CISSP Practice Exams, Third Edition (2015)
CHAPTER 4
Physical and Environmental Security
This domain includes questions from the following topics:
• Administrative, technical, and physical controls
• Facility location, construction, and management
• Physical security risks, threats, and countermeasures
• Fire prevention, detection, and suppression
• Intrusion detection systems
There’s a lot more to physical security than the card keys your users carry to enter the building or show to the security guard in the parking lot. Physical security addresses a wide variety of threats that can be technical, wildly unpredictable, and catastrophic—and security professionals need to know how to plan for and deal with them. Every organization should develop, implement, and maintain a physical security program that has its foundation in risk management and mitigation. You should understand the physical security mechanisms that protect an organization’s data, equipment, systems, and its greatest asset—people.
Q QUESTIONS
1. Robert has been given the responsibility of installing doors that provide different types of protection. He has been told to install doors that provide fail-safe, fail-secure, and fail-soft protection. Which of the following statements is true about secure door types?
A. Fail-soft defaults to the sensitivity of the area.
B. Fail-safe defaults to locked.
C. Fail-secure defaults to unlocked.
D. Fail-secure defaults to double locked.
2. Paul and his team are responsible for integrating the proper type of lighting into his company’s physical security architecture. He needs to ensure that when visitors drive up to the security guard’s building at the perimeter that the light from the oncoming vehicle does not shine in the guard’s eyes. He needs to also ensure that when no employees are in the facility overnight that interior lights turn off and on periodically to give the illusion that the facility is populated. He also needs to make sure that when the intrusion detection systems detect something suspicious that the surrounding lights in that area turn on. Which of the following best describes the types of lights described in this scenario?
A. Glare protection, standby, responsive
B. Standby, continuous, controlled
C. Controlled, responsive, trip
D. Glare, controlled, continuous
3. As with logical access controls, audit logs should be produced and monitored for physical access controls. Which of the following statements is correct about auditing physical access?
A. Unsuccessful access attempts should be logged but only need to be reviewed by a security guard.
B. Only successful access attempts should be logged and reviewed.
C. Only unsuccessful access attempts during unauthorized hours should be logged and reviewed.
D. All unsuccessful access attempts should be logged and reviewed.
4. Surveillance techniques are used to watch for unusual behaviors, whereas intrusion detection systems (IDSs) are automated devices used to sense unusual changes that take place in an environment. These changes could represent behavior that could be malicious in nature. IDSs can be used to detect unauthorized entries and to alert a responsible entity to respond. These systems can monitor entries, doors, or windows. Which of the following provides an incorrect characteristic of a physical security IDS?
A. Commonly expensive and requires human intervention
B. Should have a redundant power supply and an emergency backup power supply
C. Should detect and be resistant to tampering
D. Should have a fail-stop configuration
5. CCTV can use fixed focal length or varifocal lenses. Which of the following correctly describes the lenses used in CCTV?
A. A fixed focal length lens allows you to move between various fields of view with a single lens.
B. To cover a large area and not focus on specific items, use a large lens opening.
C. An auto-iris lens should be used in an area with fixed lighting.
D. A shallow depth of focus allows you to focus on smaller details.
6. Which of the following describes the type of construction materials most commonly used to build a bank’s exterior walls?
A. Dense woods fastened with metal bolts and plates
B. Steel rods encased inside of concrete walls and support beams
C. Untreated lumber
D. Steel
7. Which of the following is a light-sensitive chip used in most of today’s CCTV cameras?
A. Digital Light Processing
B. Cathode ray tube
C. Annunciator
D. Charged-coupled devices
8. John is installing a sprinkler system that makes use of a thermal-fusible link for a data center located in Canada. Which of the following statements is true of the system he’s installing?
A. The pipes of a dry pipe system are filled with water when pressurized air within the pipes is reduced.
B. The pipes of a preaction system are filled with water when pressurized air within the pipes is reduced.
C. The sprinkler heads of a deluge system are wide open to allow a larger volume of water to be released in a shorter period.
D. The pipes in a wet pipe system always contain water.
9. What of the following allows security personnel to change the field of view of a CCTV lens to different angles and distances?
A. Depth of field
B. Manual iris
C. Zoom
D. Illumination
10. An outline for a physical security design should include program categories and the necessary countermeasures for each. What category do locks and access controls belong to?
A. Assessment
B. Deterrence
C. Response
D. Delay
11. A number of factors need to be considered when buying and implementing a CCTV system. Which of the following is the primary factor in determining whether a lens should have a manual iris or an auto-iris?
A. If the camera must be able to move in response to commands
B. If the environment has fixed lighting
C. If objects to be viewed are wide angle, such as a parking lot, or narrow, such as a door
D. The amount of light present in the environment
12. IDSs can detect intruders by employing electromechanical systems or volumetric systems. Which of the following correctly describes these systems?
A. Because they detect changes in subtle environmental characteristics, electromechanical systems are more sensitive than volumetric.
B. Electromechanical systems are less sensitive than volumetric systems, which detect subtle changes in environmental characteristics.
C. Electromagnetic systems deal with environmental changes such as ultrasonic frequencies, while volumetric systems can employ pressure mats or metallic foil in windows.
D. Electromagnetic systems are more sensitive because they detect a change or break in a circuit, while volumetric systems detect environmental changes.
13. What discipline combines the physical environment and sociology issues that surround it to reduce crime rates and the fear of crime?
A. Layered defense model
B. Target hardening
C. Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design
D. Natural access control
14. There are several types of volumetric IDSs. What type of IDS emits a measurable magnetic field that it monitors for disruptions?
A. Capacitance detector
B. Passive infrared system
C. Wave-pattern motion detectors
D. Photoelectric system
15. Paisley is helping her company identify potential site locations for a new facility. Which of the following is not an important factor when choosing a location?
A. Distance to police and fire stations
B. Lighting
C. Natural disaster occurrence
D. Crime rate
16. Sarah recently learned that the painting she inherited from a relative and hung in her downtown coffee shop is worth a lot of money. She is worried about its protection and wants to install an IDS. Which of the following intrusion detection systems is the most appropriate for protecting the painting?
A. Acoustical detection system
B. Proximity detector
C. Photoelectric system
D. Vibration sensor
17. David is preparing a server room at a new branch office. What locking mechanisms should he use for the primary and secondary server room entry doors?
A. The primary and secondary entrance doors should have access controlled through a swipe card or cipher lock.
B. The primary entrance door should have access controlled through a security guard. The secondary doors should be secured from the inside and allow no entry.
C. The primary entrance door should have access controlled through a swipe card or cipher lock. The secondary doors should have a security guard.
D. The primary entrance door should have access controlled through a swipe card or cipher lock. Secondary doors should be secured from the inside and allow no entry.
18. Which of the following is not true of IDSs?
A. They can be hindered by items within the room.
B. They are expensive and require human intervention to respond to the alarms.
C. They usually come with a redundant power supply and emergency backup power.
D. They should detect, and be resistant to, tampering.
19. Before an effective physical security program can be rolled out, a number of steps must be taken. Which of the following steps comes first in the process of rolling out a security program?
A. Create countermeasure performance metrics.
B. Conduct a risk analysis.
C. Design the program.
D. Implement countermeasures.
20. A number of measures should be taken to help protect devices and the environment from electric power issues. Which of the following is best to keep voltage steady and power clean?
A. Power line monitor
B. Surge protector
C. Shielded cabling
D. Regulator
21. What type of fence detects if someone attempts to climb or cut it?
A. Class IV
B. PIDAS
C. CPTED
D. PCCIP
22. Several different types of smoke and fire detectors can be used. What type of detector is shown in the following graphic?
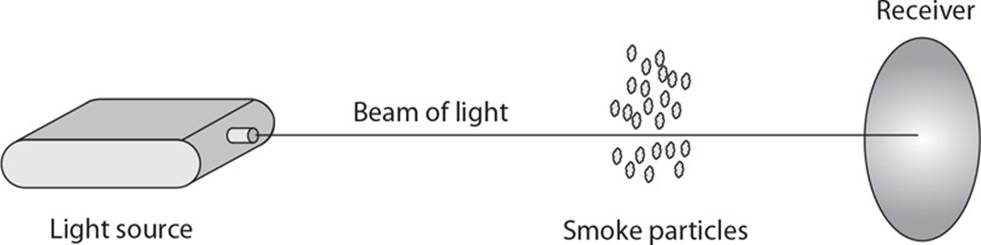
A. Photoelectric
B. Heat-activated
C. Infrared flame
D. Ionization
23. Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) is a discipline that outlines how the proper design of a physical environment can reduce crime by directly affecting human behavior. Of CPTED’s three main components, what is illustrated in the following photo?
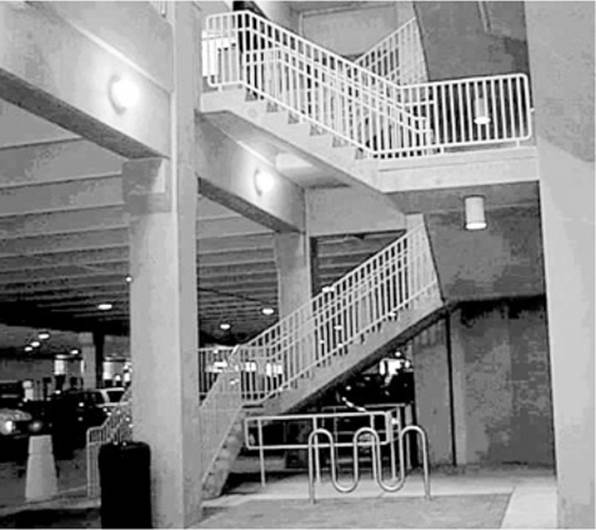

A. Natural surveillance
B. Target hardening
C. Natural access control
D. Territorial reinforcement
24. Different types of material are built into walls and other constructs of various types of buildings and facilities. What type of material is shown in the following photo?
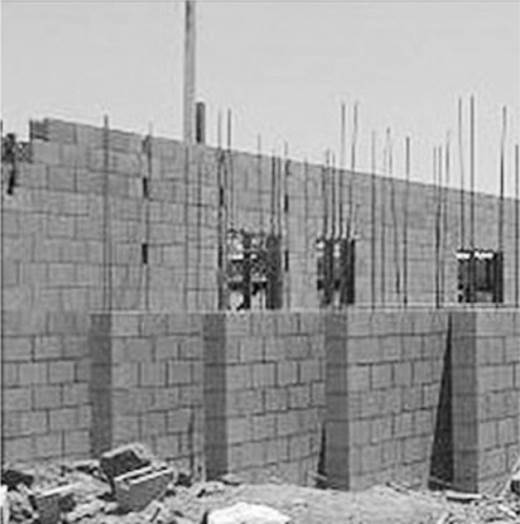

A. Fire-resistant material
B. Light frame construction material
C. Heavy timber construction material
D. Rebar material
25. There are five different classes of fire. Each depends upon what is on fire. Which of the following is the proper mapping for the items missing in the provided table?
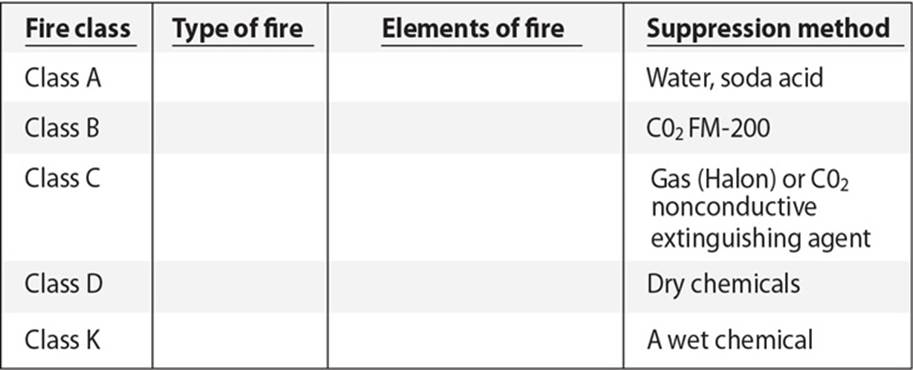
A. Class D—combustible metals
B. Class C—liquid
C. Class B—electrical
D. Class A—electrical
26. Electrical power is being provided more through smart grids, which allow for self-healing, resistance to physical and cyberattacks, increased efficiency, and better integration of renewable energy sources. Countries want their grids to be more reliable, resilient, flexible, and efficient. Why does this type of evolution in power infrastructure concern many security professionals?
A. Allows for direct attacks through Power over Ethernet
B. Increased embedded software and computing capabilities
C. Does not have proper protection against common web-based attacks
D. Power fluctuation and outages directly affect computing systems
The following scenario is to be used for questions 27, 28, and 29.
Mike is the new CSO of a large pharmaceutical company. He has been asked to revamp the company’s physical security program and better align it with the company’s information security practices. Mike knows that the new physical security program should be made up of controls and processes that support the following categories: deterrent, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
27. Mike’s team has decided to implement new perimeter fences and warning signs against trespassing around the company’s facility. Which of the categories listed in the scenario do these countermeasures map to?
A. Deterrent
B. Delaying
C. Detection
D. Assessment
28. Mike’s team has decided to implement stronger locks on the exterior doors of the new company’s facility. Which of the categories listed in the scenario does this countermeasure map to?
A. Deterrent
B. Delaying
C. Detection
D. Assessment
29. Mike’s team has decided to hire and deploy security guards to monitor activities within the company’s facility. Which of the categories listed in the scenario does this countermeasure map to?
A. Delaying
B. Detection
C. Assessment
D. Recall
The following scenario is to be used for questions 30, 31, and 32.
Greg is the security facility officer of a financial institution. His boss has told him that visitors need a secondary screening before they are allowed into sensitive areas within the building. Greg has also been told by the network administrators that after the new HVAC system was installed throughout the facility, they have noticed that power voltage to the systems in the data center sags.
30. Which of the following is the best control that Greg should ensure is implemented to deal with his boss’s concern?
A. Access and audit logs
B. Mantrap
C. Proximity readers
D. Smart card readers
31. Which of the following best describes the situation that the network administrators are experiencing?
A. Brownouts
B. Surges
C. In-rush current
D. Power line interference
32. Which of the following is a control that Greg’s team could implement to address the network administrators’ issue?
A. Secondary feeder line
B. Insulated grounded wiring
C. Line conditioner
D. Generator
QUICK ANSWER KEY
1. A
2. A
3. D
4. D
5. D
6. B
7. D
8. B
9. C
10. D
11. B
12. B
13. C
14. A
15. B
16. B
17. D
18. C
19. B
20. D
21. B
22. A
23. A
24. D
25. A
26. B
27. A
28. B
29. C
30. B
31. C
32. C
A ANSWERS
1. Robert has been given the responsibility of installing doors that provide different types of protection. He has been told to install doors that provide fail-safe, fail-secure, and fail-soft protection. Which of the following statements is true about secure door types?
A. Fail-soft defaults to the sensitivity of the area.
B. Fail-safe defaults to locked.
C. Fail-secure defaults to unlocked.
D. Fail-secure defaults to double locked.
![]() A. Doorways with automatic locks can be configured to be fail-secure, fail-safe, or fail-soft. Fail-soft means that locks need to default to being locked or unlocked, depending on the sensitivity of the data and systems in an area, and if people are working in specific areas of the building. The objective of a fail-soft system is to fail in a way that preserves as much data and capability as possible.
A. Doorways with automatic locks can be configured to be fail-secure, fail-safe, or fail-soft. Fail-soft means that locks need to default to being locked or unlocked, depending on the sensitivity of the data and systems in an area, and if people are working in specific areas of the building. The objective of a fail-soft system is to fail in a way that preserves as much data and capability as possible.
![]() B is incorrect because fail-safe does not default to locked. A fail-safe setting means that if a power disruption occurs that affects the automated locking system, the doors default to being unlocked. Fail-safe deals directly with protecting people. If people work in an area and there is a fire or the power is lost, it is not a good idea to lock them in.
B is incorrect because fail-safe does not default to locked. A fail-safe setting means that if a power disruption occurs that affects the automated locking system, the doors default to being unlocked. Fail-safe deals directly with protecting people. If people work in an area and there is a fire or the power is lost, it is not a good idea to lock them in.
![]() C is incorrect because fail-secure does not default to unlocked. A fail-secure configuration means that the doors default to being locked if there are any problems with the power. Be careful not to confuse fail-secure with fail-safe. You can think of it this way: If a fail-secure lock fails, the door is secure; i.e., the door is locked. If a fail-safe lock fails, then the people it protects are safe because they can leave through the door.
C is incorrect because fail-secure does not default to unlocked. A fail-secure configuration means that the doors default to being locked if there are any problems with the power. Be careful not to confuse fail-secure with fail-safe. You can think of it this way: If a fail-secure lock fails, the door is secure; i.e., the door is locked. If a fail-safe lock fails, then the people it protects are safe because they can leave through the door.
![]() D is incorrect because fail-secure does not default to double locked. The doors simply lock if there are problems with the power in a fail-secure configuration.
D is incorrect because fail-secure does not default to double locked. The doors simply lock if there are problems with the power in a fail-secure configuration.
2. Paul and his team are responsible for integrating the proper type of lighting into his company’s physical security architecture. He needs to ensure that when visitors drive up to the security guard’s building at the perimeter that the light from the oncoming vehicle does not shine in the guard’s eyes. He needs to also ensure that when no employees are in the facility overnight that interior lights turn off and on periodically to give the illusion that the facility is populated. He also needs to make sure that when the intrusion detection systems detect something suspicious that the surrounding lights in that area turn on. Which of the following best describes the types of lights described in this scenario?
A. Glare protection, standby, responsive
B. Standby, continuous, controlled
C. Controlled, responsive, trip
D. Glare, controlled, continuous
![]() A. Glare protection is directed toward areas where potential intruders would most likely be coming from and away from the security force posts. Standby lighting is in use when different lights turn on and off so that potential intruders will think that different areas of the facility are populated. When an intrusion detection system (IDS) detects suspicious activities and turns on the lights within a specific area, this is referred to as responsive lighting, also called trip lighting.
A. Glare protection is directed toward areas where potential intruders would most likely be coming from and away from the security force posts. Standby lighting is in use when different lights turn on and off so that potential intruders will think that different areas of the facility are populated. When an intrusion detection system (IDS) detects suspicious activities and turns on the lights within a specific area, this is referred to as responsive lighting, also called trip lighting.
![]() B is incorrect because standby lighting is in use when different lights turn on and off so that potential intruders will think that different areas of the facility are populated. This type of lighting was the second type of lighting identified in the scenario but the first within the response. Also, continuous lighting is an array of lights that provide an even amount of illumination across an area. Continuous lighting can be provided when light poles in a parking lot, light fixtures that run across the outside of a building, or a series of fluorescent lighting used in underground parking lots are in place. Controlled lighting is commonly used to ensure that lighting does not “bleed over” property lines. These two types of lighting were not addressed in the scenario question.
B is incorrect because standby lighting is in use when different lights turn on and off so that potential intruders will think that different areas of the facility are populated. This type of lighting was the second type of lighting identified in the scenario but the first within the response. Also, continuous lighting is an array of lights that provide an even amount of illumination across an area. Continuous lighting can be provided when light poles in a parking lot, light fixtures that run across the outside of a building, or a series of fluorescent lighting used in underground parking lots are in place. Controlled lighting is commonly used to ensure that lighting does not “bleed over” property lines. These two types of lighting were not addressed in the scenario question.
![]() C is incorrect because controlled lighting is commonly used to ensure that lighting does not “bleed over” property lines. This was not addressed in the scenario question. Also, responsive and trip lighting are considered the same thing and take place when an intrusion detection system (IDS) detects suspicious activities and turns on the lights within a specific area.
C is incorrect because controlled lighting is commonly used to ensure that lighting does not “bleed over” property lines. This was not addressed in the scenario question. Also, responsive and trip lighting are considered the same thing and take place when an intrusion detection system (IDS) detects suspicious activities and turns on the lights within a specific area.
![]() D is incorrect because when controlled lighting is being used, the illumination is being controlled in a way to ensure that it does not spill over into an unwanted area. The lights provide a particular coverage and do not “bleed over” across the defined boundaries. This was not identified in this question. Also, continuous lighting is an array of lights that provide an even amount of illumination across an area. Continuous lighting is used to ensure that the same amount of illumination is provided in an even manner across the necessary area.
D is incorrect because when controlled lighting is being used, the illumination is being controlled in a way to ensure that it does not spill over into an unwanted area. The lights provide a particular coverage and do not “bleed over” across the defined boundaries. This was not identified in this question. Also, continuous lighting is an array of lights that provide an even amount of illumination across an area. Continuous lighting is used to ensure that the same amount of illumination is provided in an even manner across the necessary area.
3. As with logical access controls, audit logs should be produced and monitored for physical access controls. Which of the following statements is correct about auditing physical access?
A. Unsuccessful access attempts should be logged but only need to be reviewed by a security guard.
B. Only successful access attempts should be logged and reviewed.
C. Only unsuccessful access attempts during unauthorized hours should be logged and reviewed.
D. All unsuccessful access attempts should be logged and reviewed.
![]() D. Physical access control systems can use software and auditing features to produce audit trails or access logs pertaining to access attempts. The following information should be logged and reviewed: the date and time of the access attempt, the entry point at which access was attempted, the user ID employed when access was attempted, and any unsuccessful access attempts, especially if they occur during unauthorized hours.
D. Physical access control systems can use software and auditing features to produce audit trails or access logs pertaining to access attempts. The following information should be logged and reviewed: the date and time of the access attempt, the entry point at which access was attempted, the user ID employed when access was attempted, and any unsuccessful access attempts, especially if they occur during unauthorized hours.
![]() A is incorrect because as with audit logs produced by computers, access logs are useless unless someone actually reviews them. A security guard may be required to review these logs, but a security professional or a facility manager should also review these logs periodically. Management needs to know where entry points into the facility exist and who attempts to use them. Audit and access logs are detective controls, not preventive. They are used to piece together a situation after the fact instead of attempting to prevent an access attempt in the first place.
A is incorrect because as with audit logs produced by computers, access logs are useless unless someone actually reviews them. A security guard may be required to review these logs, but a security professional or a facility manager should also review these logs periodically. Management needs to know where entry points into the facility exist and who attempts to use them. Audit and access logs are detective controls, not preventive. They are used to piece together a situation after the fact instead of attempting to prevent an access attempt in the first place.
![]() B is incorrect because unsuccessful access attempts should be logged and reviewed. Even though auditing is not an activity that will deny an entity access to a network, computer, or location, it will track activities so that a security professional can be warned of suspicious activity. This information can be used to point out weaknesses of other controls and help security personnel understand where changes must be made to preserve the necessary level of security in the environment.
B is incorrect because unsuccessful access attempts should be logged and reviewed. Even though auditing is not an activity that will deny an entity access to a network, computer, or location, it will track activities so that a security professional can be warned of suspicious activity. This information can be used to point out weaknesses of other controls and help security personnel understand where changes must be made to preserve the necessary level of security in the environment.
![]() C is incorrect because all unauthorized access attempts should be logged and reviewed, regardless of when they occurred. Attempted break-ins can occur at any time. Operating parameters can be set up for some physical access controls to allow a certain number of failed access attempts to be accepted before a user is locked out; this is a type of clipping level. An audit trail of this information can alert security personnel to a possible intrusion.
C is incorrect because all unauthorized access attempts should be logged and reviewed, regardless of when they occurred. Attempted break-ins can occur at any time. Operating parameters can be set up for some physical access controls to allow a certain number of failed access attempts to be accepted before a user is locked out; this is a type of clipping level. An audit trail of this information can alert security personnel to a possible intrusion.
4. Surveillance techniques are used to watch for unusual behaviors, whereas intrusion detection systems (IDSs) are automated devices used to sense unusual changes that take place in an environment. These changes could represent behavior that could be malicious in nature. IDSs can be used to detect unauthorized entries and to alert a responsible entity to respond. These systems can monitor entries, doors, or windows. Which of the following provides an incorrect characteristic of a physical security IDS?
A. Commonly expensive and requires human intervention
B. Should have a redundant power supply and an emergency backup power supply
C. Should detect and be resistant to tampering
D. Should have a fail-stop configuration
![]() D. A physical security IDS should have a fail-safe configuration, which means that if something happens to the device, it defaults to locking or securing itself. So if it loses power, a wire is cut, it is physically damaged, or a sensor indicates that someone is attempting to modify it, the device should not default to “unlock” itself and make itself vulnerable, but should default to “lock” and make itself secure. Fail-stop is not an actual configuration and is a distractor answer.
D. A physical security IDS should have a fail-safe configuration, which means that if something happens to the device, it defaults to locking or securing itself. So if it loses power, a wire is cut, it is physically damaged, or a sensor indicates that someone is attempting to modify it, the device should not default to “unlock” itself and make itself vulnerable, but should default to “lock” and make itself secure. Fail-stop is not an actual configuration and is a distractor answer.
![]() A is incorrect because most IDSs are expensive relative to other types of physical security controls. The system also requires human intervention, meaning that the IDS will sound an alarm or in some way alert the responsible entity that needs to investigate the situation. An IDS just detects a change in an environment and cannot actually do anything when something suspicious is detected. Most IDSs will alert a security guard so that he can go to the location and see what type of activity is taking place.
A is incorrect because most IDSs are expensive relative to other types of physical security controls. The system also requires human intervention, meaning that the IDS will sound an alarm or in some way alert the responsible entity that needs to investigate the situation. An IDS just detects a change in an environment and cannot actually do anything when something suspicious is detected. Most IDSs will alert a security guard so that he can go to the location and see what type of activity is taking place.
![]() B is incorrect because an IDS should have a redundant power supply just in case the main power supply is affected. An IDS would not provide much security if an intruder could just cut its power supply and gain entrance to a sensitive area. An IDS should also have a backup power supply in case the main supply is negatively affected, either intentionally or through some type of unintentional method such as a storm, flood, lightning, or some other environmental situation.
B is incorrect because an IDS should have a redundant power supply just in case the main power supply is affected. An IDS would not provide much security if an intruder could just cut its power supply and gain entrance to a sensitive area. An IDS should also have a backup power supply in case the main supply is negatively affected, either intentionally or through some type of unintentional method such as a storm, flood, lightning, or some other environmental situation.
![]() C is incorrect because the IDS should be able to detect if someone is attempting to tamper with it, and it should be built in a way that makes it very difficult to successfully tamper with it. An intruder will most likely attempt to turn off or disable the detection system so that he can carry out his malicious activities without being tracked. A useful IDS will not allow this to happen and will sound an alarm and default to a fail-safe configuration if it detects modification attempts.
C is incorrect because the IDS should be able to detect if someone is attempting to tamper with it, and it should be built in a way that makes it very difficult to successfully tamper with it. An intruder will most likely attempt to turn off or disable the detection system so that he can carry out his malicious activities without being tracked. A useful IDS will not allow this to happen and will sound an alarm and default to a fail-safe configuration if it detects modification attempts.
5. CCTV can use fixed focal length or varifocal lenses. Which of the following correctly describes the lenses used in CCTV?
A. A fixed focal length lens allows you to move between various fields of view with a single lens.
B. To cover a large area and not focus on specific items, use a large lens opening.
C. An auto-iris lens should be used in an area with fixed lighting.
D. A shallow depth of focus allows you to focus on smaller details.
![]() D. A shallow depth of focus allows you to focus on smaller details as opposed to a larger field. To understand depth of field, think about pictures you might take while on vacation with your family. For example, say you are on the beach on the Hawaiian island of Oahu with your family and you want to take their picture at the shoreline. Because the main object of the picture is your family, your camera will zoom in. This shallow depth of focus provides a softer backdrop, leading the viewer’s eye to the foreground of the photograph. Now you want a scenic picture of Diamond Head. Your camera uses a greater depth of focus, lessening the distinction between objects in the foreground and background.
D. A shallow depth of focus allows you to focus on smaller details as opposed to a larger field. To understand depth of field, think about pictures you might take while on vacation with your family. For example, say you are on the beach on the Hawaiian island of Oahu with your family and you want to take their picture at the shoreline. Because the main object of the picture is your family, your camera will zoom in. This shallow depth of focus provides a softer backdrop, leading the viewer’s eye to the foreground of the photograph. Now you want a scenic picture of Diamond Head. Your camera uses a greater depth of focus, lessening the distinction between objects in the foreground and background.
![]() A is incorrect because a fixed focal length lens must be changed to get a different field of view. Fixed focal length lenses are available in wide, medium, and narrow fields of view. A lens that provides a “normal” focal length creates a picture that approximates the field of view of the human eye. A wide-angle lens has a short focal length, and a telephoto lens has a long focal length. When a company selects a fixed focal length lens for a particular view of an environment, it should understand that if the field of view needs to be changed (from wide to narrow, for example), the lens must be changed.
A is incorrect because a fixed focal length lens must be changed to get a different field of view. Fixed focal length lenses are available in wide, medium, and narrow fields of view. A lens that provides a “normal” focal length creates a picture that approximates the field of view of the human eye. A wide-angle lens has a short focal length, and a telephoto lens has a long focal length. When a company selects a fixed focal length lens for a particular view of an environment, it should understand that if the field of view needs to be changed (from wide to narrow, for example), the lens must be changed.
![]() B is incorrect because it is best to use a wide-angle lens and a small lens opening to get the correct depth of field for a large area. It is necessary to understand the depth of field when choosing the correct lenses and configurations for your company’s CCTV. The depth of field refers to the portion of the environment that is in focus when shown on the monitor. The depth of field varies depending upon the size of the lens opening, the distance of the object being focused on, and the focal length of the lens. The depth of field increases as the size of the lens opening decreases, the subject distance increases, or the focal length of the lens decreases.
B is incorrect because it is best to use a wide-angle lens and a small lens opening to get the correct depth of field for a large area. It is necessary to understand the depth of field when choosing the correct lenses and configurations for your company’s CCTV. The depth of field refers to the portion of the environment that is in focus when shown on the monitor. The depth of field varies depending upon the size of the lens opening, the distance of the object being focused on, and the focal length of the lens. The depth of field increases as the size of the lens opening decreases, the subject distance increases, or the focal length of the lens decreases.
![]() C is incorrect because an auto-iris lens should be used in environments where the light changes, as in an outdoor setting. As the environment brightens, this is sensed by the iris, which automatically adjusts itself. A manual iris lens should be used in an area with fixed lighting. Manual iris lenses have a ring around the CCTV lens that can be manually turned and controlled. A lens with a manual iris would be used in areas that have fixed lighting, since the iris cannot self-adjust to changes of light.
C is incorrect because an auto-iris lens should be used in environments where the light changes, as in an outdoor setting. As the environment brightens, this is sensed by the iris, which automatically adjusts itself. A manual iris lens should be used in an area with fixed lighting. Manual iris lenses have a ring around the CCTV lens that can be manually turned and controlled. A lens with a manual iris would be used in areas that have fixed lighting, since the iris cannot self-adjust to changes of light.
6. Which of the following describes the type of construction materials most commonly used to build a bank’s exterior walls?
A. Dense woods fastened with metal bolts and plates
B. Steel rods encased inside of concrete walls and support beams
C. Untreated lumber
D. Steel
![]() B. Risk analysis results help the physical security team determine the type of construction material that should be used when constructing a new facility. Several grades of building construction are available. The team should choose its construction material based on the identified threats of the organization and the fire codes to be complied with. The construction material can be fire-retardant and have steel rods encased inside of concrete walls and support beams. This provides the most protection against fire and forced entry attempts. Facilities for government organizations, which are under threat by domestic and foreign terrorists, would be built with fire-resistant materials. A financial institution would also use fire-resistant and reinforcement material within its building. This is especially true for its exterior walls, through which thieves may attempt to drive vehicles to gain access to the vaults.
B. Risk analysis results help the physical security team determine the type of construction material that should be used when constructing a new facility. Several grades of building construction are available. The team should choose its construction material based on the identified threats of the organization and the fire codes to be complied with. The construction material can be fire-retardant and have steel rods encased inside of concrete walls and support beams. This provides the most protection against fire and forced entry attempts. Facilities for government organizations, which are under threat by domestic and foreign terrorists, would be built with fire-resistant materials. A financial institution would also use fire-resistant and reinforcement material within its building. This is especially true for its exterior walls, through which thieves may attempt to drive vehicles to gain access to the vaults.
![]() A is incorrect because dense woods fastened with metal bolts and plates are used in heavy timber construction material, which is commonly used for office buildings. Combustible lumber is used in this type of construction, but there are requirements on the thickness and composition of the materials to provide more protection from fire. The construction materials must be at least four inches in thickness. Whereas light frame construction material has a fire survival rate of 30 minutes, the heavy timber construction material has a fire survival rate of one hour.
A is incorrect because dense woods fastened with metal bolts and plates are used in heavy timber construction material, which is commonly used for office buildings. Combustible lumber is used in this type of construction, but there are requirements on the thickness and composition of the materials to provide more protection from fire. The construction materials must be at least four inches in thickness. Whereas light frame construction material has a fire survival rate of 30 minutes, the heavy timber construction material has a fire survival rate of one hour.
![]() C is incorrect because untreated lumber is used as light frame construction material, which provides the least amount of protection against fire and forcible entry attempts. The untreated lumber is combustible during a fire. Light frame construction is usually used to build homes, primarily because it is cheap but also because homes typically are not under the same types of fire and intrusion threats that office buildings are.
C is incorrect because untreated lumber is used as light frame construction material, which provides the least amount of protection against fire and forcible entry attempts. The untreated lumber is combustible during a fire. Light frame construction is usually used to build homes, primarily because it is cheap but also because homes typically are not under the same types of fire and intrusion threats that office buildings are.
![]() D is incorrect because steel, an example of an incombustible material, provides a higher level of fire protection than the previously mentioned materials but loses its strength under extreme temperatures, something that may cause the building to collapse. So, although steel will not burn, it may melt and weaken.
D is incorrect because steel, an example of an incombustible material, provides a higher level of fire protection than the previously mentioned materials but loses its strength under extreme temperatures, something that may cause the building to collapse. So, although steel will not burn, it may melt and weaken.
7. Which of the following is a light-sensitive chip used in most of today’s CCTV cameras?
A. Digital Light Processing
B. Cathode ray tube
C. Annunciator
D. Charged-coupled devices
![]() D. Most of the CCTV cameras in use today employ light-sensitive chips called charged-coupled devices (CCD). The CCD is an electrical circuit that receives input light from the lens and converts it into an electronic signal, which is then displayed on the monitor. Images are focused through a lens onto the CCD chip surface, which forms the electrical representation of the optical image. It is this technology that allows for the capture of extraordinary detail of objects and precise representation, because it has sensors that work in the infrared range, which extends beyond human perception. The CCD sensor picks up this extra “data” and integrates it into the images shown on the monitor to allow for better granularity and quality in the video. In addition to CCTV, CCDs are used in fax machines, photocopiers, bar code readers, and even telescopes.
D. Most of the CCTV cameras in use today employ light-sensitive chips called charged-coupled devices (CCD). The CCD is an electrical circuit that receives input light from the lens and converts it into an electronic signal, which is then displayed on the monitor. Images are focused through a lens onto the CCD chip surface, which forms the electrical representation of the optical image. It is this technology that allows for the capture of extraordinary detail of objects and precise representation, because it has sensors that work in the infrared range, which extends beyond human perception. The CCD sensor picks up this extra “data” and integrates it into the images shown on the monitor to allow for better granularity and quality in the video. In addition to CCTV, CCDs are used in fax machines, photocopiers, bar code readers, and even telescopes.
![]() A is incorrect because Digital Light Processing (DLP) is a trademarked technology owned by Texas Instruments that is used in DLP front projectors and DLP rear projection television. Images are created by tiny mirrors that are organized as a matrix on a semiconductor chip. The mirrors are toggled to reflect light, thereby producing grayscales. Color is produced by a single-chip projector via a color wheel placed between the lamp and DLP chip or via individual light sources, such as LEDs or LASERs. A three-chip DLP projector splits light from the lamp with a prism. Individual primary colors of light are routed to their own DLP chip. They are then recombined and sent through the lens.
A is incorrect because Digital Light Processing (DLP) is a trademarked technology owned by Texas Instruments that is used in DLP front projectors and DLP rear projection television. Images are created by tiny mirrors that are organized as a matrix on a semiconductor chip. The mirrors are toggled to reflect light, thereby producing grayscales. Color is produced by a single-chip projector via a color wheel placed between the lamp and DLP chip or via individual light sources, such as LEDs or LASERs. A three-chip DLP projector splits light from the lamp with a prism. Individual primary colors of light are routed to their own DLP chip. They are then recombined and sent through the lens.
![]() B is incorrect because a cathode ray tube (CRT) uses electrons to display an image. The CRT is a vacuum tube that contains an electron emitter and a fluorescent screen. An electron beam is accelerated and deflected to create an image in the form of light given off by the fluorescent screen. Most of today’s CCTVs use charged-coupled devices (CCDs) to allow for more granular information within an environment to be captured and shown on the monitor when compared to the older CCTV technology that relied upon CRTs. CRTs have also been replaced in other applications by technologies that are lighter and less fragile.
B is incorrect because a cathode ray tube (CRT) uses electrons to display an image. The CRT is a vacuum tube that contains an electron emitter and a fluorescent screen. An electron beam is accelerated and deflected to create an image in the form of light given off by the fluorescent screen. Most of today’s CCTVs use charged-coupled devices (CCDs) to allow for more granular information within an environment to be captured and shown on the monitor when compared to the older CCTV technology that relied upon CRTs. CRTs have also been replaced in other applications by technologies that are lighter and less fragile.
![]() C is incorrect because an annunciator system can either “listen” for noise and activate electrical devices, such as lights, sirens, or CCTV cameras, or detect movement. Instead of expecting a security guard to stare at a CCTV monitor for eight hours straight, the guard can carry out other activities and be alerted by an annunciator if movement is detected on the screen. While monitor watching is a mentally deadening activity, the CCTV monitors must be watched to be effective. An annunciator system is a solution to that.
C is incorrect because an annunciator system can either “listen” for noise and activate electrical devices, such as lights, sirens, or CCTV cameras, or detect movement. Instead of expecting a security guard to stare at a CCTV monitor for eight hours straight, the guard can carry out other activities and be alerted by an annunciator if movement is detected on the screen. While monitor watching is a mentally deadening activity, the CCTV monitors must be watched to be effective. An annunciator system is a solution to that.
8. John is installing a sprinkler system that makes use of a thermal-fusible link for a data center located in Canada. Which of the following statements is true of the system he’s installing?
A. The pipes of a dry pipe system are filled with water when pressurized air within the pipes is reduced.
B. The pipes of a preaction system are filled with water when pressurized air within the pipes is reduced.
C. The sprinkler heads of a deluge system are wide open to allow a larger volume of water to be released in a shorter period.
D. The pipes in a wet pipe system always contain water.
![]() B. Preaction systems and dry pipe systems are similar in that the water is not held in the pipes but is released when the pressurized air within the pipes is reduced. Once this happens, the pipes are filled with water, but it is not released right away. In a preaction system, a thermal-fusible link on the sprinkler head has to melt before the water is released. The purpose of combining these two techniques is to give people more time to respond to false alarms or to small fires that can be handled by other means. Putting out a small fire with a handheld extinguisher is better than losing a lot of electrical equipment to water damage. Due to their higher cost, these systems are usually used only in data processing environments rather than the whole building.
B. Preaction systems and dry pipe systems are similar in that the water is not held in the pipes but is released when the pressurized air within the pipes is reduced. Once this happens, the pipes are filled with water, but it is not released right away. In a preaction system, a thermal-fusible link on the sprinkler head has to melt before the water is released. The purpose of combining these two techniques is to give people more time to respond to false alarms or to small fires that can be handled by other means. Putting out a small fire with a handheld extinguisher is better than losing a lot of electrical equipment to water damage. Due to their higher cost, these systems are usually used only in data processing environments rather than the whole building.
![]() A is incorrect because dry pipe systems do not use a thermal-fusible link. Like preaction systems, water is not held in the pipes. The water is contained in a “holding tank” until it is released. The pipes hold pressurized air, which is reduced when a fire or a smoke alarm is activated, allowing the water valve to be opened by the water pressure. Water is not allowed into the pipes that feed the sprinklers until an actual fire is detected. First, a heat or smoke sensor is activated; then, the water fills the pipes leading to the sprinkler heads, the fire alarm sounds, the electric power supply is disconnected, and finally water is allowed to flow from the sprinklers. These pipes are best used in colder climates because the pipes will not freeze.
A is incorrect because dry pipe systems do not use a thermal-fusible link. Like preaction systems, water is not held in the pipes. The water is contained in a “holding tank” until it is released. The pipes hold pressurized air, which is reduced when a fire or a smoke alarm is activated, allowing the water valve to be opened by the water pressure. Water is not allowed into the pipes that feed the sprinklers until an actual fire is detected. First, a heat or smoke sensor is activated; then, the water fills the pipes leading to the sprinkler heads, the fire alarm sounds, the electric power supply is disconnected, and finally water is allowed to flow from the sprinklers. These pipes are best used in colder climates because the pipes will not freeze.
![]() C is incorrect because deluge systems are not usually used in data processing environments because the water being released is in such large volumes. Instead, deluge systems are used in environments where a fire could spread quickly. The pipes of a deluge system do not have water in them until a deluge valve is tripped by a fire alarm system. However, the deluge valve is nonresetting, so once the valve is tripped, it stays open.
C is incorrect because deluge systems are not usually used in data processing environments because the water being released is in such large volumes. Instead, deluge systems are used in environments where a fire could spread quickly. The pipes of a deluge system do not have water in them until a deluge valve is tripped by a fire alarm system. However, the deluge valve is nonresetting, so once the valve is tripped, it stays open.
![]() D is incorrect because a wet pipe system should not be used in a colder climate or a data processing environment, nor does it use a thermal-fusible link. Wet pipe systems always contain water in the pipes and are usually discharged by temperature control level sensors. One disadvantage of wet pipe systems is that the water in the pipes may freeze in colder climates. Also, if there is a nozzle or pipe break, it can cause extensive water damage. These types of systems are also called closed-head systems.
D is incorrect because a wet pipe system should not be used in a colder climate or a data processing environment, nor does it use a thermal-fusible link. Wet pipe systems always contain water in the pipes and are usually discharged by temperature control level sensors. One disadvantage of wet pipe systems is that the water in the pipes may freeze in colder climates. Also, if there is a nozzle or pipe break, it can cause extensive water damage. These types of systems are also called closed-head systems.
9. Which of the following allows security personnel to change the field of view of a CCTV lens to different angles and distances?
A. Depth of field
B. Manual iris
C. Zoom
D. Illumination
![]() C. Zoom lenses provide flexibility by allowing the viewer to change the field of view to different angles and distances. The security personnel usually have a remote-control component integrated within the centralized CCTV monitoring area that allows them to move the cameras, and zoom in and out on objects as needed. When both wide scenes and close-up captures are needed, a zoom lens is best. This type of lens allows the focal length to change from wide angle to telephoto while maintaining the focus of the image.
C. Zoom lenses provide flexibility by allowing the viewer to change the field of view to different angles and distances. The security personnel usually have a remote-control component integrated within the centralized CCTV monitoring area that allows them to move the cameras, and zoom in and out on objects as needed. When both wide scenes and close-up captures are needed, a zoom lens is best. This type of lens allows the focal length to change from wide angle to telephoto while maintaining the focus of the image.
![]() A is incorrect because depth of field refers to the portion of the environment that is in focus when shown on the CCTV monitor. The depth of field varies depending upon the size of the lens opening, the distance of the object being focused on, and the focal length of the lens. The depth of field increases as the size of the lens opening decreases, the subject distance increases, or the focal length of the lens decreases. So, if you want to cover a large area and not focus on specific items, it is best to use a wide-angle lens and a small lens opening.
A is incorrect because depth of field refers to the portion of the environment that is in focus when shown on the CCTV monitor. The depth of field varies depending upon the size of the lens opening, the distance of the object being focused on, and the focal length of the lens. The depth of field increases as the size of the lens opening decreases, the subject distance increases, or the focal length of the lens decreases. So, if you want to cover a large area and not focus on specific items, it is best to use a wide-angle lens and a small lens opening.
![]() B is incorrect because an iris controls the amount of light that enters the lens. Manual iris lenses have a ring around the CCTV lens that can be manually turned and controlled. A lens with a manual iris would be used in areas that have fixed lighting, since the iris cannot self-adjust to changes of light. For example, it may be used in hospital hallways that are always lit.
B is incorrect because an iris controls the amount of light that enters the lens. Manual iris lenses have a ring around the CCTV lens that can be manually turned and controlled. A lens with a manual iris would be used in areas that have fixed lighting, since the iris cannot self-adjust to changes of light. For example, it may be used in hospital hallways that are always lit.
![]() D is incorrect because illumination refers to the intensity of light present in an environment. Different CCTV camera and lens products have specific illumination requirements to ensure the best quality images possible. The illumination requirements are usually represented in the lux value, which is a metric used to represent illumination strengths. The illumination can be measured using a light meter. The intensity of light is measured and represented in measurement units of lux or footcandles. (The conversion between the two is one footcandle = 10.76 lux.) The illumination measurement is not something that can be accurately provided by the vendor of a light bulb, because the environment can directly affect the illumination. This is why illumination strengths are most effectively measured where the light source is implemented.
D is incorrect because illumination refers to the intensity of light present in an environment. Different CCTV camera and lens products have specific illumination requirements to ensure the best quality images possible. The illumination requirements are usually represented in the lux value, which is a metric used to represent illumination strengths. The illumination can be measured using a light meter. The intensity of light is measured and represented in measurement units of lux or footcandles. (The conversion between the two is one footcandle = 10.76 lux.) The illumination measurement is not something that can be accurately provided by the vendor of a light bulb, because the environment can directly affect the illumination. This is why illumination strengths are most effectively measured where the light source is implemented.
10. An outline for a physical security design should include program categories and the necessary countermeasures for each. What category do locks and access controls belong to?
A. Assessment
B. Deterrence
C. Response
D. Delay
![]() D. The physical security program design phase should begin with a structured outline that lists each category of the program: deterrence, delaying, detection, assessment, and response. The outline evolves into a framework, which is fleshed out with the necessary controls and countermeasures. The intent behind the delay category is to stall intruders to help ensure they get caught. Examples of countermeasures that belong to this category are locks, defense-in-depth measures, and access controls. Other types of delaying mechanisms include reinforced walls and rebar. The idea is that it will take a bad guy longer to get through two reinforced walls, which gives the response force sufficient time to arrive at the scene and stop the attacker. Of the categories listed in the answer options, detection is missing. Detection refers to the determination or awareness that an intrusion has occurred. Examples of detection controls include external intruder sensors and internal intruder sensors.
D. The physical security program design phase should begin with a structured outline that lists each category of the program: deterrence, delaying, detection, assessment, and response. The outline evolves into a framework, which is fleshed out with the necessary controls and countermeasures. The intent behind the delay category is to stall intruders to help ensure they get caught. Examples of countermeasures that belong to this category are locks, defense-in-depth measures, and access controls. Other types of delaying mechanisms include reinforced walls and rebar. The idea is that it will take a bad guy longer to get through two reinforced walls, which gives the response force sufficient time to arrive at the scene and stop the attacker. Of the categories listed in the answer options, detection is missing. Detection refers to the determination or awareness that an intrusion has occurred. Examples of detection controls include external intruder sensors and internal intruder sensors.
![]() A is incorrect because assessment countermeasures include security guard procedures and communication structure (calling tree). When an incident occurs, the assessment team (or security guard) is first on the scene to determine what has taken place and what needs to happen next; for example, a call to the police or fire station, management, a security service, etc. The assessment determines what type of response is needed.
A is incorrect because assessment countermeasures include security guard procedures and communication structure (calling tree). When an incident occurs, the assessment team (or security guard) is first on the scene to determine what has taken place and what needs to happen next; for example, a call to the police or fire station, management, a security service, etc. The assessment determines what type of response is needed.
![]() B is incorrect because deterrence refers to those controls that will discourage potential intruders from conducting criminal activity. Examples include fences, warning signs, security guards, and dogs. Another example found in residential areas is a “Neighborhood Crime Watch” sign that is erected in neighborhoods or even in home windows. The idea is that a casual intruder will be less likely to attempt an intrusion if he thinks that the neighborhood is making a concerted effort to watch for criminals and that he may be caught.
B is incorrect because deterrence refers to those controls that will discourage potential intruders from conducting criminal activity. Examples include fences, warning signs, security guards, and dogs. Another example found in residential areas is a “Neighborhood Crime Watch” sign that is erected in neighborhoods or even in home windows. The idea is that a casual intruder will be less likely to attempt an intrusion if he thinks that the neighborhood is making a concerted effort to watch for criminals and that he may be caught.
![]() C is incorrect because response refers to an organization’s processes and the personnel it assigns to react to intrusions and disruptions. Controls in this category include a response force, emergency response procedures, and police, fire, and medical personnel.
C is incorrect because response refers to an organization’s processes and the personnel it assigns to react to intrusions and disruptions. Controls in this category include a response force, emergency response procedures, and police, fire, and medical personnel.
11. A number of factors need to be considered when buying and implementing a CCTV system. Which of the following is the primary factor in determining whether a lens should have a manual iris or an auto-iris?
A. If the camera must be able to move in response to commands
B. If the environment has fixed lighting
C. If objects to be viewed are wide angle, such as a parking lot, or narrow, such as a door
D. The amount of light present in the environment
![]() B. CCTV lenses have irises, which control the amount of light that enters the lens. If the environment has fixed lighting, then a lens with a manual iris can be used. Manual iris lenses cannot self-adjust to changes in light. They have to be manually turned and controlled by moving a ring around the lens. If the environment has changing light, as in an outdoor setting, then an auto-iris lens should be used. As the environment brightens, this is sensed by the iris, which automatically adjusts itself. Security personnel will configure the CCTV to have a specific fixed exposure value, which the iris is responsible for maintaining. On a sunny day, the iris lens closes to reduce the amount of light entering the camera, while at night, the iris opens to capture more light—just like our eyes.
B. CCTV lenses have irises, which control the amount of light that enters the lens. If the environment has fixed lighting, then a lens with a manual iris can be used. Manual iris lenses cannot self-adjust to changes in light. They have to be manually turned and controlled by moving a ring around the lens. If the environment has changing light, as in an outdoor setting, then an auto-iris lens should be used. As the environment brightens, this is sensed by the iris, which automatically adjusts itself. Security personnel will configure the CCTV to have a specific fixed exposure value, which the iris is responsible for maintaining. On a sunny day, the iris lens closes to reduce the amount of light entering the camera, while at night, the iris opens to capture more light—just like our eyes.
![]() A is incorrect because a camera’s ability to move in response to security personnel commands determines its mounting requirements. Cameras can be implemented in a fixed mounting or a mounting that allows the cameras to move when necessary. A fixed camera cannot move in response to security personnel commands, whereas cameras that provide PTZ capabilities can pan, tilt, or zoom as necessary.
A is incorrect because a camera’s ability to move in response to security personnel commands determines its mounting requirements. Cameras can be implemented in a fixed mounting or a mounting that allows the cameras to move when necessary. A fixed camera cannot move in response to security personnel commands, whereas cameras that provide PTZ capabilities can pan, tilt, or zoom as necessary.
![]() C is incorrect because the angle of items to be viewed influences the focal length required of the lens. The focal length of a lens defines its effectiveness in viewing objects from a horizontal and vertical view. The focal length value relates to the angle of view that can be achieved. Short focal length lenses provide wider-angle views, while long focal length lenses provide a narrower view. The size of the images shown on a monitor, along with the area covered by one camera, is defined by the focal length. For example, if a company implements a CCTV camera in a warehouse, the focal length lens should be between 2.8 and 4.3 millimeters (mm) so that the whole area can be captured. If the company implements another CCTV camera that monitors an entrance, then the lens value should be around 8 mm, which allows a smaller area to be monitored.
C is incorrect because the angle of items to be viewed influences the focal length required of the lens. The focal length of a lens defines its effectiveness in viewing objects from a horizontal and vertical view. The focal length value relates to the angle of view that can be achieved. Short focal length lenses provide wider-angle views, while long focal length lenses provide a narrower view. The size of the images shown on a monitor, along with the area covered by one camera, is defined by the focal length. For example, if a company implements a CCTV camera in a warehouse, the focal length lens should be between 2.8 and 4.3 millimeters (mm) so that the whole area can be captured. If the company implements another CCTV camera that monitors an entrance, then the lens value should be around 8 mm, which allows a smaller area to be monitored.
![]() D is incorrect because the amount of light present in the environment does not determine the type of iris that should be used. The iris is determined by whether the light is fixed (the amount of light in the area is constant) or changes. The amount of light present in the environment helps determine the illumination requirements that must be met by the CCTV system. Illumination measurements must be taken within the environment itself because characteristics of the environment, such as exposure to outside light, the paint on the walls, etc., can affect illumination.
D is incorrect because the amount of light present in the environment does not determine the type of iris that should be used. The iris is determined by whether the light is fixed (the amount of light in the area is constant) or changes. The amount of light present in the environment helps determine the illumination requirements that must be met by the CCTV system. Illumination measurements must be taken within the environment itself because characteristics of the environment, such as exposure to outside light, the paint on the walls, etc., can affect illumination.
12. IDSs can detect intruders by employing electromechanical systems or volumetric systems. Which of the following correctly describes these systems?
A. Because they detect changes in subtle environmental characteristics, electromechanical systems are more sensitive than volumetric.
B. Electromechanical systems are less sensitive than volumetric systems, which detect subtle changes in environmental characteristics.
C. Electromagnetic systems deal with environmental changes such as ultrasonic frequencies, while volumetric systems can employ pressure mats or metallic foil in windows.
D. Electromagnetic systems are more sensitive because they detect a change or break in a circuit, while volumetric systems detect environmental changes.
![]() B. A physical IDS can employ an electromechanical or volumetric system to detect intruders. An electromechanical system is less sensitive than a volumetric system. An electromechanical system detects a change or break in a circuit. For example, electromechanical detectors can detect movement on walls, screens, ceilings, and floors when the fine wires embedded within the structure are broken. Or magnetic contact switches can be installed on windows and doors. If the contacts are separated because the window or door is opened, an alarm will sound. Volumetric systems can detect changes in vibration, microwaves, ultrasonic frequencies, infrared values, and photoelectric changes.
B. A physical IDS can employ an electromechanical or volumetric system to detect intruders. An electromechanical system is less sensitive than a volumetric system. An electromechanical system detects a change or break in a circuit. For example, electromechanical detectors can detect movement on walls, screens, ceilings, and floors when the fine wires embedded within the structure are broken. Or magnetic contact switches can be installed on windows and doors. If the contacts are separated because the window or door is opened, an alarm will sound. Volumetric systems can detect changes in vibration, microwaves, ultrasonic frequencies, infrared values, and photoelectric changes.
![]() A is incorrect because volumetric systems are more sensitive than electromechanical systems. Also, volumetric systems—not electromechanical systems—detect changes in subtle environmental characteristics, such as vibration and ultrasonic frequencies. Electromechanical systems work by detecting a change or break in a circuit.
A is incorrect because volumetric systems are more sensitive than electromechanical systems. Also, volumetric systems—not electromechanical systems—detect changes in subtle environmental characteristics, such as vibration and ultrasonic frequencies. Electromechanical systems work by detecting a change or break in a circuit.
![]() C is incorrect because the statement is backward. Electromechanical systems make use of metallic foil in windows or pressure mats to detect a change or break in a circuit. The electrical circuits can be strips of foil embedded or connected to windows. If the window breaks, the foil strip breaks, which sounds an alarm. A pressure pad is another type of electromechanical detector. It is placed underneath a rug or portion of the carpet and is activated after hours. If someone steps on the pad, an alarm activates because no one is supposed to be in the area during this time. Volumetric systems deal with environmental changes, such as ultrasonic frequencies, but also vibration, microwaves, infrared values, and photoelectric changes.
C is incorrect because the statement is backward. Electromechanical systems make use of metallic foil in windows or pressure mats to detect a change or break in a circuit. The electrical circuits can be strips of foil embedded or connected to windows. If the window breaks, the foil strip breaks, which sounds an alarm. A pressure pad is another type of electromechanical detector. It is placed underneath a rug or portion of the carpet and is activated after hours. If someone steps on the pad, an alarm activates because no one is supposed to be in the area during this time. Volumetric systems deal with environmental changes, such as ultrasonic frequencies, but also vibration, microwaves, infrared values, and photoelectric changes.
![]() D is incorrect because volumetric systems are more sensitive, the reason being that they detect subtle changes in environmental characteristics. Electromechanical systems are less sensitive and work by detecting a change or break in a circuit.
D is incorrect because volumetric systems are more sensitive, the reason being that they detect subtle changes in environmental characteristics. Electromechanical systems are less sensitive and work by detecting a change or break in a circuit.
13. What discipline combines the physical environment and sociology issues that surround it to reduce crime rates and the fear of crime?
A. Layered defense model
B. Target hardening
C. Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design
D. Natural access control
![]() C. Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) is a discipline that outlines how the proper design of a physical environment can reduce crime by directly affecting human behavior. It provides guidance in loss and crime prevention through proper facility construction and environmental components and procedures. The crux of CPTED is that the physical environment can be manipulated to create behavioral effects that will reduce crime and the fear of crime. It looks at the components that make up the relationship between humans and their environment. This encompasses the physical, social, and psychological needs of the users of different types of environments and predictable behaviors of these users and offenders. For example, CCTV cameras should be mounted in full view so that criminals know their activities will be captured and other people know the environment is well monitored and thus safer.
C. Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) is a discipline that outlines how the proper design of a physical environment can reduce crime by directly affecting human behavior. It provides guidance in loss and crime prevention through proper facility construction and environmental components and procedures. The crux of CPTED is that the physical environment can be manipulated to create behavioral effects that will reduce crime and the fear of crime. It looks at the components that make up the relationship between humans and their environment. This encompasses the physical, social, and psychological needs of the users of different types of environments and predictable behaviors of these users and offenders. For example, CCTV cameras should be mounted in full view so that criminals know their activities will be captured and other people know the environment is well monitored and thus safer.
![]() A is incorrect because a layered defense model is a tiered architecture of physical, logical, and administrative security controls. The concept is that if one layer fails, other layers will protect the valuable asset. Layers should be implemented moving from the perimeter toward the asset. For example, you would have a fence, then your facility walls, then an access control card device, then a guard, then an IDS, and then locked computer cases and safes. This series of layers will protect the company’s most sensitive assets, which would be placed in the innermost control zone of the environment. So if the bad guy were able to climb over your fence and outsmart the security guard, he would still have to circumvent several layers of controls before getting to your precious resources and systems.
A is incorrect because a layered defense model is a tiered architecture of physical, logical, and administrative security controls. The concept is that if one layer fails, other layers will protect the valuable asset. Layers should be implemented moving from the perimeter toward the asset. For example, you would have a fence, then your facility walls, then an access control card device, then a guard, then an IDS, and then locked computer cases and safes. This series of layers will protect the company’s most sensitive assets, which would be placed in the innermost control zone of the environment. So if the bad guy were able to climb over your fence and outsmart the security guard, he would still have to circumvent several layers of controls before getting to your precious resources and systems.
![]() B is incorrect because target hardening focuses on denying access through physical and artificial barriers (alarms, locks, fences, and so on). Traditional target hardening can lead to restrictions on the use, enjoyment, and aesthetics of an environment. Remember that security entails maintaining a delicate balance between ease of use and protection. A Parks and Recreation department could implement fences, intimidating signs, and barriers around its parks and green areas to discourage gangs from congregating, but who would want to play or have a picnic there? The same goes for an office building. You must provide the necessary levels of protection, but your protection mechanisms should be more subtle and unobtrusive.
B is incorrect because target hardening focuses on denying access through physical and artificial barriers (alarms, locks, fences, and so on). Traditional target hardening can lead to restrictions on the use, enjoyment, and aesthetics of an environment. Remember that security entails maintaining a delicate balance between ease of use and protection. A Parks and Recreation department could implement fences, intimidating signs, and barriers around its parks and green areas to discourage gangs from congregating, but who would want to play or have a picnic there? The same goes for an office building. You must provide the necessary levels of protection, but your protection mechanisms should be more subtle and unobtrusive.
![]() D is incorrect because natural access control is the guidance of people entering and leaving a space by the placement of doors, fences, lighting, and even landscaping. For example, an office building may have external bollards with lights in them. These bollards carry out different safety and security services. The bollards themselves protect the facility from physical destruction by preventing people from driving their cars into the building. The light emitted helps ensure that criminals do not have a dark place to hide. And the lights and bollard placement guides people along the sidewalk to the entrance, instead of using signs or railings.
D is incorrect because natural access control is the guidance of people entering and leaving a space by the placement of doors, fences, lighting, and even landscaping. For example, an office building may have external bollards with lights in them. These bollards carry out different safety and security services. The bollards themselves protect the facility from physical destruction by preventing people from driving their cars into the building. The light emitted helps ensure that criminals do not have a dark place to hide. And the lights and bollard placement guides people along the sidewalk to the entrance, instead of using signs or railings.
14. There are several types of volumetric IDSs. What type of IDS emits a measurable magnetic field that it monitors for disruptions?
A. Capacitance detector
B. Passive infrared system
C. Wave-pattern motion detectors
D. Photoelectric system
![]() A. A capacitance detector, or proximity detector, emits a measurable magnetic field. The detector monitors this magnetic field, and an alarm sounds if the field is disrupted. Capacitance change in an electrostatic field can be used to catch a bad guy, but first you need to understand what capacitance change means. An electrostatic IDS creates an electrostatic magnetic field, which is just an electric field associated with static electric charges. All objects have a static electric charge. They are all made up of many subatomic particles, and when everything is stable and static, these particles constitute one holistic electric charge. This means there is a balance between the electric capacitance and inductance. Now if an intruder enters the area his subatomic particles will mess up this lovely balance in the electrostatic field, causing capacitance change, and an alarm will sound.
A. A capacitance detector, or proximity detector, emits a measurable magnetic field. The detector monitors this magnetic field, and an alarm sounds if the field is disrupted. Capacitance change in an electrostatic field can be used to catch a bad guy, but first you need to understand what capacitance change means. An electrostatic IDS creates an electrostatic magnetic field, which is just an electric field associated with static electric charges. All objects have a static electric charge. They are all made up of many subatomic particles, and when everything is stable and static, these particles constitute one holistic electric charge. This means there is a balance between the electric capacitance and inductance. Now if an intruder enters the area his subatomic particles will mess up this lovely balance in the electrostatic field, causing capacitance change, and an alarm will sound.
![]() B is incorrect because a passive infrared system (PIR) identifies the changes of heat waves in an area it is configured to monitor. If the particles’ temperature within the air rises, it could be an indication of the presence of an intruder, so an alarm is sounded.
B is incorrect because a passive infrared system (PIR) identifies the changes of heat waves in an area it is configured to monitor. If the particles’ temperature within the air rises, it could be an indication of the presence of an intruder, so an alarm is sounded.
![]() C is incorrect because wave-pattern motion detectors generate a wave pattern that is one of several frequencies: microwave, ultrasonic, or low frequency. The IDS generates a wave pattern that is sent over a sensitive area and reflected back to a receiver. If the pattern is returned undisturbed, the device does nothing. If the pattern returns altered because something in the room is moving, an alarm sounds.
C is incorrect because wave-pattern motion detectors generate a wave pattern that is one of several frequencies: microwave, ultrasonic, or low frequency. The IDS generates a wave pattern that is sent over a sensitive area and reflected back to a receiver. If the pattern is returned undisturbed, the device does nothing. If the pattern returns altered because something in the room is moving, an alarm sounds.
![]() D is incorrect because a photoelectric system (or photometric system) detects the change in a light beam and thus can be used only in windowless rooms. These systems work like photoelectric smoke detectors, which emit a beam that hits the receiver. If this beam of light is interrupted, an alarm sounds. The beams emitted can be cross-sectional and can be invisible or visible beams. Cross-sectional means that one area can have several different light beams extending across it, which is usually carried out by using hidden mirrors to bounce the beam from one place to another until it hits the light receiver.
D is incorrect because a photoelectric system (or photometric system) detects the change in a light beam and thus can be used only in windowless rooms. These systems work like photoelectric smoke detectors, which emit a beam that hits the receiver. If this beam of light is interrupted, an alarm sounds. The beams emitted can be cross-sectional and can be invisible or visible beams. Cross-sectional means that one area can have several different light beams extending across it, which is usually carried out by using hidden mirrors to bounce the beam from one place to another until it hits the light receiver.
15. Paisley is helping her company identify potential site locations for a new facility. Which of the following is not an important factor when choosing a location?
A. Distance to police and fire stations
B. Lighting
C. Natural disaster occurrence
D. Crime rate
![]() B. Lighting is an important issue for physical security, but not a component that is evaluated during site location. The necessary lighting can be installed while the facility is built or later. Indeed, a security professional should understand that the right illumination needs to be in place, that no dead spots (unlit areas) should exist between the lights, and that all areas where individuals may walk should be properly lit. A security professional should also understand the various types of lighting available and where they should be used. If an organization does not implement the right types of lights and ensure they provide proper coverage, it increases the probability of criminal activity, accidents, and lawsuits.
B. Lighting is an important issue for physical security, but not a component that is evaluated during site location. The necessary lighting can be installed while the facility is built or later. Indeed, a security professional should understand that the right illumination needs to be in place, that no dead spots (unlit areas) should exist between the lights, and that all areas where individuals may walk should be properly lit. A security professional should also understand the various types of lighting available and where they should be used. If an organization does not implement the right types of lights and ensure they provide proper coverage, it increases the probability of criminal activity, accidents, and lawsuits.
![]() A is incorrect because a location’s distance from police and fire stations is an important factor to consider when evaluating potential site locations. Many times, the proximity of these entities raises the real estate value of properties, but for good reason. Each of these issues—police station, fire station, and even medical facility proximity—can also reduce insurance rates and must be looked at carefully. Remember that the ultimate goal of physical security is to ensure the safety of personnel. Always keep that in mind when implementing any sort of physical security control.
A is incorrect because a location’s distance from police and fire stations is an important factor to consider when evaluating potential site locations. Many times, the proximity of these entities raises the real estate value of properties, but for good reason. Each of these issues—police station, fire station, and even medical facility proximity—can also reduce insurance rates and must be looked at carefully. Remember that the ultimate goal of physical security is to ensure the safety of personnel. Always keep that in mind when implementing any sort of physical security control.
![]() C is incorrect because when evaluating a location for a facility, it is critical to take into account the risk of natural disasters. Decision makers should consider the likelihood of floods, tornadoes, earthquakes, or hurricanes, as well as hazardous terrain (mudslides, falling rock from mountains, or excessive rain or snow). The likelihood of these risks will affect the organization’s business continuity and disaster recovery programs.
C is incorrect because when evaluating a location for a facility, it is critical to take into account the risk of natural disasters. Decision makers should consider the likelihood of floods, tornadoes, earthquakes, or hurricanes, as well as hazardous terrain (mudslides, falling rock from mountains, or excessive rain or snow). The likelihood of these risks will affect the organization’s business continuity and disaster recovery programs.
![]() D is incorrect because it is important to consider the area’s crime rate when evaluating site locations for a facility. It is also wise to consider the likelihood of riots and terrorism attacks, and other possible hazards from the surrounding area.
D is incorrect because it is important to consider the area’s crime rate when evaluating site locations for a facility. It is also wise to consider the likelihood of riots and terrorism attacks, and other possible hazards from the surrounding area.
16. Sarah recently learned that the painting she inherited from a relative and hung in her downtown coffee shop is worth a lot of money. She is worried about its protection and wants to install an IDS. Which of the following intrusion detection systems is the most appropriate for protecting the painting?
A. Acoustical detection system
B. Proximity detector
C. Photoelectric system
D. Vibration sensor
![]() B. Proximity detectors, or capacitance detectors, are usually used to protect specific objects (artwork, cabinets, or a safe) versus protecting a whole room or area. A proximity detector emits and monitors a measurable magnetic field. If the field is disrupted, the detector sounds an alarm to alert a responsible entity of a possible intrusion. All IDSs are support mechanisms that are intended to detect and announce an attempted intrusion. They will not prevent or apprehend intruders, so they should be seen as an aid to the organization’s security forces. While an IDS is a very valuable control, the technology is expensive and the system requires a redundant power supply and emergency backup power.
B. Proximity detectors, or capacitance detectors, are usually used to protect specific objects (artwork, cabinets, or a safe) versus protecting a whole room or area. A proximity detector emits and monitors a measurable magnetic field. If the field is disrupted, the detector sounds an alarm to alert a responsible entity of a possible intrusion. All IDSs are support mechanisms that are intended to detect and announce an attempted intrusion. They will not prevent or apprehend intruders, so they should be seen as an aid to the organization’s security forces. While an IDS is a very valuable control, the technology is expensive and the system requires a redundant power supply and emergency backup power.
![]() A is incorrect because an acoustical detection system, although easy to install, is very sensitive and cannot be used in areas open to sounds of storms or traffic. An acoustical detection system uses microphones installed on floors, walls, or ceilings. The goal is to detect any sound made during a forced entry.
A is incorrect because an acoustical detection system, although easy to install, is very sensitive and cannot be used in areas open to sounds of storms or traffic. An acoustical detection system uses microphones installed on floors, walls, or ceilings. The goal is to detect any sound made during a forced entry.
![]() C is incorrect because a photoelectric system cannot be used in a room with windows. A photoelectric system triggers an alarm when it detects changes in a light beam that is emitted. The beams can be visible or invisible. Photoelectric systems are commonly used in museums to protect works of art. If a visitor attempts to cross a room to steal a priceless sculpture, a beam will be broken and an alarm will sound.
C is incorrect because a photoelectric system cannot be used in a room with windows. A photoelectric system triggers an alarm when it detects changes in a light beam that is emitted. The beams can be visible or invisible. Photoelectric systems are commonly used in museums to protect works of art. If a visitor attempts to cross a room to steal a priceless sculpture, a beam will be broken and an alarm will sound.
![]() D is incorrect because, similar to an acoustical detection system, vibration sensors are sensitive to things like traffic and storms that could cause false positives. A vibration sensor senses vibrations in walls and floors. Financial institutions may choose to implement them on exterior walls where bank robbers may attempt to drive a vehicle through. They are also commonly used around the ceiling and flooring of vaults to detect someone attempting to break in.
D is incorrect because, similar to an acoustical detection system, vibration sensors are sensitive to things like traffic and storms that could cause false positives. A vibration sensor senses vibrations in walls and floors. Financial institutions may choose to implement them on exterior walls where bank robbers may attempt to drive a vehicle through. They are also commonly used around the ceiling and flooring of vaults to detect someone attempting to break in.
17. David is preparing a server room at a new branch office. What locking mechanisms should he use for the primary and secondary server room entry doors?
A. The primary and secondary entrance doors should have access controlled through a swipe card or cipher lock.
B. The primary entrance door should have access controlled through a security guard. The secondary doors should be secured from the inside and allow no entry.
C. The primary entrance door should have access controlled through a swipe card or cipher lock. The secondary doors should have a security guard.
D. The primary entrance door should have access controlled through a swipe card or cipher lock. Secondary doors should be secured from the inside and allow no entry.
![]() D. Data centers, server rooms, and wiring closets should be located in the core areas of a facility, near wiring distribution centers. Strict access control mechanisms and procedures should be implemented for these areas. The access control mechanisms may be smart card readers, biometric readers, or combination locks. These restricted areas should have only one access door, but fire code requirements typically dictate there must be at least two doors to most data centers and server rooms. Only one door should be used for daily entry and exit and the other door should be used only in emergency situations. This second door should not be an access door, which means people should not be able to come in through this door. It should be locked, but it should have a panic bar that will release the lock if pressed from inside and used as an exit.
D. Data centers, server rooms, and wiring closets should be located in the core areas of a facility, near wiring distribution centers. Strict access control mechanisms and procedures should be implemented for these areas. The access control mechanisms may be smart card readers, biometric readers, or combination locks. These restricted areas should have only one access door, but fire code requirements typically dictate there must be at least two doors to most data centers and server rooms. Only one door should be used for daily entry and exit and the other door should be used only in emergency situations. This second door should not be an access door, which means people should not be able to come in through this door. It should be locked, but it should have a panic bar that will release the lock if pressed from inside and used as an exit.
![]() A is incorrect because entrance should not be permitted through the secondary door—even with identification, authentication, and authorization processes. There should only be one entry point into a server room. Other doors should not provide entrance but can be used for emergency exits. Thus, the secondary doors should be secured from the inside to prevent entry.
A is incorrect because entrance should not be permitted through the secondary door—even with identification, authentication, and authorization processes. There should only be one entry point into a server room. Other doors should not provide entrance but can be used for emergency exits. Thus, the secondary doors should be secured from the inside to prevent entry.
![]() B is incorrect because the primary entrance door to a server room needs to carry out identification, authentication, and authorization processes. A swipe card or cipher lock fulfills these functions. A server room, ideally, should not be directly accessible from public areas like stairways, corridors, loading docks, elevators, and restrooms. This helps prevent foot traffic from casual passersby. Those who are by the doors to secured areas should have a legitimate reason for being there, as opposed to being on their way to a meeting room, for example.
B is incorrect because the primary entrance door to a server room needs to carry out identification, authentication, and authorization processes. A swipe card or cipher lock fulfills these functions. A server room, ideally, should not be directly accessible from public areas like stairways, corridors, loading docks, elevators, and restrooms. This helps prevent foot traffic from casual passersby. Those who are by the doors to secured areas should have a legitimate reason for being there, as opposed to being on their way to a meeting room, for example.
![]() C is incorrect because the secondary door should not have a security guard. The door should simply be secured from the inside so that it cannot be used as an entry. The secondary door should serve as an emergency exit.
C is incorrect because the secondary door should not have a security guard. The door should simply be secured from the inside so that it cannot be used as an entry. The secondary door should serve as an emergency exit.
18. Which of the following is not true of IDSs?
A. They can be hindered by items within the room.
B. They are expensive and require human intervention to respond to the alarms.
C. They usually come with a redundant power supply and emergency backup power.
D. They should detect, and be resistant to, tampering.
![]() C. Intrusion detection systems do not commonly come with a redundant power supply and emergency backup power. However, these things are necessary. Without them, an IDS will be inoperable if the main source of power becomes unavailable, leaving assets at risk.
C. Intrusion detection systems do not commonly come with a redundant power supply and emergency backup power. However, these things are necessary. Without them, an IDS will be inoperable if the main source of power becomes unavailable, leaving assets at risk.
![]() A is incorrect because IDSs can be hindered by items within a room. In fact, the items within the room, as well as the size and shape of the room, may cause barriers, in which case more detectors are needed to provide the necessary level of coverage.
A is incorrect because IDSs can be hindered by items within a room. In fact, the items within the room, as well as the size and shape of the room, may cause barriers, in which case more detectors are needed to provide the necessary level of coverage.
![]() B is incorrect because IDSs are relatively expensive and they do require human intervention to respond to the alarms. IDSs are used to detect unauthorized entries and alert a responsible entity to respond. These systems can monitor entries, doors, windows, devices, or removable coverings of equipment. Many work with magnetic contacts or vibration-detection devices that are sensitive to certain types of changes in the environment. When a change is detected, the IDS device sounds an alarm either in the local area, or in both the local area and a remote police or guard station.
B is incorrect because IDSs are relatively expensive and they do require human intervention to respond to the alarms. IDSs are used to detect unauthorized entries and alert a responsible entity to respond. These systems can monitor entries, doors, windows, devices, or removable coverings of equipment. Many work with magnetic contacts or vibration-detection devices that are sensitive to certain types of changes in the environment. When a change is detected, the IDS device sounds an alarm either in the local area, or in both the local area and a remote police or guard station.
![]() D is incorrect because IDSs should detect, and be resistant to, tampering. Intruders like to cover their tracks to avoid detection. Obviously, if the IDS can be disabled or tampered with so that an alarm does not trigger or evidence of an intrusion is destroyed, then the IDS cannot do its job. So an IDS worth its salt should have its own intrusion prevention mechanisms.
D is incorrect because IDSs should detect, and be resistant to, tampering. Intruders like to cover their tracks to avoid detection. Obviously, if the IDS can be disabled or tampered with so that an alarm does not trigger or evidence of an intrusion is destroyed, then the IDS cannot do its job. So an IDS worth its salt should have its own intrusion prevention mechanisms.
19. Before an effective physical security program can be rolled out, a number of steps must be taken. Which of the following steps comes first in the process of rolling out a security program?
A. Create countermeasure performance metrics.
B. Conduct a risk analysis.
C. Design the program.
D. Implement countermeasures.
![]() B. Of the steps listed, the first in the process of rolling out an effective physical security program is to carry out a risk analysis to identify the vulnerabilities and threats, and calculate the business impact of each threat. But before this is done, a team of internal employees and/or external consultants needs to be identified to build the physical security program. The team presents the risk analysis findings to management and works with them to define an acceptable risk level for the physical security program. From there, the team must develop baselines and metrics in order to evaluate and determine if the baselines are being met by the implemented countermeasures. Once the team identifies and implements the countermeasures, the performance of these countermeasures should be continually evaluated and expressed in the previously created metrics. These performance values are compared to the set baselines. If the baselines are continually maintained, then the security program is successful because the company’s acceptable risk level is not being exceeded.
B. Of the steps listed, the first in the process of rolling out an effective physical security program is to carry out a risk analysis to identify the vulnerabilities and threats, and calculate the business impact of each threat. But before this is done, a team of internal employees and/or external consultants needs to be identified to build the physical security program. The team presents the risk analysis findings to management and works with them to define an acceptable risk level for the physical security program. From there, the team must develop baselines and metrics in order to evaluate and determine if the baselines are being met by the implemented countermeasures. Once the team identifies and implements the countermeasures, the performance of these countermeasures should be continually evaluated and expressed in the previously created metrics. These performance values are compared to the set baselines. If the baselines are continually maintained, then the security program is successful because the company’s acceptable risk level is not being exceeded.
![]() A is incorrect because of the steps listed, creating countermeasure performance metrics is not the first step in creating a physical security program. It is, however, a very important one because it is only possible to determine how beneficial and effective the program is if it is monitored through a performance-based approach. This means you should devise measurements and metrics to measure the effectiveness of the chosen countermeasures. This enables management to make informed business decisions when investing in the protection of the organization’s physical security. The goal is to increase the performance of the physical security program and decrease the risk to the company in a cost-effective manner. You should establish a baseline of performance and thereafter continually evaluate performance to make sure that the company’s protection objectives are being met. Examples of possible performance metrics include number of successful crimes, number of successful disruptions, and the time it took for a criminal to defeat a control.
A is incorrect because of the steps listed, creating countermeasure performance metrics is not the first step in creating a physical security program. It is, however, a very important one because it is only possible to determine how beneficial and effective the program is if it is monitored through a performance-based approach. This means you should devise measurements and metrics to measure the effectiveness of the chosen countermeasures. This enables management to make informed business decisions when investing in the protection of the organization’s physical security. The goal is to increase the performance of the physical security program and decrease the risk to the company in a cost-effective manner. You should establish a baseline of performance and thereafter continually evaluate performance to make sure that the company’s protection objectives are being met. Examples of possible performance metrics include number of successful crimes, number of successful disruptions, and the time it took for a criminal to defeat a control.
![]() C is incorrect because designing the program should take place after the risk analysis. Once the level of risk is understood then the design phase can take place to protect from the threats identified in the risk analysis. The design will incorporate the controls required for each category of the program: deterrence, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
C is incorrect because designing the program should take place after the risk analysis. Once the level of risk is understood then the design phase can take place to protect from the threats identified in the risk analysis. The design will incorporate the controls required for each category of the program: deterrence, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
![]() D is incorrect because implementing countermeasures is one of the last steps in the process rolling out a physical security program. Before countermeasures can be identified and implemented, it is important to conduct a risk analysis and work with management to define an acceptable level of risk. From the acceptable risk level, the team should derive the required performance baselines, and then create countermeasure performance metrics. Next, the team should develop criteria from the results of the analysis, outlining the level of protection and performance required for deterrence, delaying, detection, assessment, and response. Only after these steps are completed should the team identify and implement countermeasures for each of these categories.
D is incorrect because implementing countermeasures is one of the last steps in the process rolling out a physical security program. Before countermeasures can be identified and implemented, it is important to conduct a risk analysis and work with management to define an acceptable level of risk. From the acceptable risk level, the team should derive the required performance baselines, and then create countermeasure performance metrics. Next, the team should develop criteria from the results of the analysis, outlining the level of protection and performance required for deterrence, delaying, detection, assessment, and response. Only after these steps are completed should the team identify and implement countermeasures for each of these categories.
20. A number of measures should be taken to help protect devices and the environment from electric power issues. Which of the following is best to keep voltage steady and power clean?
A. Power line monitor
B. Surge protector
C. Shielded cabling
D. Regulator
![]() D. When clean power is being provided, the power supply contains no interference or voltage fluctuation. Mechanisms should be in place to detect unwanted power fluctuations and protect the integrity of your data processing environment. Voltage regulators and line conditioners can be used to ensure a clean and smooth distribution of power. The primary power runs through a regulator or conditioner. They have the capability to absorb extra current if there is a spike, and to store energy to add current to the line if there is a sag. The goal is to keep the current flowing at a nice, steady level so neither motherboard components nor employees get fried.
D. When clean power is being provided, the power supply contains no interference or voltage fluctuation. Mechanisms should be in place to detect unwanted power fluctuations and protect the integrity of your data processing environment. Voltage regulators and line conditioners can be used to ensure a clean and smooth distribution of power. The primary power runs through a regulator or conditioner. They have the capability to absorb extra current if there is a spike, and to store energy to add current to the line if there is a sag. The goal is to keep the current flowing at a nice, steady level so neither motherboard components nor employees get fried.
![]() A is incorrect because power line monitors are employed to detect frequency and voltage amplitude changes. Interference interrupts the flow of an electrical current, and fluctuations can actually deliver a different level of voltage than what was expected. Each fluctuation can be damaging to devices and people. In order to effectively monitor frequency and voltage amplitude changes, you should understand what they are. Power excess can be described as a spike, which is momentary high voltage, or a surge, which is prolonged high voltage. Power loss can be experienced as a fault—momentary power outage—or a blackout—prolonged, complete loss of electric power. A sag or dip is a momentary low voltage condition, from one cycle to a few seconds. A brownout, also a type of power degradation, is a prolonged power supply that is below normal voltage. Finally, an in-rush current is an initial surge of current required to start a load.
A is incorrect because power line monitors are employed to detect frequency and voltage amplitude changes. Interference interrupts the flow of an electrical current, and fluctuations can actually deliver a different level of voltage than what was expected. Each fluctuation can be damaging to devices and people. In order to effectively monitor frequency and voltage amplitude changes, you should understand what they are. Power excess can be described as a spike, which is momentary high voltage, or a surge, which is prolonged high voltage. Power loss can be experienced as a fault—momentary power outage—or a blackout—prolonged, complete loss of electric power. A sag or dip is a momentary low voltage condition, from one cycle to a few seconds. A brownout, also a type of power degradation, is a prolonged power supply that is below normal voltage. Finally, an in-rush current is an initial surge of current required to start a load.
![]() B is incorrect because a surge protector is used to move excess voltage to ground when a surge occurs. A surge is a prolonged rise in voltage from a power source. Surges can cause a lot of damage very quickly. A surge is one of the most common power problems and is controlled with surge protectors. A surge can come from a strong lightning strike, a power plant going online or offline, a shift in the commercial utility power grid, and electrical equipment within a business starting and stopping. Most computers have a built-in surge protector in their power supplies, but these are small surge protectors and cannot provide protection against the damage that larger surges (say, from storms) can cause. So, you need to ensure all devices are properly plugged into larger surge protectors, whose only job is to absorb any extra current before it is passed to electrical devices.
B is incorrect because a surge protector is used to move excess voltage to ground when a surge occurs. A surge is a prolonged rise in voltage from a power source. Surges can cause a lot of damage very quickly. A surge is one of the most common power problems and is controlled with surge protectors. A surge can come from a strong lightning strike, a power plant going online or offline, a shift in the commercial utility power grid, and electrical equipment within a business starting and stopping. Most computers have a built-in surge protector in their power supplies, but these are small surge protectors and cannot provide protection against the damage that larger surges (say, from storms) can cause. So, you need to ensure all devices are properly plugged into larger surge protectors, whose only job is to absorb any extra current before it is passed to electrical devices.
![]() C is incorrect because shielded cabling should be used for long cable runs and cables that run in buildings with fluorescent lighting or other interference mechanisms. Fluorescent lighting gives off radio frequency interference (RFI), which is disturbance to the flow of electric power while it travels across a power line. We could rip out all the fluorescent lighting in our buildings—or we can use shielded cabling where fluorescent lighting could cause a problem. If you were to climb up into your office’s dropped ceiling and look around, you would probably see wires bundled and tied up to the true ceiling. If your office is using fluorescent lighting, the power and data lines should not be running over, or on top of, the fluorescent lights. This is because the radio frequencies being given off can interfere with the data or power current as it travels through these wires.
C is incorrect because shielded cabling should be used for long cable runs and cables that run in buildings with fluorescent lighting or other interference mechanisms. Fluorescent lighting gives off radio frequency interference (RFI), which is disturbance to the flow of electric power while it travels across a power line. We could rip out all the fluorescent lighting in our buildings—or we can use shielded cabling where fluorescent lighting could cause a problem. If you were to climb up into your office’s dropped ceiling and look around, you would probably see wires bundled and tied up to the true ceiling. If your office is using fluorescent lighting, the power and data lines should not be running over, or on top of, the fluorescent lights. This is because the radio frequencies being given off can interfere with the data or power current as it travels through these wires.
21. What type of fence detects if someone attempts to climb or cut it?
A. Class IV
B. PIDAS
C. CPTED
D. PCCIP
![]() B. Perimeter Intrusion Detection and Assessment System (PIDAS) is a type of fencing that has sensors located on the wire mesh and at the base of the fence. It is used to detect if someone attempts to cut or climb the fence. It has a passive cable vibration sensor that sets off an alarm if an intrusion is detected. PIDAS is very sensitive and can cause many false alarms. PIDAS fencing serves as a detective control. It is used in high-security areas, such as around military and prison facilities, and is also useful in areas that cannot be easily observed.
B. Perimeter Intrusion Detection and Assessment System (PIDAS) is a type of fencing that has sensors located on the wire mesh and at the base of the fence. It is used to detect if someone attempts to cut or climb the fence. It has a passive cable vibration sensor that sets off an alarm if an intrusion is detected. PIDAS is very sensitive and can cause many false alarms. PIDAS fencing serves as a detective control. It is used in high-security areas, such as around military and prison facilities, and is also useful in areas that cannot be easily observed.
![]() A is incorrect because fencing is not classified in this manner. Classes are used to refer to gates. A Class IV gate means that it provides restricted access. This includes a prison entrance that is monitored in person or via closed circuitry. Each gate classification has its own long list of implementation and maintenance guidelines in order to ensure the necessary level of protection. These classifications and guidelines are developed by Underwriters Laboratory (UL), a nonprofit organization that tests, inspects, and classifies electronic devices, fire protection equipment, and specific construction materials.
A is incorrect because fencing is not classified in this manner. Classes are used to refer to gates. A Class IV gate means that it provides restricted access. This includes a prison entrance that is monitored in person or via closed circuitry. Each gate classification has its own long list of implementation and maintenance guidelines in order to ensure the necessary level of protection. These classifications and guidelines are developed by Underwriters Laboratory (UL), a nonprofit organization that tests, inspects, and classifies electronic devices, fire protection equipment, and specific construction materials.
![]() C is incorrect because CPTED is not a type of fencing. CPTED stands for Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design. It is a discipline that describes how to design a physical environment to affect human behavior, thereby reducing crime. CPTED has been used to develop physical security programs, as well as neighborhoods, towns, and cities. It addresses landscaping, entrances, facility and neighborhood layouts, lighting, road placement, and traffic circulation patterns—all in an effort to discourage criminal activity.
C is incorrect because CPTED is not a type of fencing. CPTED stands for Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design. It is a discipline that describes how to design a physical environment to affect human behavior, thereby reducing crime. CPTED has been used to develop physical security programs, as well as neighborhoods, towns, and cities. It addresses landscaping, entrances, facility and neighborhood layouts, lighting, road placement, and traffic circulation patterns—all in an effort to discourage criminal activity.
![]() D is incorrect because the PCCIP is the President’s Commission on Critical Infrastructure Protection. PCCIP is an executive order that requires organizations that are part of the national critical infrastructure to have adequate protection mechanisms in place. This includes the technical protection of systems and data, as well as the physical protection of the facilities themselves. It outlines that power systems, emergency services, water supply systems, gas and oil transportation, and government services must be evaluated to ensure that proper physical security is implemented.
D is incorrect because the PCCIP is the President’s Commission on Critical Infrastructure Protection. PCCIP is an executive order that requires organizations that are part of the national critical infrastructure to have adequate protection mechanisms in place. This includes the technical protection of systems and data, as well as the physical protection of the facilities themselves. It outlines that power systems, emergency services, water supply systems, gas and oil transportation, and government services must be evaluated to ensure that proper physical security is implemented.
22. Several different types of smoke and fire detectors can be used. What type of detector is shown in the following graphic?
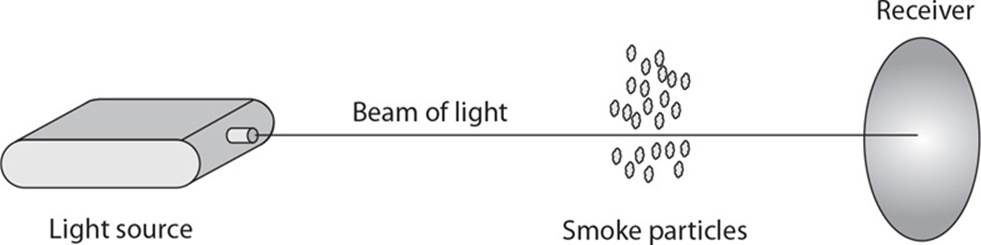
A. Photoelectric
B. Heat-activated
C. Infrared flame
D. Ionization
![]() A. A photoelectric device, also referred to as an optical detector, detects the variation in light intensity. The detector produces a beam of light across a protected area, and if the beam is obstructed, the alarm sounds. If the light source is obscured, the alarm will sound.
A. A photoelectric device, also referred to as an optical detector, detects the variation in light intensity. The detector produces a beam of light across a protected area, and if the beam is obstructed, the alarm sounds. If the light source is obscured, the alarm will sound.
![]() B is incorrect because heat-activated detectors can be configured to sound an alarm either when a predefined temperature (fixed temperature) is reached or when the temperature increases over a period of time (rate-of-rise). Rate-of-rise temperature sensors usually provide a quicker warning than fixed-temperature sensors because they are more sensitive, but they can also cause more false alarms.
B is incorrect because heat-activated detectors can be configured to sound an alarm either when a predefined temperature (fixed temperature) is reached or when the temperature increases over a period of time (rate-of-rise). Rate-of-rise temperature sensors usually provide a quicker warning than fixed-temperature sensors because they are more sensitive, but they can also cause more false alarms.
![]() C is incorrect because an infrared flame detector reacts to emissions of flames and senses pulsation of flames. This type of detector does not use a beam of light to identify smoke; thus, it is not a smoke detector. This type is a fire detector because it actually initiates when it is affected by flames.
C is incorrect because an infrared flame detector reacts to emissions of flames and senses pulsation of flames. This type of detector does not use a beam of light to identify smoke; thus, it is not a smoke detector. This type is a fire detector because it actually initiates when it is affected by flames.
![]() D is incorrect because an ionization detector reacts to charged particles of smoke. It is a smoke detector and not a fire detector because it activates when it encounters smoke particles. It does not use a beam of light to identify smoke, but has sensors that can identify the charged (ionized) components within the smoke itself.
D is incorrect because an ionization detector reacts to charged particles of smoke. It is a smoke detector and not a fire detector because it activates when it encounters smoke particles. It does not use a beam of light to identify smoke, but has sensors that can identify the charged (ionized) components within the smoke itself.
23. Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) is a discipline that outlines how the proper design of a physical environment can reduce crime by directly affecting human behavior. Of CPTED’s three main components, what is illustrated in the following photo?
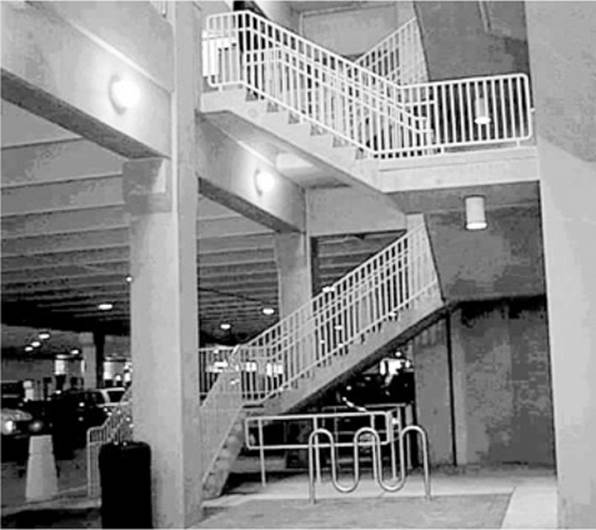

A. Natural surveillance
B. Target hardening
C. Natural access control
D. Territorial reinforcement
![]() A. CPTED provides three main strategies to bring together the physical environment and social behavior to increase overall protection: natural access control, natural surveillance, and territorial reinforcement. Surveillance can take place through organized means (security guards), mechanical means (CCTV), and natural strategies (straight lines of sight, low landscaping, raised entrances). The goal of natural surveillance is to make criminals feel uncomfortable by providing many ways observers could potentially see them, and make all other people feel safe and comfortable, by providing an open and well-designed environment. Natural surveillance is the use and placement of physical environmental features, personnel walkways, and activity areas in ways that maximize visibility. This photo shows a stairway in a building designed to be open and allow easy observation.
A. CPTED provides three main strategies to bring together the physical environment and social behavior to increase overall protection: natural access control, natural surveillance, and territorial reinforcement. Surveillance can take place through organized means (security guards), mechanical means (CCTV), and natural strategies (straight lines of sight, low landscaping, raised entrances). The goal of natural surveillance is to make criminals feel uncomfortable by providing many ways observers could potentially see them, and make all other people feel safe and comfortable, by providing an open and well-designed environment. Natural surveillance is the use and placement of physical environmental features, personnel walkways, and activity areas in ways that maximize visibility. This photo shows a stairway in a building designed to be open and allow easy observation.
![]() B is incorrect because target hardening focuses on denying access through physical and artificial barriers (alarms, locks, fences, and so on). Target hardening is not a component of CPTED. Traditional target hardening can lead to restrictions on the use, enjoyment, and aesthetics of an environment. If your environment is a prison, this look might be just what you need. But if your environment is an office building, you’re not looking for Fort Knox décor. Nevertheless, you still must provide the necessary levels of protection, but your protection mechanisms should be more subtle and unobtrusive. Let’s say your organization’s team needs to protect a side door at your facility. The traditional target-hardening approach would be to put locks, alarms, and cameras on the door; install an access control mechanism, such as a proximity reader; and instruct security guards to monitor this door.
B is incorrect because target hardening focuses on denying access through physical and artificial barriers (alarms, locks, fences, and so on). Target hardening is not a component of CPTED. Traditional target hardening can lead to restrictions on the use, enjoyment, and aesthetics of an environment. If your environment is a prison, this look might be just what you need. But if your environment is an office building, you’re not looking for Fort Knox décor. Nevertheless, you still must provide the necessary levels of protection, but your protection mechanisms should be more subtle and unobtrusive. Let’s say your organization’s team needs to protect a side door at your facility. The traditional target-hardening approach would be to put locks, alarms, and cameras on the door; install an access control mechanism, such as a proximity reader; and instruct security guards to monitor this door.
![]() C is incorrect because natural access control is the guidance of people entering and leaving a space by the placement of doors, fences, lighting, and even landscaping. For example, an office building may have external bollards with lights in them. These bollards actually carry out different safety and security services. The bollards themselves protect the facility from physical destruction by preventing people from driving their cars into the building. The light emitted helps ensure that criminals do not have a dark place to hide. And the lights and bollard placement guides people along the sidewalk to the entrance, instead of using signs or railings. They work together to give individuals a feeling of being in a safe environment and help dissuade criminals by working as deterrents.
C is incorrect because natural access control is the guidance of people entering and leaving a space by the placement of doors, fences, lighting, and even landscaping. For example, an office building may have external bollards with lights in them. These bollards actually carry out different safety and security services. The bollards themselves protect the facility from physical destruction by preventing people from driving their cars into the building. The light emitted helps ensure that criminals do not have a dark place to hide. And the lights and bollard placement guides people along the sidewalk to the entrance, instead of using signs or railings. They work together to give individuals a feeling of being in a safe environment and help dissuade criminals by working as deterrents.
![]() D is incorrect because the third CPTED strategy is territorial reinforcement, which creates physical designs that emphasize or extend the company’s physical sphere of influence so legitimate users feel a sense of ownership of that space. Territorial reinforcement can be implemented through the use of walls, fences, landscaping, light fixtures, flags, clearly marked addresses, and decorative sidewalks. The goal of territorial reinforcement is to create a sense of a dedicated community. Companies implement these elements so employees feel proud of their environment and have a sense of belonging, which they will defend if required to do so. These elements are also implemented to give potential offenders the impression that they do not belong there, that their activities are at risk of being observed, and that their illegal activities will not be tolerated or ignored.
D is incorrect because the third CPTED strategy is territorial reinforcement, which creates physical designs that emphasize or extend the company’s physical sphere of influence so legitimate users feel a sense of ownership of that space. Territorial reinforcement can be implemented through the use of walls, fences, landscaping, light fixtures, flags, clearly marked addresses, and decorative sidewalks. The goal of territorial reinforcement is to create a sense of a dedicated community. Companies implement these elements so employees feel proud of their environment and have a sense of belonging, which they will defend if required to do so. These elements are also implemented to give potential offenders the impression that they do not belong there, that their activities are at risk of being observed, and that their illegal activities will not be tolerated or ignored.
24. Different types of material are built into walls and other constructs of various types of buildings and facilities. What type of material is shown in the following photo?
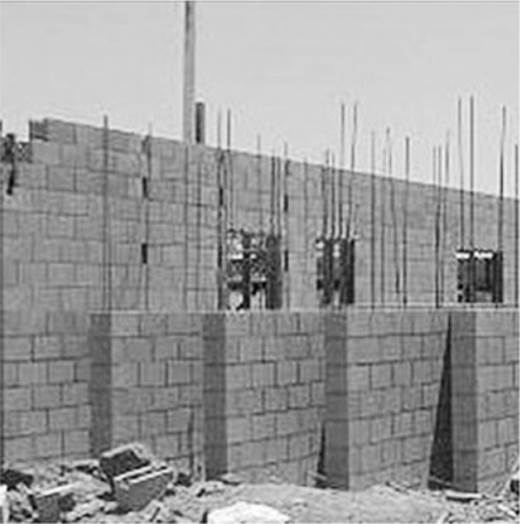

A. Fire-resistant material
B. Light frame construction material
C. Heavy timber construction material
D. Rebar material
![]() D. Calculations of approximate penetration times for different types of explosives and attacks are based on the thickness of the concrete walls and the gauge of rebar used. (Rebar refers to the steel rods encased within the concrete.) So even if the concrete can be damaged, it will take longer to actually cut or break through the rebar. Using thicker rebar and properly placing it within the concrete provides even more protection. Reinforced walls, rebar, and the use of double walls can be used as delaying mechanisms.
D. Calculations of approximate penetration times for different types of explosives and attacks are based on the thickness of the concrete walls and the gauge of rebar used. (Rebar refers to the steel rods encased within the concrete.) So even if the concrete can be damaged, it will take longer to actually cut or break through the rebar. Using thicker rebar and properly placing it within the concrete provides even more protection. Reinforced walls, rebar, and the use of double walls can be used as delaying mechanisms.
![]() A is incorrect because a building could be made up of incombustible material, such as steel, which provides a higher level of fire protection but loses its strength under extreme temperatures, something that may cause the building to collapse. This type of material has to do with the reduction of time and amount of fire damage instead of the difficulty of getting through a wall. The photo illustrates rebar, which is a material that reinforces the strength of walls.
A is incorrect because a building could be made up of incombustible material, such as steel, which provides a higher level of fire protection but loses its strength under extreme temperatures, something that may cause the building to collapse. This type of material has to do with the reduction of time and amount of fire damage instead of the difficulty of getting through a wall. The photo illustrates rebar, which is a material that reinforces the strength of walls.
![]() B is incorrect because light frame construction material is not illustrated in this photo. Light frame construction is composed of untreated lumber and is usually used to build homes, primarily because it is cheap but also because homes typically are not under the same types of fire and intrusion threats that office buildings are. The photo illustrates rebar, which is a material that reinforces the strength of walls.
B is incorrect because light frame construction material is not illustrated in this photo. Light frame construction is composed of untreated lumber and is usually used to build homes, primarily because it is cheap but also because homes typically are not under the same types of fire and intrusion threats that office buildings are. The photo illustrates rebar, which is a material that reinforces the strength of walls.
![]() C is incorrect because heavy timber construction material is not illustrated in this photo. Heavy timber is commonly used for office buildings. The photo illustrates rebar, which is a material that reinforces the strength of walls.
C is incorrect because heavy timber construction material is not illustrated in this photo. Heavy timber is commonly used for office buildings. The photo illustrates rebar, which is a material that reinforces the strength of walls.
25. There are five different classes of fire. Each depends upon what is on fire. Which of the following is the proper mapping for the items missing in the provided table?
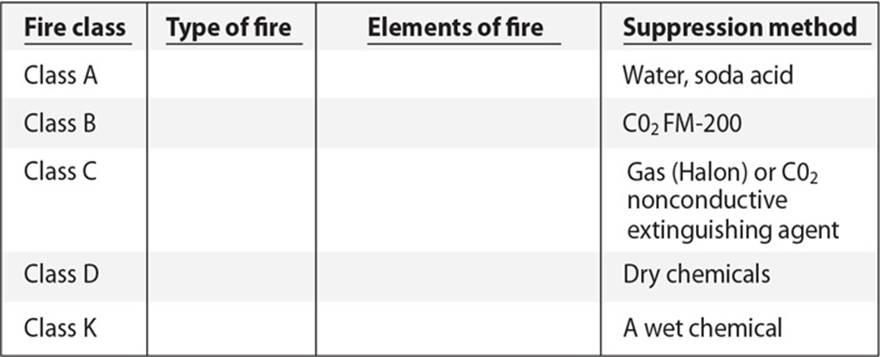
A. Class D—combustible metals
B. Class C—liquid
C. Class B—electrical
D. Class A—electrical
![]() A. There are five classes (A, B, C, D, and K) of fire. You need to know the differences among the types of fire so that you know how to properly extinguish each type. Portable fire extinguishers have markings that indicate what type of fire they should be used on. A fire is a Class D if there are combustible metals on fire. These metals can be magnesium, sodium, or potassium. These types of fires should be suppressed and extinguished with dry chemicals.
A. There are five classes (A, B, C, D, and K) of fire. You need to know the differences among the types of fire so that you know how to properly extinguish each type. Portable fire extinguishers have markings that indicate what type of fire they should be used on. A fire is a Class D if there are combustible metals on fire. These metals can be magnesium, sodium, or potassium. These types of fires should be suppressed and extinguished with dry chemicals.
![]() B is incorrect because a fire is a Class C if there is something electrical on fire. This can be computers or any other types of devices that run on electricity. These types of fires should be suppressed and extinguished with a type of gas as in Halon or CO2.
B is incorrect because a fire is a Class C if there is something electrical on fire. This can be computers or any other types of devices that run on electricity. These types of fires should be suppressed and extinguished with a type of gas as in Halon or CO2.
![]() C is incorrect because a fire is a Class B if there is something liquid on fire. This can be petroleum, tars, or oils. These types of fires should be suppressed and extinguished with a type of gas as in FM-200 or CO2.
C is incorrect because a fire is a Class B if there is something liquid on fire. This can be petroleum, tars, or oils. These types of fires should be suppressed and extinguished with a type of gas as in FM-200 or CO2.
![]() D is incorrect because a fire is a Class A if there is a type of common combustible material on fire. This can be wood, paper, or cloth. These types of fires should be suppressed and extinguished with water or soda acid.
D is incorrect because a fire is a Class A if there is a type of common combustible material on fire. This can be wood, paper, or cloth. These types of fires should be suppressed and extinguished with water or soda acid.
26. Electrical power is being provided more through smart grids, which allow for self-healing, resistance to physical and cyberattacks, increased efficiency, and better integration of renewable energy sources. Countries want their grids to be more reliable, resilient, flexible, and efficient. Why does this type of evolution in power infrastructure concern many security professionals?
A. Allows for direct attacks through Power over Ethernet
B. Increased embedded software and computing capabilities
C. Does not have proper protection against common web-based attacks
D. Power fluctuation and outages directly affect computing systems
![]() B. We are moving to smart grids, which mean that there is a lot more computing software and technology embedded into the grids and the items that make up the grids to optimize and automate these functions. This means that almost every component of the new power grid has to be computerized in some manner; thus, it can be vulnerable to digital-based attacks. Power grids are considered critical infrastructures to countries and can have negative consequences for a country if it is affected.
B. We are moving to smart grids, which mean that there is a lot more computing software and technology embedded into the grids and the items that make up the grids to optimize and automate these functions. This means that almost every component of the new power grid has to be computerized in some manner; thus, it can be vulnerable to digital-based attacks. Power grids are considered critical infrastructures to countries and can have negative consequences for a country if it is affected.
![]() A is incorrect because smart grids do not directly deal with providing Power over Ethernet (PoE). PoE provides both data and power connections on one cable. This means that a company does not need to have one cable for Ethernet and one for power—the power and network data can be converged onto one cable. For equipment that does not already have a power or data connection, PoE can be attractive when the power demand is low.
A is incorrect because smart grids do not directly deal with providing Power over Ethernet (PoE). PoE provides both data and power connections on one cable. This means that a company does not need to have one cable for Ethernet and one for power—the power and network data can be converged onto one cable. For equipment that does not already have a power or data connection, PoE can be attractive when the power demand is low.
![]() C is incorrect because implementing computing capabilities in various power grid components does not have a direct correlation to web-based attacks. Power grid components are not going to necessarily have direct access to web servers and sites. The general term for infrastructure types of systems is SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) and generally refers to industrial control systems (ICSs). These systems monitor and control industrial, infrastructure, or facility-based processes. An attacker needs to know how to specifically exploit vulnerabilities in these types of systems, which would be different from common web site vulnerabilities.
C is incorrect because implementing computing capabilities in various power grid components does not have a direct correlation to web-based attacks. Power grid components are not going to necessarily have direct access to web servers and sites. The general term for infrastructure types of systems is SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) and generally refers to industrial control systems (ICSs). These systems monitor and control industrial, infrastructure, or facility-based processes. An attacker needs to know how to specifically exploit vulnerabilities in these types of systems, which would be different from common web site vulnerabilities.
![]() D is incorrect because power fluctuations and outages are not necessarily security issues, and these are not the most critical topics most security professionals would be concerned with as the traditional power grid moves to a smart grid. A smart grid is made up of many embedded systems, which contain software that can have vulnerabilities for exploitation.
D is incorrect because power fluctuations and outages are not necessarily security issues, and these are not the most critical topics most security professionals would be concerned with as the traditional power grid moves to a smart grid. A smart grid is made up of many embedded systems, which contain software that can have vulnerabilities for exploitation.
The following scenario is to be used for questions 27, 28, and 29.
Mike is the new CSO of a large pharmaceutical company. He has been asked to revamp the company’s physical security program and better align it with the company’s information security practices. Mike knows that the new physical security program should be made up of controls and processes that support the following categories: deterrent, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
27. Mike’s team has decided to implement new perimeter fences and warning signs against trespassing around the company’s facility. Which of the categories listed in the scenario do these countermeasures map to?
A. Deterrent
B. Delaying
C. Detection
D. Assessment
![]() A. Fences, warning signs, and security guards are examples of countermeasures that can be put into place to deter unauthorized entry. A physical security program should contain controls in each of the following categories: deterrent, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
A. Fences, warning signs, and security guards are examples of countermeasures that can be put into place to deter unauthorized entry. A physical security program should contain controls in each of the following categories: deterrent, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
![]() B is incorrect because reinforced walls, rebar, locks, and the use of double walls can be used as delaying mechanisms. The idea is that it will take the bad guy longer to get through these types of controls, which gives the response force sufficient time to arrive at the scene and stop the attacker. Deterrent controls reduce the likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited; a delaying control tries to ensure that if a bad thing happens, it will slow down the intruder.
B is incorrect because reinforced walls, rebar, locks, and the use of double walls can be used as delaying mechanisms. The idea is that it will take the bad guy longer to get through these types of controls, which gives the response force sufficient time to arrive at the scene and stop the attacker. Deterrent controls reduce the likelihood of a vulnerability being exploited; a delaying control tries to ensure that if a bad thing happens, it will slow down the intruder.
![]() C is incorrect because detection tools are implemented not to deter malicious individuals but to detect their activities. Detection tools can be intrusion detection systems, sensors, and PIDAS fencing.
C is incorrect because detection tools are implemented not to deter malicious individuals but to detect their activities. Detection tools can be intrusion detection systems, sensors, and PIDAS fencing.
![]() D is incorrect because assessment controls pertain to how different situations will be identified and assessed. The most common control in this category is a security guard because he can connect the pieces of a situation together and determine what next steps should take place. It is important that there are controls in place that will carry out incident assessment and procedures that will be followed depending upon the outcome of the assessment.
D is incorrect because assessment controls pertain to how different situations will be identified and assessed. The most common control in this category is a security guard because he can connect the pieces of a situation together and determine what next steps should take place. It is important that there are controls in place that will carry out incident assessment and procedures that will be followed depending upon the outcome of the assessment.
28. Mike’s team has decided to implement stronger locks on the exterior doors of the new company’s facility. Which of the categories listed in the scenario does this countermeasure map to?
A. Deterrent
B. Delaying
C. Detection
D. Assessment
![]() B. Locks, defense-in-depth measures, and access controls are commonly used to delay potential intruders. A physical security program should contain controls in each of the following categories: deterrent, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
B. Locks, defense-in-depth measures, and access controls are commonly used to delay potential intruders. A physical security program should contain controls in each of the following categories: deterrent, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
![]() A is incorrect because fences, warning signs, and security guards are examples of countermeasures that can be put into place to deter unauthorized entry. The goal of these types of controls is for a potential attacker to not carry out his activities in the first place.
A is incorrect because fences, warning signs, and security guards are examples of countermeasures that can be put into place to deter unauthorized entry. The goal of these types of controls is for a potential attacker to not carry out his activities in the first place.
![]() C is incorrect because detection tools are implemented not to deter malicious individuals but to detect their activities. Detection tools can be intrusion detection systems, sensors, and PIDAS fencing.
C is incorrect because detection tools are implemented not to deter malicious individuals but to detect their activities. Detection tools can be intrusion detection systems, sensors, and PIDAS fencing.
![]() D is incorrect because assessment controls pertain to how different situations will be identified and assessed. The most common control in this category is a security guard because he can connect the pieces of a situation together and determine what next steps should take place. It is important that there are controls in place that will carry out incident assessment and procedures that will be followed depending upon the outcome of the assessment.
D is incorrect because assessment controls pertain to how different situations will be identified and assessed. The most common control in this category is a security guard because he can connect the pieces of a situation together and determine what next steps should take place. It is important that there are controls in place that will carry out incident assessment and procedures that will be followed depending upon the outcome of the assessment.
29. Mike’s team has decided to hire and deploy security guards to monitor activities within the company’s facility. Which of the categories listed in the scenario does this countermeasure map to?
A. Delaying
B. Detection
C. Assessment
D. Recall
![]() C. The assessment requirement of a physical security program pertains to how various situations will be assessed, triaged, and dealt with. The most common countermeasure to meet this need is the use of security guards.
C. The assessment requirement of a physical security program pertains to how various situations will be assessed, triaged, and dealt with. The most common countermeasure to meet this need is the use of security guards.
![]() A is incorrect because locks, defense-in-depth measures, and access controls are commonly used to delay potential intruders. A physical security program should contain controls in each of the following categories: deterrent, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
A is incorrect because locks, defense-in-depth measures, and access controls are commonly used to delay potential intruders. A physical security program should contain controls in each of the following categories: deterrent, delaying, detection, assessment, and response.
![]() B is incorrect because detection tools are implemented not to deter malicious individuals but to detect their activities. Detection tools can be intrusion detection systems, sensors, and PIDAS fencing.
B is incorrect because detection tools are implemented not to deter malicious individuals but to detect their activities. Detection tools can be intrusion detection systems, sensors, and PIDAS fencing.
![]() D is incorrect because it is a distracter answer.
D is incorrect because it is a distracter answer.
The following scenario is to be used for questions 30, 31, and 32.
Greg is the security facility officer of a financial institution. His boss has told him that visitors need a secondary screening before they are allowed into sensitive areas within the building. Greg has also been told by the network administrators that after the new HVAC system was installed throughout the facility, they have noticed that power voltage to the systems in the data center sags.
30. Which of the following is the best control that Greg should ensure is implemented to deal with his boss’s concern?
A. Access and audit logs
B. Mantrap
C. Proximity readers
D. Smart card readers
![]() B. Mantraps can be used so unauthorized individuals entering a facility cannot get in or out if it is activated. A mantrap is a small room with two doors. The first door is locked; a person is identified and authenticated by a security guard, biometric system, smart card reader, or swipe card reader. Once the person is authenticated and access is authorized, the first door opens and allows the person into the mantrap. The first door locks and the person is trapped. The person must be authenticated again before the second door unlocks and allows him into the facility. This requires two different authentication and authorization processes to complete successfully before someone is allowed entrance.
B. Mantraps can be used so unauthorized individuals entering a facility cannot get in or out if it is activated. A mantrap is a small room with two doors. The first door is locked; a person is identified and authenticated by a security guard, biometric system, smart card reader, or swipe card reader. Once the person is authenticated and access is authorized, the first door opens and allows the person into the mantrap. The first door locks and the person is trapped. The person must be authenticated again before the second door unlocks and allows him into the facility. This requires two different authentication and authorization processes to complete successfully before someone is allowed entrance.
![]() A is incorrect because access and audit logs are not controls that can be used to carry out secondary screening activities. These are detective controls that are commonly reviewed after an incident has occurred.
A is incorrect because access and audit logs are not controls that can be used to carry out secondary screening activities. These are detective controls that are commonly reviewed after an incident has occurred.
![]() C is incorrect because it is not necessarily the best answer to this question. Proximity cards are most commonly used to gain physical access to a facility or location. The question specifically points out a requirement of secondary authentication to take place before someone can enter a sensitive area within a facility, and this is the reason that mantraps exist.
C is incorrect because it is not necessarily the best answer to this question. Proximity cards are most commonly used to gain physical access to a facility or location. The question specifically points out a requirement of secondary authentication to take place before someone can enter a sensitive area within a facility, and this is the reason that mantraps exist.
![]() D is incorrect because it is not necessarily the best answer to this question. Smart cards can be used for authentication purposes in many different situations. The question specifically points out a requirement of secondary authentication to take place before someone can enter a sensitive area within a facility, and this is the reason that mantraps exist. The mantrap might use smart cards as one of its authentication steps.
D is incorrect because it is not necessarily the best answer to this question. Smart cards can be used for authentication purposes in many different situations. The question specifically points out a requirement of secondary authentication to take place before someone can enter a sensitive area within a facility, and this is the reason that mantraps exist. The mantrap might use smart cards as one of its authentication steps.
31. Which of the following best describes the situation that the network administrators are experiencing?
A. Brownouts
B. Surges
C. In-rush current
D. Power line interference
![]() C. When a heavy electrical device is turned on, it can draw a large amount of current, which is referred to as in-rush current. If the device sucks up enough current, it can cause a sag in the available power for surrounding devices. This could negatively affect their performance. It is a good idea to have the data processing center and devices on a different electrical wiring segment from that of the rest of the facility, if possible, so the devices will not be affected by these issues.
C. When a heavy electrical device is turned on, it can draw a large amount of current, which is referred to as in-rush current. If the device sucks up enough current, it can cause a sag in the available power for surrounding devices. This could negatively affect their performance. It is a good idea to have the data processing center and devices on a different electrical wiring segment from that of the rest of the facility, if possible, so the devices will not be affected by these issues.
![]() A is incorrect because when power companies are experiencing high demand, they frequently reduce the voltage in an electrical grid, which is referred to as a brownout. Constant-voltage transformers can be used to regulate this fluctuation of power. They can use different ranges of voltage and only release the expected 120 volts of alternating current to devices. Brownouts are not usually associated with HVAC systems.
A is incorrect because when power companies are experiencing high demand, they frequently reduce the voltage in an electrical grid, which is referred to as a brownout. Constant-voltage transformers can be used to regulate this fluctuation of power. They can use different ranges of voltage and only release the expected 120 volts of alternating current to devices. Brownouts are not usually associated with HVAC systems.
![]() B is incorrect because a surge is a quick rise in voltage from a power source. Surges can cause a lot of damage very quickly. A surge is one of the most common power problems and is controlled with surge protectors. These protectors use a device called a metal oxide varistor, which moves the excess voltage to ground when a surge occurs.
B is incorrect because a surge is a quick rise in voltage from a power source. Surges can cause a lot of damage very quickly. A surge is one of the most common power problems and is controlled with surge protectors. These protectors use a device called a metal oxide varistor, which moves the excess voltage to ground when a surge occurs.
![]() D is incorrect because when clean power is being provided, the power supply contains no interference or voltage fluctuation. The possible types of interference (line noise) are electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which is disturbance to the flow of electric power while it travels across a power line. This question does not address interference issues like these.
D is incorrect because when clean power is being provided, the power supply contains no interference or voltage fluctuation. The possible types of interference (line noise) are electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI), which is disturbance to the flow of electric power while it travels across a power line. This question does not address interference issues like these.
32. Which of the following is a control that Greg’s team could implement to address the network administrators’ issue?
A. Secondary feeder line
B. Insulated grounded wiring
C. Line conditioner
D. Generator
![]() C. Because these and other occurrences are common, mechanisms should be in place to detect unwanted power fluctuations and protect the integrity of data processing environments. Voltage regulators and line conditioners can be used to ensure a clean and smooth distribution of power. The primary power runs through a regulator or conditioner. They have the capability to absorb extra current if there is a spike, and to store energy to add current to the line if there is a sag.
C. Because these and other occurrences are common, mechanisms should be in place to detect unwanted power fluctuations and protect the integrity of data processing environments. Voltage regulators and line conditioners can be used to ensure a clean and smooth distribution of power. The primary power runs through a regulator or conditioner. They have the capability to absorb extra current if there is a spike, and to store energy to add current to the line if there is a sag.
![]() A is incorrect because a secondary feeder line from a transformer does not address the issue outlined in this scenario. A secondary line would be put into place for redundancy and failover purposes.
A is incorrect because a secondary feeder line from a transformer does not address the issue outlined in this scenario. A secondary line would be put into place for redundancy and failover purposes.
![]() B is incorrect because an insulated grounded wire does not address the issue outlined in the scenario. The issue in the scenario has to do with in-rush currents, which means that the voltage of the power supply is uneven and potentially damaging. Wires are grounded to ensure that an excessive current goes to the ground and not to a piece of equipment or person. Grounding wires does not address voltage and current fluctuation.
B is incorrect because an insulated grounded wire does not address the issue outlined in the scenario. The issue in the scenario has to do with in-rush currents, which means that the voltage of the power supply is uneven and potentially damaging. Wires are grounded to ensure that an excessive current goes to the ground and not to a piece of equipment or person. Grounding wires does not address voltage and current fluctuation.
![]() D is incorrect because a generator is implemented in case there is a power outage. A generator does not have any effect on power voltage changes.
D is incorrect because a generator is implemented in case there is a power outage. A generator does not have any effect on power voltage changes.