manage.microsoft.com hostname.
2. You must configure an Intune administrator account. You should not use the account that you used to sign up for Intune (the Outlook.com, Hotmail.com, or live.com Microsoft account) to configure the connector.
Objective review
1. Correct Answers: C and D
A. Incorrect: You cannot perform an operating system upgrade by using Intune.
B. Incorrect: You cannot perform BitLocker unlock by using Intune.
C. Correct: You can perform application deployment by using Intune.
D. Correct: You can perform hardware inventory by using Intune.
2. Correct Answer: A
A. Correct: Prior to configuring a connection between an on-premises Configuration Manager deployment and Intune, you must create a canonical name (CNAME) record in DNS that maps enterpriseenrollment.organizationame.com (where organizationname.com is your organization’s DNS suffix) to manage.microsoft.com.
B. Incorrect: You must create a CNAME record. MX records are used to locate mail servers.
C. Incorrect: You must create a CNAME record. NS records are used to locate name servers.
D. Incorrect: You must create a CNAME record. SRV records are used to locate services.
3. Correct Answers: A and C
A. Correct: To deploy an application to computers running Windows RT 8.1 through Intune, you must obtain sideloading keys, and you must have a code-signing certificate to sign the applications.
B. Incorrect: You need a code-signing certificate
C. Correct: To deploy an application to computers running Windows RT 8.1 through Intune, you must obtain sideloading keys, and you must have a code-signing certificate to sign the applications.
D. Incorrect: You need sideloading keys.
Objective 7.3
Thought experiment
1. You can configure a certificate profile to deploy the CA certificate of the standalone CA on the perimeter network to managed devices. This will ensure that the managed iOS devices trust certificates issued by the standalone CA.
2. You can configure a Wi-Fi profile with the authentication details of Wi-Fi networks at Contoso. This will ensure that managed iOS devices can automatically connect to wireless networks.
Objective review
1. Correct Answer: D
A. Incorrect: You use an email profile to provision a device with email, calendar, task, and contacts settings.
B. Incorrect: You can use a certificate profile to deploy a certificate, including a root certificate or a self-signed certificate, to a managed device. This certificate will be trusted.
C. Incorrect: You can use a VPN profile to deploy VPN connection information automatically to managed devices.
D. Correct: You can use a remote connection profile to configure computers so that they will accept inbound Remote Desktop connection requests if specific conditions are met.
2. Correct Answer: B
A. Incorrect: You use an email profile to provision a device with email, calendar, task, and contacts settings.
B. Correct: You can use a certificate profile to deploy a certificate, including a root certificate or a self-signed certificate, to a managed device. This certificate will be trusted.
C. Incorrect: You can use a VPN profile to deploy VPN connection information automatically to managed devices.
D. Incorrect: You can use a remote connection profile to configure computers so that they will accept inbound Remote Desktop connection requests if specific conditions are met.
3. Correct Answer: C
A. Incorrect: You can use a remote connection profile to configure computers so that they will accept inbound Remote Desktop connection requests if specific conditions are met.
B. Incorrect: You can use a certificate profile to deploy a certificate, including a root certificate or a self-signed certificate, to a managed device. This certificate will be trusted.
C. Correct: You can use a VPN profile to deploy VPN connection information automatically to managed devices.
D. Incorrect: You use an email profile to provision a device with email, calendar, task, and contacts settings.
4. Correct Answer: A
A. Correct: You use an email profile to provision a device with email, calendar, task, and contacts settings.
B. Incorrect: You can use a certificate profile to deploy a certificate, including a root certificate or a self-signed certificate, to a managed device. This certificate will be trusted.
C. Incorrect: You can use a VPN profile to deploy VPN connection information automatically to managed devices.
D. Incorrect: You can use a remote connection profile to configure computers so that they will accept inbound remote desktop connection requests if specific conditions are met.