How a Computer Works (2015)
Glossary
PCI Bus Expansion cards connect to the PCI bus
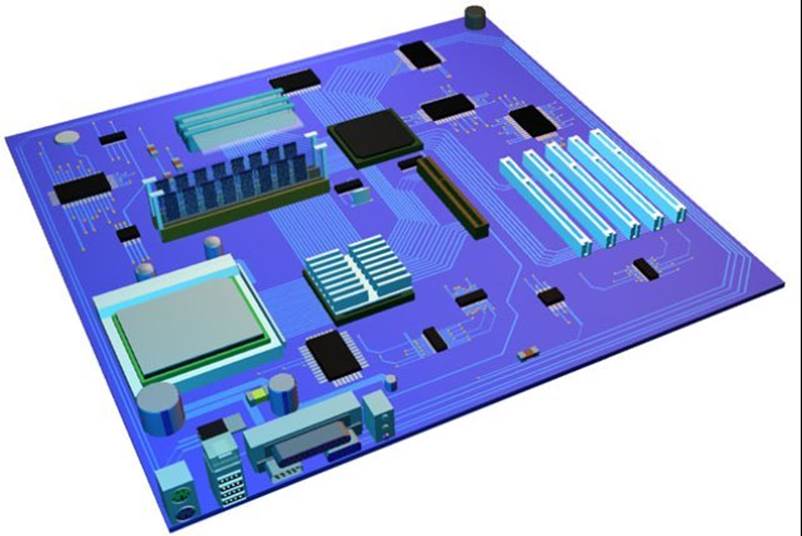
Motherboard A large circuit board that contains the computers CPU and Memory. All peripherals connect to the motherboard.
POST (The power on self-test) When you first switch on your PC a test is performed inside called POST (Power-On Self Test).
This operation tests your system to make sure everything is functioning before loading the operating system.
BOOT UP A collection of programs and checks are run after the POST operation is completed.
CPU The heart of the computer, all data at one stage or another will travel through the CPU. The Intel Pentium is a popular CPU.
Memory Temporarily Stores data in memory chips that are on the motherboard. Memory sizes can be 2 Gigabyte 4 Gigabyte etc.
Hard Drive The hard disk drive is the primary device used for storing data. Every computer has a hard drive built into the machine. The computer’s hard drive is where the operating system and most installed programs are loaded from. With its high-speed operation programs can be loaded quickly.
CD-ROM The optical CD-ROM (compact disk read only memory) disk stores large amounts of data, up to 650 MB on one small disk.
DVD is similar to optical CD-ROM but can store huge amounts of data.
Modem The Modem connects your computer to the Internet.
Printer The Printer allows a permanent record of a document or picture to be made.
Interrupts When a peripheral communicates with the computer it generates a special signal known as an interrupt. An interrupt is generated every time you press a key on the keyboard or move the mouse.
FireWire is the name for an interface which connects devices to your PC. FireWire is particularly useful when transferring large amounts of data to the computer.
Expansion Cards plug directly into the motherboard. This enables them to connect to local or system buses. Expansion cards are used for communicating with devices/ peripherals as data can be moved to them at a much higher speed than using USB ports.
Serial Port is provided on the back of the system box to connect external devices. Modems’ connect to the port. The serial port is now being superseded by USB.
Parallel Port is situated on the back of the system box to connect external devices. Printers, scanners connect to the port. The parallel port is now being superseded by USB.
BIOS The ROM BIOS chip contains the start up code, which is used, when your computer is switched on.
Plug and Play standard was introduced to enable devices and peripherals to connect to the computer and work first time.
Mouse The device that moves the on-screen pointer and selects icons and menu options.
Keyboard Connects to the motherboard and provides a number of keys that enable letters, numbers and symbols to be inputted to programs.
Floppy Disk is a re-moveable magnetic media that stores a small amount of data.
USB universal system bus is the main way of connecting external devices to the computers motherboard.
Scanner A device that scans documents and pictures and converts them into images that can be stored and viewed by a computer.
MIDI A standard for connecting certain types of musical instruments to a computer.
SCSI Interface standard to connect external devices such as hard drives, CD-ROM to the computers motherboard.
Monitor The device that shows what is on the computers desktop.
Resources
In addition to this book you can purchase software that allows you to see the inner workings of a computer in a graphical form.
Visual PC
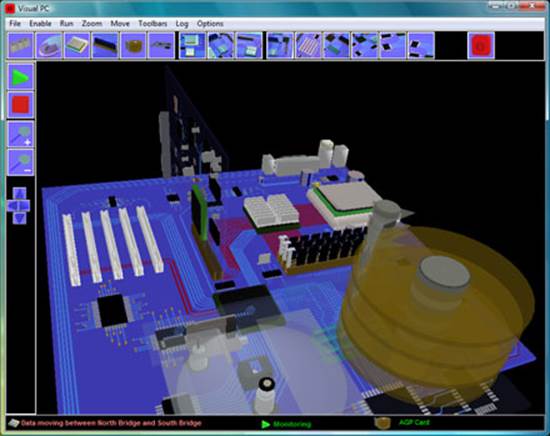
Visual PC is a brilliant demonstration of the inner works of a personal computer. The virtual reality simulations change in unison with changes on the systems motherboard, this enables a realistic demo of a computer system to be achieved.
The Mouse
When you click with computers mouse button Visual PC simulates what is going on inside your computer, with Visual PC you can see the path the data travels along on the virtual motherboard.
Keyboard
The virtual motherboard displays the data path a key press takes as it journeys to the computers CPU.
Motherboard
The Motherboard is based on a Intel Pentium processor. The board includes all the chips that would be found on a basic PC. Data flow is simulated between all the main chips. The main processes of the motherboard are simulated. These simulate data transfer between the CPU and Memory showing data flow between the North Bridge hub. The IDE interface is simulated to the CPU. CPU to AGP slot (Graphics card).
Mouse and Keyboard port simulated to CPU through LPC controller, South bridge and North bridge.
CPU
Visual PC monitors the computers processor as load changes are detected, the CPU to north bridge bus data lines turn red.
Memory Card
Simulates a Memory card with option of including operation with Motherboard simulations, so works when CPU reads/writes to memory.
Hard Disk(XP only)
Simulates data being read/write from a IDE hard drive. Data is read/write from the hard drive and simulated through the South bridge to the North bridge into the CPU. This is simulated in real time when the computers’ hard disk has a read/write cycle. As data moves through the controller the data lines turn to red.
AGP Graphics Card
Simulates the operation of the Graphics card including on board memory, this simulation can optionally be included with the Motherboard simulations when the CPU updates the screen memory.
Motherboard
The motherboard can be rotated and moved, you can zoom in onto the motherboard to see simulations close up. Visual PC is highly configurable you can set up the program to just monitor hard disk activity or key presses.
Visual PC can be purchased as a download from www.camboard.com