CISSP Practice Exams, Third Edition (2015)
CHAPTER 7
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
This domain includes questions from the following topics:
• Business continuity management
• Business continuity planning components
• Standards and best practices
• Selecting, developing, and implementing disaster and continuity solutions
• Recovery and redundant technologies
• Backup and offsite facilities
• Types of drills and tests
A single, catastrophic act of nature or terrorist attack can effectively put a company out of business. In order to survive such traumas, organizations must think ahead, plan for the worst, estimate the possible damages that could occur, and implement controls to protect themselves. This is all part of disaster recovery and business continuity planning. These are not easy tasks, and their accomplishment does not show immediate returns. But organizations that choose not to plan accordingly are accepting a significant risk. As a CISSP, you need to know how to create and carry out a business continuity and disaster recovery plan to ensure that your organization can recover from a disaster.
Q QUESTIONS
1. The NIST organization has defined best practices for creating continuity plans. Which of the following phases deals with identifying and prioritizing critical functions and systems?
A. Identify preventive controls.
B. Develop the continuity planning policy statement.
C. Develop recovery strategies.
D. Conduct the business impact analysis.
2. As his company’s business continuity coordinator, Matthew is responsible for helping recruit members to the business continuity planning (BCP) committee. Which of the following does not correctly describe this effort?
A. Committee members should be involved with the planning stages, as well as the testing and implementation stages.
B. The smaller the team the better, to keep meetings under control.
C. The business continuity coordinator should work with management to appoint committee members.
D. The team should consist of people from different departments across the company.
3. A business impact analysis is considered a functional analysis. Which of the following is not carried out during a business impact analysis?
A. A parallel or full-interruption test
B. The application of a classification scheme based on criticality levels
C. The gathering of information via interviews
D. Documentation of business functions
4. When developing a recovery and continuity program within an organization, different metrics can be used to properly measure potential damages and recovery requirements. These metrics help us quantify our risks and the benefits of controls we can put into place. Two metrics commonly used in the development of recovery programs is Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO). Data restoration (RPO) requirements can be different from service restoration (RTO) requirements. Which of the following best defines these two main recovery measurements in this type of scenario?
A. RPO is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. RTO is the acceptable time period before a service level must be restored.
B. RTO is the earliest time period in which a data set must be restored. RPO is the acceptable amount of downtime in a given period.
C. RPO is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. RTO is the earliest time period in which data must be restored.
D. RPO is the acceptable amount of downtime measured. RTO is the earliest time period in which a service level must be restored.
5. An approach to alternate offsite facilities is to establish a reciprocal agreement. Which of the following describes the pros and cons of a reciprocal agreement?
A. It is fully configured and ready to operate within a few hours, but is the most expensive of the offsite choices.
B. It is an inexpensive option, but it takes the most time and effort to get up and running after a disaster.
C. It is a good alternative for companies that depend upon proprietary software, but annual testing is not usually available.
D. It is the cheapest of the offsite choices, but mixing operations could introduce many security issues.
6. Which of the following steps comes first in a business impact analysis?
A. Calculate the risk for each different business function.
B. Identify critical business functions.
C. Create data-gathering techniques.
D. Identify vulnerabilities and threats to business functions.
7. The operations team is responsible for defining which data gets backed up and how often. Which type of backup process backs up files that have been modified since the last time all data was backed up?
A. Incremental process
B. Full backup
C. Partial backup
D. Differential process
8. After a disaster occurs, a damage assessment needs to take place. Which of the following steps occurs last in a damage assessment?
A. Determine the cause of the disaster.
B. Identify the resources that must be replaced immediately.
C. Declare a disaster.
D. Determine how long it will take to bring critical functions back online.
9. Of the following plans, which establishes senior management and a headquarters after a disaster?
A. Continuity of operations plan
B. Cyber-incident response plan
C. Occupant emergency plan
D. IT contingency plan
10. It is not unusual for business continuity plans to become out of date. Which of the following is not a reason why plans become outdated?
A. Changes in hardware, software, and applications
B. Infrastructure and environment changes
C. Personnel turnover
D. That the business continuity process is integrated into the change management process
11. Preplanned business continuity procedures provide organizations a number of benefits. Which of the following is not a capability enabled by business continuity planning?
A. Resuming critical business functions
B. Letting business partners know your company is unprepared
C. Protecting lives and ensuring safety
D. Ensuring survivability of the business
12. Management support is critical to the success of a business continuity plan. Which of the following is the most important to be provided to management to obtain their support?
A. Business case
B. Business impact analysis
C. Risk analysis
D. Threat report
13. Gizmos and Gadgets has restored its original facility after a disaster. What should be moved in first?
A. Management
B. Most critical systems
C. Most critical functions
D. Least critical functions
14. Which of the following is a critical first step in disaster recovery and contingency planning?
A. Plan testing and drills.
B. Complete a business impact analysis.
C. Determine offsite backup facility alternatives.
D. Organize and create relevant documentation.
15. Which of the following is not a reason to develop and implement a disaster recovery plan?
A. Provide steps for a post-disaster recovery.
B. Extend backup operations to include more than just backing up data.
C. Outline business functions and systems.
D. Provide procedures for emergency responses.
16. When designing a system or environment, fault tolerance capabilities are commonly built in to ensure that a disruption does not negatively affect the organization. There are different approaches to fault tolerance that need to be understood. Which of the following has the best definitions associated with the identified tolerance approach?
A. Replication provides multiple different instances that can be used in parallel. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. Diversity provides multiple identical implementations.
B. Replication provides multiple identical instances that can be used in parallel. Redundancy provides multiple different instances, which allows for failover protection. Diversity provides multiple different implementations.
C. Replication provides multiple identical instances that can be used only in a failover situation. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. Diversity provides single implementations.
D. Replication provides multiple identical instances that can be used in parallel. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. Diversity provides multiple different implementations.
17. With what phase of a business continuity plan does a company proceed when it is ready to move back into its original site or a new site?
A. Reconstitution phase
B. Recovery phase
C. Project initiation phase
D. Damage assessment phase
18. Several teams should be involved in carrying out the business continuity plan. Which team is responsible for starting the recovery of the original site?
A. Damage assessment team
B. BCP team
C. Salvage team
D. Restoration team
19. ACME Inc. paid a software vendor to develop specialized software, and that vendor has gone out of business. ACME Inc. does not have access to the code and therefore cannot keep it updated. What mechanism should the company have implemented to prevent this from happening?
A. Reciprocal agreement
B. Software escrow
C. Electronic vaulting
D. Business interruption insurance
20. Which of the following incorrectly describes the concept of executive succession planning?
A. Predetermined steps protect the company if a senior executive leaves.
B. Two or more senior staff cannot be exposed to a particular risk at the same time.
C. It documents the assignment of deputy roles.
D. It covers assigning a skeleton crew to resume operations after a disaster.
21. What is the missing second step in the graphic that follows?
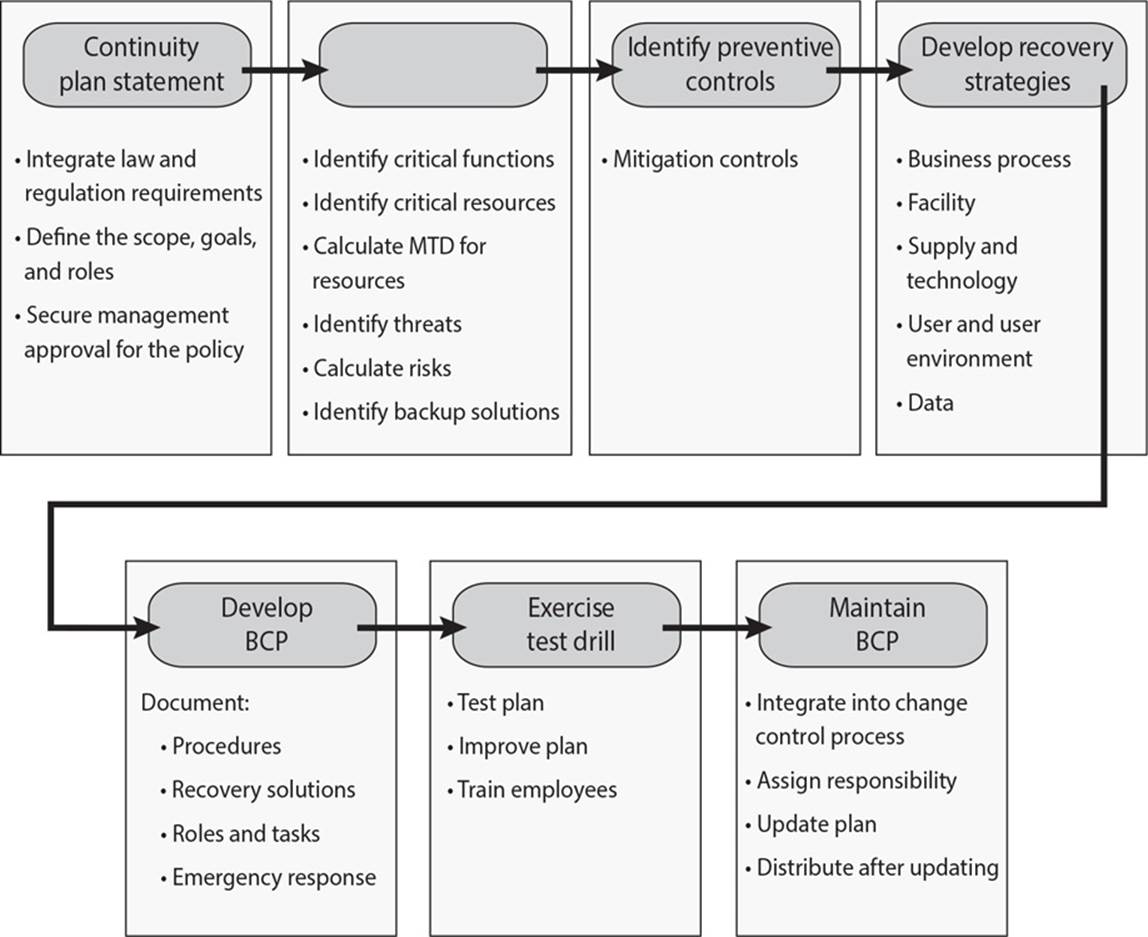
A. Identify continuity coordinator
B. Business impact analysis
C. Identify BCP committee
D. Dependency identification
22. Different threats need to be evaluated and ranked based upon their severity of business risk when developing a BCP. Which ranking approach is illustrated in the graphic that follows?

A. Mean time to repair
B. Mean time between failures
C. Maximum critical downtime
D. Maximum tolerable downtime
23. What type of infrastructural setup is illustrated in the graphic that follows?
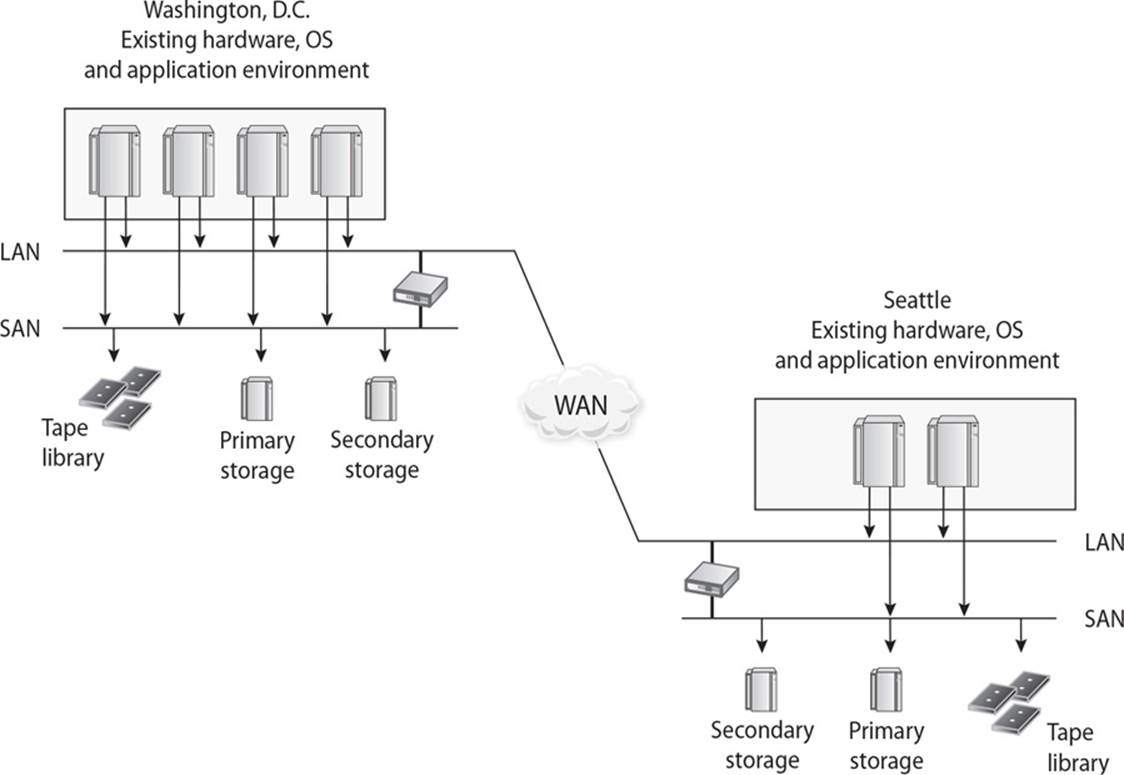
A. Hot site
B. Warm site
C. Cold site
D. Reciprocal agreement
24. There are several types of redundant technologies that can be put into place. What type of technology is shown in the graphic that follows?
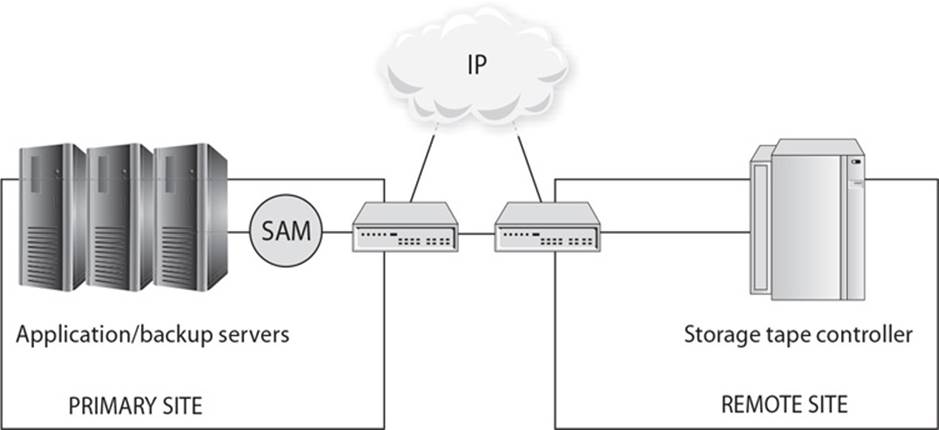
A. Tape vaulting
B. Remote journaling
C. Electronic vaulting
D. Redundant site
25. Here is a graphic of a business continuity policy. Which component is missing from this graphic?
A. Damage assessment phase
B. Reconstitution phase
C. Business resumption phase
D. Continuity of operations plan
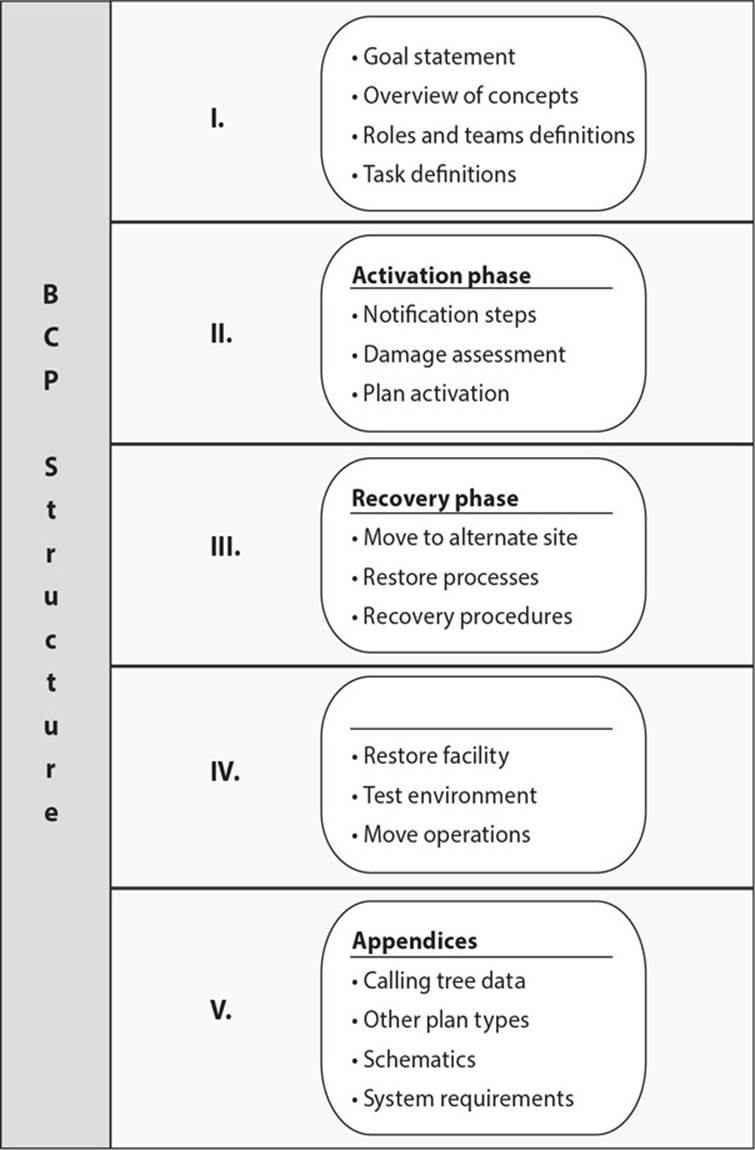
26. The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) metrics have similar roles, but their values are very different. Which of the following best describes the difference between RTO and MTD metrics?
A. The RTO is a time period that represents the inability to recover, and the MTD represents an allowable amount of downtime.
B. The RTO is an allowable amount of downtime, and the MTD represents a time period that represents the inability to recover.
C. The RTO is a metric used in disruptions, and the MTD is a metric used in disasters.
D. The RTO is a metric pertaining to loss of access to data, and the MTD is a metric pertaining to loss of access to hardware and processing capabilities.
27. High availability (HA) is a combination of technologies and processes that work together to ensure that specific critical functions are always up and running at the necessary level. To provide this level of high availability, a company has to have a long list of technologies and processes that provide redundancy, fault tolerance, and failover capabilities. Which of the following best describes these characteristics?
A. Redundancy is the duplication of noncritical components or functions of a system with the intention of decreasing reliability of the system. Fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to discontinue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place. If a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a working system.
B. Redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system. Fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to continue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place. If a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a working system.
C. Redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system. Fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to continue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place. If a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a nonworking system.
D. Redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system. Fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to continue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place. If a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a working system.
The following scenario will be used to answer questions 28 and 29.
Sean has been hired as business continuity coordinator. He has been told by his management that he needed to ensure that the company is in compliance with the ISO/IEC standard that pertained to technology readiness for business continuity. He has also been instructed to find a way to transfer the risk of being unable to carry out critical business functions for a period of time because of a disaster.
28. Which of the following is most likely the standard that Sean has been asked to comply with?
A. ISO/IEC 27031
B. ISO/IEC 27005
C. ISO/IEC BS7799
D. ISO/IEC 2899
29. Which of the following would be best for Sean to implement as it pertains to his company’s needs?
A. Infrastructure cloud computing
B. Co-location at a multiprocessing center
C. Business interruption insurance
D. Shared partner extranet with integrated redundancy
The following scenario will be used to answer questions 30, 31 and 32.
Jeff is leading the business continuity group in his company. They have completed a business impact analysis and have determined that if the company’s credit card processing functionality was unavailable for 48 hours the company would most likely experience such a large financial hit that it would have to go out of business. The team has calculated that this functionality needs to be up and running within 28 hours after experiencing a disaster for the company to stay in business. The team has also determined that the restoration steps must be able to restore data that are one hour old or less.
30. In this scenario, which of the following is the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) value?
A. 48 hours
B. 28 hours
C. 20 hours
D. 1 hour
31. In this scenario, which of the following is the Work Recovery Time value?
A. 48 hours
B. 28 hours
C. 20 hours
D. 1 hour
32. In this scenario, what would the 1-hour time period be referred to as?
A. Recovery Time Period
B. Maximum Tolerable Downtime
C. Recovery Point Objective
D. Recovery Point Time Period
QUICK ANSWER KEY
1. D
2. B
3. A
4. A
5. D
6. C
7. D
8. C
9. A
10. D
11. B
12. A
13. D
14. B
15. C
16. D
17. A
18. C
19. B
20. D
21. B
22. D
23. A
24. A
25. B
26. B
27. D
28. A
29. C
30. B
31. C
32. C
A ANSWERS
1. The NIST organization has defined best practices for creating continuity plans. Which of the following phases deals with identifying and prioritizing critical functions and systems?
A. Identify preventive controls.
B. Develop the continuity planning policy statement.
C. Develop recovery strategies.
D. Conduct the business impact analysis.
![]() D. Although no specific scientific equation must be followed to create continuity plans, certain best practices have proven themselves over time. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) organization is responsible for developing many of these best practices and documenting them so that they are easily available to all. NIST outlines seven steps in its Special Publication 800-34, Continuity Planning Guide for Information Technology Systems: develop the continuity planning statement; conduct the business impact analysis; identify preventive controls; develop recovery strategies; develop the contingency plan; test the plan and conduct training and exercises; and maintain the plan. Conducting a business impact analysis involves identifying critical functions and systems, and allowing the organization to prioritize them based on necessity. It also includes identifying vulnerabilities and threats, and calculating risks.
D. Although no specific scientific equation must be followed to create continuity plans, certain best practices have proven themselves over time. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) organization is responsible for developing many of these best practices and documenting them so that they are easily available to all. NIST outlines seven steps in its Special Publication 800-34, Continuity Planning Guide for Information Technology Systems: develop the continuity planning statement; conduct the business impact analysis; identify preventive controls; develop recovery strategies; develop the contingency plan; test the plan and conduct training and exercises; and maintain the plan. Conducting a business impact analysis involves identifying critical functions and systems, and allowing the organization to prioritize them based on necessity. It also includes identifying vulnerabilities and threats, and calculating risks.
![]() A is incorrect because identifying preventive controls must be done after critical functions and systems have been prioritized, and their vulnerabilities, threats, and risks identified—which is all part of the business impact analysis. Conducting a business impact analysis is step two of creating a continuity plan, and identifying preventive controls is step three.
A is incorrect because identifying preventive controls must be done after critical functions and systems have been prioritized, and their vulnerabilities, threats, and risks identified—which is all part of the business impact analysis. Conducting a business impact analysis is step two of creating a continuity plan, and identifying preventive controls is step three.
![]() B is incorrect because developing the continuity planning policy statement involves writing a policy that provides the guidance necessary to develop a business continuity plan and that assigns authority to the necessary roles to carry out these tasks. It is the first step in creating a business continuity plan and thus comes before identifying and prioritizing critical systems and functions, which is part of the business impact analysis.
B is incorrect because developing the continuity planning policy statement involves writing a policy that provides the guidance necessary to develop a business continuity plan and that assigns authority to the necessary roles to carry out these tasks. It is the first step in creating a business continuity plan and thus comes before identifying and prioritizing critical systems and functions, which is part of the business impact analysis.
![]() C is incorrect because developing recovery strategies involves formulating methods to ensure systems and critical functions can be brought online quickly. Before this can be done, a business impact analysis must be carried out to determine which systems and functions are critical and should be given priority during recovery.
C is incorrect because developing recovery strategies involves formulating methods to ensure systems and critical functions can be brought online quickly. Before this can be done, a business impact analysis must be carried out to determine which systems and functions are critical and should be given priority during recovery.
2. As his company’s business continuity coordinator, Matthew is responsible for helping recruit members to the business continuity planning (BCP) committee. Which of the following does not correctly describe this effort?
A. Committee members should be involved with the planning stages, as well as the testing and implementation stages.
B. The smaller the team the better, to keep meetings under control.
C. The business continuity coordinator should work with management to appoint committee members.
D. The team should consist of people from different departments across the company.
![]() B. The BCP committee should be as large as it needs to be in order to represent each department within the organization. The team must be composed of people who are familiar with the different departments within the company, because each department is unique in its functionality and has distinctive risks and threats. The best plan is when all issues and threats are brought to the table and discussed. This cannot be done effectively with a few people who are familiar with only a couple of departments. The committee should be made up of representatives from at least the following departments: business units, senior management, IT department, security department, communications department, and legal department.
B. The BCP committee should be as large as it needs to be in order to represent each department within the organization. The team must be composed of people who are familiar with the different departments within the company, because each department is unique in its functionality and has distinctive risks and threats. The best plan is when all issues and threats are brought to the table and discussed. This cannot be done effectively with a few people who are familiar with only a couple of departments. The committee should be made up of representatives from at least the following departments: business units, senior management, IT department, security department, communications department, and legal department.
![]() A is incorrect because it is true that committee members should be involved with the planning stages, as well as the testing and implementation stages. If Matthew, the BCP coordinator, is a good management leader, he will understand that it is best to make team members feel a sense of ownership pertaining to their tasks and roles. The people who develop the BCP should also be the ones who execute it. If you knew that in a time of crisis you would be expected to carry out some critical tasks, you might pay more attention during the planning and testing phases.
A is incorrect because it is true that committee members should be involved with the planning stages, as well as the testing and implementation stages. If Matthew, the BCP coordinator, is a good management leader, he will understand that it is best to make team members feel a sense of ownership pertaining to their tasks and roles. The people who develop the BCP should also be the ones who execute it. If you knew that in a time of crisis you would be expected to carry out some critical tasks, you might pay more attention during the planning and testing phases.
![]() C is incorrect because the BCP coordinator should work with management to appoint committee members. But management’s involvement does not stop there. The BCP team should work with management to develop the ultimate goals of the plan, identify the critical parts of the business that must be dealt with first during a disaster, and ascertain the priorities of departments and tasks. Management also needs to help direct the team on the scope of the project and the specific objectives.
C is incorrect because the BCP coordinator should work with management to appoint committee members. But management’s involvement does not stop there. The BCP team should work with management to develop the ultimate goals of the plan, identify the critical parts of the business that must be dealt with first during a disaster, and ascertain the priorities of departments and tasks. Management also needs to help direct the team on the scope of the project and the specific objectives.
![]() D is incorrect because it is true that the team should be composed of people from different departments across the company. This is the only way the team will be able to consider the distinctive risks and threats that each department faces.
D is incorrect because it is true that the team should be composed of people from different departments across the company. This is the only way the team will be able to consider the distinctive risks and threats that each department faces.
3. A business impact analysis is considered a functional analysis. Which of the following is not carried out during a business impact analysis?
A. A parallel or full-interruption test
B. The application of a classification scheme based on criticality levels
C. The gathering of information via interviews
D. Documentation of business functions
![]() A. A business impact analysis (BIA) is considered a functional analysis, in which a team collects data through interviews and documentary sources; documents business functions, activities, and transactions; develops a hierarchy of business functions; and finally applies a classification scheme to indicate each individual function’s criticality level. Parallel and full-interruption tests are not part of a BIA. These tests are carried out to ensure the continued validity of a business continuity plan, since environments continually change. A parallel test is done to ensure that specific systems can actually perform adequately at the alternate offsite facility, while a full-interruption test involves shutting down the original site and resuming operations and processing at the alternate site.
A. A business impact analysis (BIA) is considered a functional analysis, in which a team collects data through interviews and documentary sources; documents business functions, activities, and transactions; develops a hierarchy of business functions; and finally applies a classification scheme to indicate each individual function’s criticality level. Parallel and full-interruption tests are not part of a BIA. These tests are carried out to ensure the continued validity of a business continuity plan, since environments continually change. A parallel test is done to ensure that specific systems can actually perform adequately at the alternate offsite facility, while a full-interruption test involves shutting down the original site and resuming operations and processing at the alternate site.
![]() B is incorrect because the application of a classification scheme based on criticality levels is carried out during a business impact analysis (BIA). This is done by identifying the critical assets of the company and mapping them to the following characteristics: maximum tolerable downtime, operational disruption and productivity, financial considerations, regulatory responsibilities, and reputation.
B is incorrect because the application of a classification scheme based on criticality levels is carried out during a business impact analysis (BIA). This is done by identifying the critical assets of the company and mapping them to the following characteristics: maximum tolerable downtime, operational disruption and productivity, financial considerations, regulatory responsibilities, and reputation.
![]() C is incorrect because the gathering of information during interviews is conducted during a business impact analysis. The BCP committee will not truly understand all business processes, the steps that must take place, or the resources and supplies those processes require. So the committee must gather this information from the people who do know, which are department managers and specific employees throughout the organization. The committee must identify the individuals who will provide information and how that information will be collected (surveys, interviews, or workshops).
C is incorrect because the gathering of information during interviews is conducted during a business impact analysis. The BCP committee will not truly understand all business processes, the steps that must take place, or the resources and supplies those processes require. So the committee must gather this information from the people who do know, which are department managers and specific employees throughout the organization. The committee must identify the individuals who will provide information and how that information will be collected (surveys, interviews, or workshops).
![]() D is incorrect because the BCP committee does document business functions as part of a business impact analysis (BIA). Business activities and transactions must also be documented. This information is obtained from the department managers and specific employees that are interviewed or surveyed. Once the information is documented, the BCP committee can conduct an analysis to determine which processes, devices, or operational activities are the most critical.
D is incorrect because the BCP committee does document business functions as part of a business impact analysis (BIA). Business activities and transactions must also be documented. This information is obtained from the department managers and specific employees that are interviewed or surveyed. Once the information is documented, the BCP committee can conduct an analysis to determine which processes, devices, or operational activities are the most critical.
4. When developing a recovery and continuity program within an organization, different metrics can be used to properly measure potential damages and recovery requirements. These metrics help us quantify our risks and the benefits of controls we can put into place. Two metrics commonly used in the development of recovery programs is Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO). Data restoration (RPO) requirements can be different from service restoration (RTO) requirements. Which of the following best defines these two main recovery measurements in this type of scenario?
A. RPO is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. RTO is the acceptable time period before a service level must be restored.
B. RTO is the earliest time period in which a data set must be restored. RPO is the acceptable amount of downtime in a given period.
C. RPO is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. RTO is the earliest time period in which data must be restored.
D. RPO is the acceptable amount of downtime measured. RTO is the earliest time period in which a service level must be restored.
![]() A. The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. This value represents the earliest point in time by which data must be recovered. The higher the value of data, the more funds or other resources that can be put into place to ensure a smaller amount of data is lost in the event of a disaster. For example, if the RPO is set to two hours, this means that the organization has to have backup and restore processes that will only allow for the loss of up to two hours of data. The restore process cannot be something as time consuming as restoring from a backup tape manually, but will need to be an automated restoration process that can restore data more quickly and allow the production environment to be up and running and carrying out business processes. The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the acceptable period before a specific service level must be restored in order to avoid unacceptable consequences after a disruption or disaster. While RPO pertains to data, RTO deals with the actual processing capabilities of an environment.
A. The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. This value represents the earliest point in time by which data must be recovered. The higher the value of data, the more funds or other resources that can be put into place to ensure a smaller amount of data is lost in the event of a disaster. For example, if the RPO is set to two hours, this means that the organization has to have backup and restore processes that will only allow for the loss of up to two hours of data. The restore process cannot be something as time consuming as restoring from a backup tape manually, but will need to be an automated restoration process that can restore data more quickly and allow the production environment to be up and running and carrying out business processes. The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the acceptable period before a specific service level must be restored in order to avoid unacceptable consequences after a disruption or disaster. While RPO pertains to data, RTO deals with the actual processing capabilities of an environment.
![]() B is incorrect because the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the earliest time period in which a service level must be restored; thus, it does not explicitly deal with recovering a data set. And the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time, not downtime in general. The definitions in this answer are backwards. The RPO provides the recovery team with a requirement or goal to work toward when establishing data recovery processes. RPO values for less critical data will be higher; thus, the recovery processes can include slower and cheaper recovery solutions. If an RPO value is high, then the data are more critical in nature and the team must implement solutions that recover this type of data more quickly. RTO values also give the recovery team requirements to work with so that they know the type of recovery solutions that must be deployed. If a production environment has to be up and running within one hour after a disruption, the team must deploy redundancy into the environment so that the systems can respond quickly.
B is incorrect because the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the earliest time period in which a service level must be restored; thus, it does not explicitly deal with recovering a data set. And the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time, not downtime in general. The definitions in this answer are backwards. The RPO provides the recovery team with a requirement or goal to work toward when establishing data recovery processes. RPO values for less critical data will be higher; thus, the recovery processes can include slower and cheaper recovery solutions. If an RPO value is high, then the data are more critical in nature and the team must implement solutions that recover this type of data more quickly. RTO values also give the recovery team requirements to work with so that they know the type of recovery solutions that must be deployed. If a production environment has to be up and running within one hour after a disruption, the team must deploy redundancy into the environment so that the systems can respond quickly.
![]() C is incorrect because the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) metric pertains to how quickly services must come back online and not how quickly data must be restored. The RTO provides the recovery team with an objective, which is a goal to achieve as it pertains to getting systems and network capabilities up and running after they went down. This metric tells the team how long the organization can endure being offline and still stay in business. A small business that does not depend upon time-sensitive transactions may be able to be offline for one to two days without negatively affecting the survivability of the company. If a company like Amazon.com was offline for two days, the financial and reputation hit that it would have to endure may not put the company out of business, but this potential loss is too much to risk, thus expensive recovery solutions are necessary. If you understand how much you can potentially lose, you will make better decisions about what to put into place to make sure that any potential loss is endurable and not devastating.
C is incorrect because the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) metric pertains to how quickly services must come back online and not how quickly data must be restored. The RTO provides the recovery team with an objective, which is a goal to achieve as it pertains to getting systems and network capabilities up and running after they went down. This metric tells the team how long the organization can endure being offline and still stay in business. A small business that does not depend upon time-sensitive transactions may be able to be offline for one to two days without negatively affecting the survivability of the company. If a company like Amazon.com was offline for two days, the financial and reputation hit that it would have to endure may not put the company out of business, but this potential loss is too much to risk, thus expensive recovery solutions are necessary. If you understand how much you can potentially lose, you will make better decisions about what to put into place to make sure that any potential loss is endurable and not devastating.
![]() D is incorrect because the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) measurement pertains to data recovery and not service downtime. RPO is the maximum tolerable time period during which data may be unavailable, which is not the same as a measurement of how much data may be lost. For example, if a company’s main database gets corrupted and the company can absorb the impact of not having the data on this database restored for 48 hours, then the recovery team can implement tape backups that are stored and retrieved from an offsite location. The restoration timeline of this data has to take into account how long it will take for someone to go get the tape from the offsite location, bring it to the production environment, carry out the restore process, and test the newly recovered data. All of those steps have to happen successfully within the RPO window of 48 hours.
D is incorrect because the Recovery Point Objective (RPO) measurement pertains to data recovery and not service downtime. RPO is the maximum tolerable time period during which data may be unavailable, which is not the same as a measurement of how much data may be lost. For example, if a company’s main database gets corrupted and the company can absorb the impact of not having the data on this database restored for 48 hours, then the recovery team can implement tape backups that are stored and retrieved from an offsite location. The restoration timeline of this data has to take into account how long it will take for someone to go get the tape from the offsite location, bring it to the production environment, carry out the restore process, and test the newly recovered data. All of those steps have to happen successfully within the RPO window of 48 hours.
5. An approach to alternate offsite facilities is to establish a reciprocal agreement. Which of the following describes the pros and cons of a reciprocal agreement?
A. It is fully configured and ready to operate within a few hours, but is the most expensive of the offsite choices.
B. It is an inexpensive option, but takes the most time and effort to get up and running after a disaster.
C. It is a good alternative for companies that depend upon proprietary software, but annual testing is not usually available.
D. It is the cheapest of the offsite choices, but mixing operations could introduce many security issues.
![]() D. A reciprocal agreement, also referred to as mutual aid, means that company A agrees to allow company B to use its facilities if company B is hit by a disaster, and vice versa. This is a cheaper way to go than the other offsite choices, but it is not always the best choice. Most environments are maxed out pertaining to the use of facility space, resources, and computing capability. To allow another company to come in and work out of the same shop could prove to be detrimental to both companies. The stress of two companies working in the same environment could cause tremendous levels of tension. If it did work out, it would only provide a short-term solution. Configuration management could be a nightmare, and the mixing of operations could introduce many security issues. Reciprocal agreements have been known to work well in specific businesses, such as newspaper printing. These businesses require very specific technology and equipment that will not be available through any subscription service. For most other organizations, they are generally, at best, a secondary option for disaster protection.
D. A reciprocal agreement, also referred to as mutual aid, means that company A agrees to allow company B to use its facilities if company B is hit by a disaster, and vice versa. This is a cheaper way to go than the other offsite choices, but it is not always the best choice. Most environments are maxed out pertaining to the use of facility space, resources, and computing capability. To allow another company to come in and work out of the same shop could prove to be detrimental to both companies. The stress of two companies working in the same environment could cause tremendous levels of tension. If it did work out, it would only provide a short-term solution. Configuration management could be a nightmare, and the mixing of operations could introduce many security issues. Reciprocal agreements have been known to work well in specific businesses, such as newspaper printing. These businesses require very specific technology and equipment that will not be available through any subscription service. For most other organizations, they are generally, at best, a secondary option for disaster protection.
![]() A is incorrect because a hot site—not a reciprocal agreement—is fully configured and ready to operate within a few hours. A hot site is also the most expensive offsite option. The only missing resources from a hot site are usually the data, which will be retrieved from a backup site, and the people who will be processing the data. The equipment and system software must be compatible with the data being restored from the main site and must not cause any negative interoperability issues. Hot sites are a good choice for a company that needs to ensure a site will be available for it as soon as possible.
A is incorrect because a hot site—not a reciprocal agreement—is fully configured and ready to operate within a few hours. A hot site is also the most expensive offsite option. The only missing resources from a hot site are usually the data, which will be retrieved from a backup site, and the people who will be processing the data. The equipment and system software must be compatible with the data being restored from the main site and must not cause any negative interoperability issues. Hot sites are a good choice for a company that needs to ensure a site will be available for it as soon as possible.
![]() B is incorrect because a cold site is an inexpensive offsite option, but it takes the most time and effort to actually get up and functioning right after a disaster. With cold sites the vendor supplies the basic environment, electrical wiring, air conditioning, plumbing, and flooring, but none of the equipment or additional services. It may take weeks to get the site activated and ready for work.
B is incorrect because a cold site is an inexpensive offsite option, but it takes the most time and effort to actually get up and functioning right after a disaster. With cold sites the vendor supplies the basic environment, electrical wiring, air conditioning, plumbing, and flooring, but none of the equipment or additional services. It may take weeks to get the site activated and ready for work.
![]() C is incorrect because a warm site is a good alternative for companies that depend upon proprietary software. A warm site is equipped with some equipment, but not the actual computers. It is a better choice than a reciprocal agreement or hot site for a company that depends upon proprietary and unusual hardware and software, because they will bring their own hardware and software with them to the site after a disaster hits. The disadvantage of using a warm site is that the vendors’ contracts do not usually include annual testing, which helps ensure that the company can return to an operating state within hours.
C is incorrect because a warm site is a good alternative for companies that depend upon proprietary software. A warm site is equipped with some equipment, but not the actual computers. It is a better choice than a reciprocal agreement or hot site for a company that depends upon proprietary and unusual hardware and software, because they will bring their own hardware and software with them to the site after a disaster hits. The disadvantage of using a warm site is that the vendors’ contracts do not usually include annual testing, which helps ensure that the company can return to an operating state within hours.
6. Which of the following steps comes first in a business impact analysis?
A. Calculate the risk for each different business function.
B. Identify critical business functions.
C. Create data-gathering techniques.
D. Identify vulnerabilities and threats to business functions.
![]() C. Of the steps listed, the first step in a business impact analysis (BIA) is creating data-gathering techniques. The BCP committee can use surveys, questionnaires, and interviews to gather information from key personnel about how different tasks get accomplished within the organization, whether it’s a process, transaction, or service, along with any relevant dependencies. Process flow diagrams should be built from this data, which will be used throughout the BIA and plan development stages.
C. Of the steps listed, the first step in a business impact analysis (BIA) is creating data-gathering techniques. The BCP committee can use surveys, questionnaires, and interviews to gather information from key personnel about how different tasks get accomplished within the organization, whether it’s a process, transaction, or service, along with any relevant dependencies. Process flow diagrams should be built from this data, which will be used throughout the BIA and plan development stages.
![]() A is incorrect because calculating the risk of each business function occurs after business functions have been identified. And before that can happen, the BCP team must gather data from key personnel. To calculate the risk of each business function, qualitative and quantitative impact information should be gathered and properly analyzed and interpreted. Upon completion of the data analysis, it should be reviewed with the most knowledgeable people within the company to ensure that the findings are appropriate and describe the real risks and impacts the organization faces. This will help flush out any additional data points not originally obtained and will give a fuller understanding of all the possible business impacts.
A is incorrect because calculating the risk of each business function occurs after business functions have been identified. And before that can happen, the BCP team must gather data from key personnel. To calculate the risk of each business function, qualitative and quantitative impact information should be gathered and properly analyzed and interpreted. Upon completion of the data analysis, it should be reviewed with the most knowledgeable people within the company to ensure that the findings are appropriate and describe the real risks and impacts the organization faces. This will help flush out any additional data points not originally obtained and will give a fuller understanding of all the possible business impacts.
![]() B is incorrect because identifying critical business functions takes place after the BCP committee has learned about the business functions that exist by interviewing and surveying key personnel. Upon completion of the data collection phase, the BCP committee conducts an analysis to establish which processes, devices, or operational activities are critical. If a system stands on its own, doesn’t affect other systems, and is of low criticality, then it can be classified as a tier two or three recovery step. This means these resources will not be dealt with during the recovery stages until the most critical (tier one) resources are up and running.
B is incorrect because identifying critical business functions takes place after the BCP committee has learned about the business functions that exist by interviewing and surveying key personnel. Upon completion of the data collection phase, the BCP committee conducts an analysis to establish which processes, devices, or operational activities are critical. If a system stands on its own, doesn’t affect other systems, and is of low criticality, then it can be classified as a tier two or three recovery step. This means these resources will not be dealt with during the recovery stages until the most critical (tier one) resources are up and running.
![]() D is incorrect because identifying vulnerabilities and threats to business functions takes place toward the end of a business impact analysis. Of the steps listed in the answers, it is the last one. Threats can be manmade, natural, or technical. It is important to identify all possible threats and estimate the probability of them happening. Some issues may not immediately come to mind when developing these plans. These issues are often best addressed in a group with scenario-based exercises. This ensures that if a threat becomes a reality, the plan includes the ramifications on all business tasks, departments, and critical operations. The more issues that are thought of and planned for, the better prepared a company will be if and when these events occur.
D is incorrect because identifying vulnerabilities and threats to business functions takes place toward the end of a business impact analysis. Of the steps listed in the answers, it is the last one. Threats can be manmade, natural, or technical. It is important to identify all possible threats and estimate the probability of them happening. Some issues may not immediately come to mind when developing these plans. These issues are often best addressed in a group with scenario-based exercises. This ensures that if a threat becomes a reality, the plan includes the ramifications on all business tasks, departments, and critical operations. The more issues that are thought of and planned for, the better prepared a company will be if and when these events occur.
7. The operations team is responsible for defining which data gets backed up and how often. Which type of backup process backs up files that have been modified since the last time all data was backed up?
A. Incremental process
B. Full backup
C. Partial backup
D. Differential process
![]() D. Backups can be full, differential, or incremental, and are usually used in some type of combination with each other. Most files are not altered every day, so to save time and resources, it is best to devise a backup plan that does not continually back up data that has not been modified. Backup software reviews the archive bit setting when making its determination on what gets backed up and what does not. If a file is modified or created, the file system sets the archive bit to 1, and the backup software knows to back up that file. A differential process backs up the files that have been modified since the last full backup; in other words, the last time all the data was backed up. When the data needs to be restored, the full backup is laid down first, and then the differential backup is put down on top of it.
D. Backups can be full, differential, or incremental, and are usually used in some type of combination with each other. Most files are not altered every day, so to save time and resources, it is best to devise a backup plan that does not continually back up data that has not been modified. Backup software reviews the archive bit setting when making its determination on what gets backed up and what does not. If a file is modified or created, the file system sets the archive bit to 1, and the backup software knows to back up that file. A differential process backs up the files that have been modified since the last full backup; in other words, the last time all the data was backed up. When the data needs to be restored, the full backup is laid down first, and then the differential backup is put down on top of it.
![]() A is incorrect because an incremental process backs up all the files that have changed since the last full or incremental backup. If a company experienced a disaster and it used the incremental process, it would first need to restore the full backup on its hard drives and lay down every incremental backup that was carried out before the disaster took place. So, if the full backup was done six months ago and the operations department carried out an incremental backup each month, the restoration team would restore the full backup and start with the older incremental backups and restore each one of them until they are all restored.
A is incorrect because an incremental process backs up all the files that have changed since the last full or incremental backup. If a company experienced a disaster and it used the incremental process, it would first need to restore the full backup on its hard drives and lay down every incremental backup that was carried out before the disaster took place. So, if the full backup was done six months ago and the operations department carried out an incremental backup each month, the restoration team would restore the full backup and start with the older incremental backups and restore each one of them until they are all restored.
![]() B is incorrect because with a full backup, all data is backed up and saved to some type of storage media. During a full backup, the archive bit is cleared, which means that it is set to 0. A company can choose to do full backups only, in which case the restoration process is just one step, but the backup and restore processes could take a long time.
B is incorrect because with a full backup, all data is backed up and saved to some type of storage media. During a full backup, the archive bit is cleared, which means that it is set to 0. A company can choose to do full backups only, in which case the restoration process is just one step, but the backup and restore processes could take a long time.
![]() C is incorrect because it is not the best answer to this question. While a backup can be a partial backup, it does not necessarily mean that it backs up all the files that have been modified since the last time a backup process was run.
C is incorrect because it is not the best answer to this question. While a backup can be a partial backup, it does not necessarily mean that it backs up all the files that have been modified since the last time a backup process was run.
8. After a disaster occurs, a damage assessment needs to take place. Which of the following steps occurs last in a damage assessment?
A. Determine the cause of the disaster.
B. Identify the resources that must be replaced immediately.
C. Declare a disaster.
D. Determine how long it will take to bring critical functions back online.
![]() C. The final step in a damage assessment is to declare a disaster. After information from the damage assessment is collected and assessed, it will indicate what teams need to be called to action and whether the BCP actually needs to be activated. The BCP coordinator and team must develop activation criteria before a disaster takes place. After the damage assessment, if one or more of the situations outlined in the criteria have taken place, then the team is moved into recovery mode. Different organizations have different criteria, because the business drivers and critical functions will vary from organization to organization. The criteria may consist of danger to human life, danger to state or national security, damage to facility, damage to critical systems, and estimated value of downtime that will be experienced.
C. The final step in a damage assessment is to declare a disaster. After information from the damage assessment is collected and assessed, it will indicate what teams need to be called to action and whether the BCP actually needs to be activated. The BCP coordinator and team must develop activation criteria before a disaster takes place. After the damage assessment, if one or more of the situations outlined in the criteria have taken place, then the team is moved into recovery mode. Different organizations have different criteria, because the business drivers and critical functions will vary from organization to organization. The criteria may consist of danger to human life, danger to state or national security, damage to facility, damage to critical systems, and estimated value of downtime that will be experienced.
![]() A is incorrect because determining the cause of the disaster is the first step of the damage assessment. The issue that caused the damage may still be taking place and the team must figure out how to stop it before a full damage assessment can take place.
A is incorrect because determining the cause of the disaster is the first step of the damage assessment. The issue that caused the damage may still be taking place and the team must figure out how to stop it before a full damage assessment can take place.
![]() B is incorrect because identifying the resources that must be replaced immediately is not the last step of a damage assessment. It does occur near the end of the assessment, however. Once the resources are identified, the team must estimate how long it will take to bring critical functions back online, and then declare a disaster, if necessary.
B is incorrect because identifying the resources that must be replaced immediately is not the last step of a damage assessment. It does occur near the end of the assessment, however. Once the resources are identified, the team must estimate how long it will take to bring critical functions back online, and then declare a disaster, if necessary.
![]() D is incorrect because determining how long it will take to bring critical functions back online is the second to last step in a damage assessment. If it will take longer than the previously determined maximum tolerable downtime (MTD) values to restore operations, then a disaster should be declared and the BCP should be put into action.
D is incorrect because determining how long it will take to bring critical functions back online is the second to last step in a damage assessment. If it will take longer than the previously determined maximum tolerable downtime (MTD) values to restore operations, then a disaster should be declared and the BCP should be put into action.
9. Of the following plans, which establishes senior management and a headquarters after a disaster?
A. Continuity of operations plan
B. Cyber-incident response plan
C. Occupant emergency plan
D. IT contingency plan
![]() A. A continuity of operations plan (COOP) establishes senior management and a headquarters after a disaster. It also outlines roles and authorities, orders of succession, and individual role tasks. Creating a COOP begins with assessing how the organization operates to identify mission-critical staff, materials, procedures, and equipment. If one exists, review the business process flowchart. Identify suppliers, partners, contractors, and other businesses the organization interacts with on a daily basis, and create a list of these and other businesses the organization could use in an emergency. It is important for an organization to make plans for what it will do if the building becomes inaccessible.
A. A continuity of operations plan (COOP) establishes senior management and a headquarters after a disaster. It also outlines roles and authorities, orders of succession, and individual role tasks. Creating a COOP begins with assessing how the organization operates to identify mission-critical staff, materials, procedures, and equipment. If one exists, review the business process flowchart. Identify suppliers, partners, contractors, and other businesses the organization interacts with on a daily basis, and create a list of these and other businesses the organization could use in an emergency. It is important for an organization to make plans for what it will do if the building becomes inaccessible.
![]() B is incorrect because a cyber-incident response plan focuses on malware, hackers, intrusions, attacks, and other security issues. It outlines procedures for incident response with the goal of limiting damage, minimizing recovery time, and reducing costs. A cyber-incident response plan should include a description of the different types of incidents, who to call when an incident occurs and each person’s responsibilities, procedures for addressing different types of incidents, and forensic procedures. The plan should be tested, and all participants should be trained on their responsibilities.
B is incorrect because a cyber-incident response plan focuses on malware, hackers, intrusions, attacks, and other security issues. It outlines procedures for incident response with the goal of limiting damage, minimizing recovery time, and reducing costs. A cyber-incident response plan should include a description of the different types of incidents, who to call when an incident occurs and each person’s responsibilities, procedures for addressing different types of incidents, and forensic procedures. The plan should be tested, and all participants should be trained on their responsibilities.
![]() C is incorrect because an occupant emergency plan establishes personnel safety and evacuation procedures. The goal of an occupant emergency plan is to reduce the risk to personnel and minimize the disruption to work and operations in the case of an emergency. The plan should include procedures for ensuring the safety of employees with disabilities, including their evacuation from the facility if necessary. All employees should have access to the occupant emergency response plan, and it should be practiced so that everyone knows how to execute it.
C is incorrect because an occupant emergency plan establishes personnel safety and evacuation procedures. The goal of an occupant emergency plan is to reduce the risk to personnel and minimize the disruption to work and operations in the case of an emergency. The plan should include procedures for ensuring the safety of employees with disabilities, including their evacuation from the facility if necessary. All employees should have access to the occupant emergency response plan, and it should be practiced so that everyone knows how to execute it.
![]() D is incorrect because an IT contingency plan establishes procedures for the recovery of systems, networks, and major applications after disruptions. Steps for creating IT contingency plans are addressed in the NIST 800-34 document.
D is incorrect because an IT contingency plan establishes procedures for the recovery of systems, networks, and major applications after disruptions. Steps for creating IT contingency plans are addressed in the NIST 800-34 document.
10. It is not unusual for business continuity plans to become out of date. Which of the following is not a reason why plans become outdated?
A. Changes in hardware, software, and applications
B. Infrastructure and environment changes
C. Personnel turnover
D. That the business continuity process is integrated into the change management process
![]() D. Unfortunately, business continuity plans can become quickly out of date. An out-of-date BCP may provide a company with a false sense of security, which could be devastating if and when a disaster actually takes place. One of the simplest and most cost-effective and process-efficient ways to keep a plan up to date is to incorporate it within the change management process of the organization. When you think about it, it makes a lot of sense. Where do you document new applications, equipment, or services? Where do you document updates and patches? Your change management process should be updated to incorporate fields and triggers that alert the BCP team when a significant change will occur and should provide a means to update the recovery documentation. Other measures that can help ensure that the BCP remains current include the performance of regular drills that use the plan, including the plan’s maintenance in personnel evaluations, and making business continuity a part of every business decision.
D. Unfortunately, business continuity plans can become quickly out of date. An out-of-date BCP may provide a company with a false sense of security, which could be devastating if and when a disaster actually takes place. One of the simplest and most cost-effective and process-efficient ways to keep a plan up to date is to incorporate it within the change management process of the organization. When you think about it, it makes a lot of sense. Where do you document new applications, equipment, or services? Where do you document updates and patches? Your change management process should be updated to incorporate fields and triggers that alert the BCP team when a significant change will occur and should provide a means to update the recovery documentation. Other measures that can help ensure that the BCP remains current include the performance of regular drills that use the plan, including the plan’s maintenance in personnel evaluations, and making business continuity a part of every business decision.
![]() A is incorrect because changes in hardware, software, and applications occur frequently, and unless the BCP is part of the change management process, then these changes are unlikely to be included in the BCP. When changes to the environment take place, the BCP needs to be updated. If it is not updated after changes, it is out of date.
A is incorrect because changes in hardware, software, and applications occur frequently, and unless the BCP is part of the change management process, then these changes are unlikely to be included in the BCP. When changes to the environment take place, the BCP needs to be updated. If it is not updated after changes, it is out of date.
![]() B is incorrect because infrastructure and environment changes occur frequently. Just as with software, hardware, and application changes, unless the BCP is part of the change management process, infrastructure and environment changes are unlikely to make it into the BCP.
B is incorrect because infrastructure and environment changes occur frequently. Just as with software, hardware, and application changes, unless the BCP is part of the change management process, infrastructure and environment changes are unlikely to make it into the BCP.
![]() C is incorrect because plans often become outdated as a result of personnel turnover. It is not unusual for a BCP to become abandoned when the person or people responsible for its maintenance leave the organization. These responsibilities must be reassigned. To ensure this happens, maintenance responsibilities should be incorporated into job descriptions and properly monitored.
C is incorrect because plans often become outdated as a result of personnel turnover. It is not unusual for a BCP to become abandoned when the person or people responsible for its maintenance leave the organization. These responsibilities must be reassigned. To ensure this happens, maintenance responsibilities should be incorporated into job descriptions and properly monitored.
11. Preplanned business continuity procedures provide organizations a number of benefits. Which of the following is not a capability enabled by business continuity planning?
A. Resuming critical business functions
B. Letting business partners know your company is unprepared
C. Protecting lives and ensuring safety
D. Ensuring survivability of the business
![]() B. Preplanned business continuity procedures afford organizations a number of benefits. They allow an organization to provide an immediate and appropriate response to emergency situations, reduce business impact, and work with outside vendors during a recovery period—in addition to the other answer options listed above. The efforts in these areas should be communicated to business partners to let them know that the company is prepared in case a disaster takes place.
B. Preplanned business continuity procedures afford organizations a number of benefits. They allow an organization to provide an immediate and appropriate response to emergency situations, reduce business impact, and work with outside vendors during a recovery period—in addition to the other answer options listed above. The efforts in these areas should be communicated to business partners to let them know that the company is prepared in case a disaster takes place.
![]() A is incorrect because a business continuity plan allows an organization to resume critical business functions. As part of the BCP creation, the BCP team conducts a business impact analysis, which includes identifying the maximum tolerable downtime for critical resources. This effort helps the team prioritize recovery efforts so that the most critical resources can be recovered first.
A is incorrect because a business continuity plan allows an organization to resume critical business functions. As part of the BCP creation, the BCP team conducts a business impact analysis, which includes identifying the maximum tolerable downtime for critical resources. This effort helps the team prioritize recovery efforts so that the most critical resources can be recovered first.
![]() C is incorrect because a business continuity plan allows an organization to protect lives and ensure safety. People are a company’s most valuable asset; thus, human resources are a critical component to any recovery and continuity process and need to be fully thought out and integrated into the plan. When this is done, a business continuity plan helps a company protect its employees.
C is incorrect because a business continuity plan allows an organization to protect lives and ensure safety. People are a company’s most valuable asset; thus, human resources are a critical component to any recovery and continuity process and need to be fully thought out and integrated into the plan. When this is done, a business continuity plan helps a company protect its employees.
![]() D is incorrect because a preplanned business continuity plan allows a company to ensure the survivability of the business. A business continuity plan provides methods and procedures for dealing with longer-term outages and disasters. It includes getting critical systems to another environment while the original facility is being repaired and conducting business operations in a different mode until regular operations are back in place. In short, the business continuity plan deals with how business is conducted during the aftermath of an emergency.
D is incorrect because a preplanned business continuity plan allows a company to ensure the survivability of the business. A business continuity plan provides methods and procedures for dealing with longer-term outages and disasters. It includes getting critical systems to another environment while the original facility is being repaired and conducting business operations in a different mode until regular operations are back in place. In short, the business continuity plan deals with how business is conducted during the aftermath of an emergency.
12. Management support is critical to the success of a business continuity plan. Which of the following is the most important to be provided to management to obtain their support?
A. Business case
B. Business impact analysis
C. Risk analysis
D. Threat report
![]() A. The most critical part of establishing and maintaining a current continuity plan is management support. Management may need to be convinced of the necessity of such a plan. Therefore, a business case must be made to obtain this support. The business case may include current vulnerabilities, regulatory and legal obligations, the current status of recovery plans, and recommendations. Management is commonly most concerned with cost/benefit issues, so preliminary numbers can be gathered and potential losses estimated. The decision of how a company should recover is a business decision and should always be treated as such.
A. The most critical part of establishing and maintaining a current continuity plan is management support. Management may need to be convinced of the necessity of such a plan. Therefore, a business case must be made to obtain this support. The business case may include current vulnerabilities, regulatory and legal obligations, the current status of recovery plans, and recommendations. Management is commonly most concerned with cost/benefit issues, so preliminary numbers can be gathered and potential losses estimated. The decision of how a company should recover is a business decision and should always be treated as such.
![]() B is incorrect because a business impact analysis (BIA) is conducted after the BCP team has obtained management’s support for their efforts. A BIA is performed to identify the areas that would suffer the greatest financial or operational loss in the event of a disaster or disruption. It identifies the company’s critical systems needed for survival and estimates the outage time that can be tolerated by the company as a result of a disaster or disruption.
B is incorrect because a business impact analysis (BIA) is conducted after the BCP team has obtained management’s support for their efforts. A BIA is performed to identify the areas that would suffer the greatest financial or operational loss in the event of a disaster or disruption. It identifies the company’s critical systems needed for survival and estimates the outage time that can be tolerated by the company as a result of a disaster or disruption.
![]() C is incorrect because a risk analysis is a method of identifying risks and assessing the possible damage that could be caused in order to justify security safeguards. In the context of BCP, risk analysis methodologies are used during a business impact analysis to establish which processes, devices, or operational activities are critical and should therefore be recovered first.
C is incorrect because a risk analysis is a method of identifying risks and assessing the possible damage that could be caused in order to justify security safeguards. In the context of BCP, risk analysis methodologies are used during a business impact analysis to establish which processes, devices, or operational activities are critical and should therefore be recovered first.
![]() D is incorrect because threat report is a distracter. However, it is critical that management understand what the real threats are to the company, the consequences of those threats, and the potential loss values for each threat. Without this understanding, management may only give lip service to continuity planning, and in some cases that is worse than not having any plans at all because of the false sense of security that it creates.
D is incorrect because threat report is a distracter. However, it is critical that management understand what the real threats are to the company, the consequences of those threats, and the potential loss values for each threat. Without this understanding, management may only give lip service to continuity planning, and in some cases that is worse than not having any plans at all because of the false sense of security that it creates.
13. Gizmos and Gadgets have restored its original facility after a disaster. What should be moved in first?
A. Management
B. Most critical systems
C. Most critical functions
D. Least critical functions
![]() D. After the primary site has been repaired, the least critical components are moved in first. This ensures that the primary site is really ready to resume processing. By doing this, you can validate that environmental controls, power, and communication links are working properly. It can also avoid putting the company into another disaster. If the less critical functions survive, then the more critical components of the company can be moved over.
D. After the primary site has been repaired, the least critical components are moved in first. This ensures that the primary site is really ready to resume processing. By doing this, you can validate that environmental controls, power, and communication links are working properly. It can also avoid putting the company into another disaster. If the less critical functions survive, then the more critical components of the company can be moved over.
![]() A is incorrect because personnel should not be moved into the facility until it is determined that the environment is safe, everything is in good working order, and all necessary equipment and supplies are present. Least critical functions should be moved back first, so if there are issues in network configurations or connectivity, or important steps were not carried out, the critical operations of the company are not negatively affected.
A is incorrect because personnel should not be moved into the facility until it is determined that the environment is safe, everything is in good working order, and all necessary equipment and supplies are present. Least critical functions should be moved back first, so if there are issues in network configurations or connectivity, or important steps were not carried out, the critical operations of the company are not negatively affected.
![]() B is incorrect because the most critical systems should not be resumed in the new environment until it has been properly tested. You do not want to go through the trouble of moving the most critical systems and operations from a safe and stable site, only to return them to a main site that is untested. When you move less critical departments over first, they act as the canary. If they survive, then move on to critical systems.
B is incorrect because the most critical systems should not be resumed in the new environment until it has been properly tested. You do not want to go through the trouble of moving the most critical systems and operations from a safe and stable site, only to return them to a main site that is untested. When you move less critical departments over first, they act as the canary. If they survive, then move on to critical systems.
![]() C is incorrect because the most critical functions should not be moved over before less critical functions, which serve to test the stability and safety of the site. If the site proves to need further preparation, then no harm is done to the critical functions.
C is incorrect because the most critical functions should not be moved over before less critical functions, which serve to test the stability and safety of the site. If the site proves to need further preparation, then no harm is done to the critical functions.
14. Which of the following is a critical first step in disaster recovery and contingency planning?
A. Plan testing and drills.
B. Complete a business impact analysis.
C. Determine offsite backup facility alternatives.
D. Organize and create relevant documentation.
![]() B. Of the steps listed in this question, completing a business impact analysis would take the highest priority. The BIA is essential in determining the most critical business functions and identifying the threats that correlate them. Qualitative and quantitative data needs to be gathered, analyzed, interpreted, and presented to management.
B. Of the steps listed in this question, completing a business impact analysis would take the highest priority. The BIA is essential in determining the most critical business functions and identifying the threats that correlate them. Qualitative and quantitative data needs to be gathered, analyzed, interpreted, and presented to management.
![]() A is incorrect because plan testing and drills are the last step in disaster recovery and contingency planning. It is important to test the business continuity plan regularly because environments continually change. Tests and disaster recovery drills and exercises should be performed at least once a year. Most companies cannot afford for these exercises to interrupt production or productivity, so the exercises may need to take place in sections or at specific times, which requires logistical planning.
A is incorrect because plan testing and drills are the last step in disaster recovery and contingency planning. It is important to test the business continuity plan regularly because environments continually change. Tests and disaster recovery drills and exercises should be performed at least once a year. Most companies cannot afford for these exercises to interrupt production or productivity, so the exercises may need to take place in sections or at specific times, which requires logistical planning.
![]() C is incorrect because determining offsite backup facility alternatives is part of the recovery strategy, which takes place in the middle of the disaster recovery and contingency planning process. Organizations must have alternative offsite backup facilities in the case of a larger disaster. Generally, contracts are established with third-party vendors to provide such services. The client pays a monthly fee to retain the right to use the facility in a time of need, and then incurs an activation fee when the facility has to be used.
C is incorrect because determining offsite backup facility alternatives is part of the recovery strategy, which takes place in the middle of the disaster recovery and contingency planning process. Organizations must have alternative offsite backup facilities in the case of a larger disaster. Generally, contracts are established with third-party vendors to provide such services. The client pays a monthly fee to retain the right to use the facility in a time of need, and then incurs an activation fee when the facility has to be used.
![]() D is incorrect because organizing and creating relevant documentation takes place toward the end of the disaster recovery and contingency planning process. Procedures need to be documented because when they are actually needed, it will most likely be a chaotic and frantic atmosphere with a demanding time schedule. The documentation may need to include information on how to install images, configure operating systems and servers, and properly install utilities and proprietary software. Other documentation could include a calling tree, and contact information for specific vendors, emergency agencies, offsite facilities, etc.
D is incorrect because organizing and creating relevant documentation takes place toward the end of the disaster recovery and contingency planning process. Procedures need to be documented because when they are actually needed, it will most likely be a chaotic and frantic atmosphere with a demanding time schedule. The documentation may need to include information on how to install images, configure operating systems and servers, and properly install utilities and proprietary software. Other documentation could include a calling tree, and contact information for specific vendors, emergency agencies, offsite facilities, etc.
15. Which of the following is not a reason to develop and implement a disaster recovery plan?
A. Provide steps for a post-disaster recovery.
B. Extend backup operations to include more than just backing up data.
C. Outline business functions and systems.
D. Provide procedures for emergency responses.
![]() C. Outlining business functions and systems is not a viable reason to create and implement a disaster recovery plan. Although these tasks will most likely be accomplished as a result of a disaster recovery plan, it is not a good reason to carry out the plan compared to the other answers in the question. You don’t develop and implement a disaster recovery plan just to outline business functions and systems, although that usually takes place during the planning process.
C. Outlining business functions and systems is not a viable reason to create and implement a disaster recovery plan. Although these tasks will most likely be accomplished as a result of a disaster recovery plan, it is not a good reason to carry out the plan compared to the other answers in the question. You don’t develop and implement a disaster recovery plan just to outline business functions and systems, although that usually takes place during the planning process.
![]() A is incorrect because providing steps for a post-disaster recovery is a good reason to develop and implement a disaster recovery plan. In fact, that is exactly what a disaster recovery plan provides. The goal of disaster recovery is to minimize the effects of a disaster and take the necessary steps to ensure that the resources, personnel, and business processes are able to resume operation in a timely manner. The goal of a disaster recovery plan is to handle the disaster and its ramifications right after the disaster hits.
A is incorrect because providing steps for a post-disaster recovery is a good reason to develop and implement a disaster recovery plan. In fact, that is exactly what a disaster recovery plan provides. The goal of disaster recovery is to minimize the effects of a disaster and take the necessary steps to ensure that the resources, personnel, and business processes are able to resume operation in a timely manner. The goal of a disaster recovery plan is to handle the disaster and its ramifications right after the disaster hits.
![]() B is incorrect because extending backup operations to include more than just backing up data is a good reason to develop and implement a disaster recovery plan. When looking at disaster recovery plans, some companies focus mainly on backing up data and providing redundant hardware. Although these items are extremely important, they are just small pieces of the company’s overall operations. Hardware and computers need people to configure and operate them, and data is usually not useful unless it is accessible by other systems and possibly outside entities. All of these things can require backups, not just data.
B is incorrect because extending backup operations to include more than just backing up data is a good reason to develop and implement a disaster recovery plan. When looking at disaster recovery plans, some companies focus mainly on backing up data and providing redundant hardware. Although these items are extremely important, they are just small pieces of the company’s overall operations. Hardware and computers need people to configure and operate them, and data is usually not useful unless it is accessible by other systems and possibly outside entities. All of these things can require backups, not just data.
![]() D is incorrect because providing procedures for emergency responses is a good reason to develop and implement a disaster recovery plan. A disaster recovery plan is carried out when everything is still in emergency mode and everyone is scrambling to get all critical systems back online. Having well-thought-out written procedures makes this whole process much more effective.
D is incorrect because providing procedures for emergency responses is a good reason to develop and implement a disaster recovery plan. A disaster recovery plan is carried out when everything is still in emergency mode and everyone is scrambling to get all critical systems back online. Having well-thought-out written procedures makes this whole process much more effective.
16. When designing a system or environment, fault tolerance capabilities are commonly built in to ensure that a disruption does not negatively affect the organization. There are different approaches to fault tolerance that need to be understood. Which of the following has the best definitions associated with the identified tolerance approach?
A. Replication provides multiple different instances that can be used in parallel. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. Diversity provides multiple identical implementations.
B. Replication provides multiple identical instances that can be used in parallel. Redundancy provides multiple different instances, which allows for failover protection. Diversity provides multiple different implementations.
C. Replication provides multiple identical instances that can be used only in a failover situation. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. Diversity provides single implementations.
D. Replication provides multiple identical instances that can be used in parallel. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. Diversity provides multiple different implementations.
![]() D. Replication provides multiple identical instances that can be used in parallel. Replicating the same data or processing capabilities to different systems allows for tasks to be sent to each instance in parallel for a load balancing capability. If one instance is overloaded, the other instances will “pick up the load” and processing times will be more uniform. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. For example, if one router goes offline, then all routing tasks can be switched over to the redundant router to ensure that network performance is not affected. Diversity provides multiple different implementations. For example, an organization may implement two different types of firewalls so if one firewall is compromised, the second firewall may not be compromised because it most likely will not have the same vulnerability.
D. Replication provides multiple identical instances that can be used in parallel. Replicating the same data or processing capabilities to different systems allows for tasks to be sent to each instance in parallel for a load balancing capability. If one instance is overloaded, the other instances will “pick up the load” and processing times will be more uniform. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. For example, if one router goes offline, then all routing tasks can be switched over to the redundant router to ensure that network performance is not affected. Diversity provides multiple different implementations. For example, an organization may implement two different types of firewalls so if one firewall is compromised, the second firewall may not be compromised because it most likely will not have the same vulnerability.
![]() A is incorrect because diversity provides multiple different implementations, not multiple identical implementations. Specific systems will be vulnerable to specific threats, and if an organization uses the exact same systems throughout an environment, an attacker could exploit just one vulnerability and negatively affect many systems at the same time. To protect against this type of issue, organizations can deploy systems that provide the same type of functionality (i.e., router, firewall, switch) but were developed by different vendors. Each vendor will use its own unique architecture, design, and programming code for its specific product line. So if there is a flaw within one vendor’s product, that flaw will most likely not be in a similar product made by a different vendor.
A is incorrect because diversity provides multiple different implementations, not multiple identical implementations. Specific systems will be vulnerable to specific threats, and if an organization uses the exact same systems throughout an environment, an attacker could exploit just one vulnerability and negatively affect many systems at the same time. To protect against this type of issue, organizations can deploy systems that provide the same type of functionality (i.e., router, firewall, switch) but were developed by different vendors. Each vendor will use its own unique architecture, design, and programming code for its specific product line. So if there is a flaw within one vendor’s product, that flaw will most likely not be in a similar product made by a different vendor.
![]() B is incorrect because redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. Redundancy means that there are at least two systems that can carry out the exact same functionality. One of the instances is used in production, and the other instance can be offline and brought online when the first instance fails. This is what failover protection describes. If there is a failure of one system, the second system takes over for the failed system and processing is not affected. If the instances were different, then this would be an example of diversity, not redundancy.
B is incorrect because redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection. Redundancy means that there are at least two systems that can carry out the exact same functionality. One of the instances is used in production, and the other instance can be offline and brought online when the first instance fails. This is what failover protection describes. If there is a failure of one system, the second system takes over for the failed system and processing is not affected. If the instances were different, then this would be an example of diversity, not redundancy.
![]() C is incorrect because replication provides multiple identical instances that are most often used in parallel. Failover protection is provided through redundancy. This answer also states that diversity provides single implementations, which is incorrect. Diversity provides multiple different implementations so that if one implementation has a specific issue, the other implementation will most likely not experience this same issue. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection.
C is incorrect because replication provides multiple identical instances that are most often used in parallel. Failover protection is provided through redundancy. This answer also states that diversity provides single implementations, which is incorrect. Diversity provides multiple different implementations so that if one implementation has a specific issue, the other implementation will most likely not experience this same issue. Redundancy provides multiple identical instances, which allows for failover protection.
17. With what phase of a business continuity plan does a company proceed when it is ready to move back into its original site or a new site?
A. Reconstitution phase
B. Recovery phase
C. Project initiation phase
D. Damage assessment phase
![]() A. When it is time for the company to move back into its original site or a new site, the company is ready to enter into the reconstitution phase. A company is not out of an emergency state until it is back in operation at the original primary site or a new site that was constructed to replace the primary site, because the company is always vulnerable while operating in a backup facility. Many logistical issues need to be considered as to when a company must return from the alternate site to the original site. Some of these issues include ensuring the safety of the employees, ensuring proper communications and connectivity methods are working, and properly testing the new environment. Once the coordinator, management, and salvage team sign off on the readiness of the facility, the salvage team should back up data from the alternate site and restore it within the new facility, carefully terminate contingency operations, and securely transport equipment and personnel to the new facility.
A. When it is time for the company to move back into its original site or a new site, the company is ready to enter into the reconstitution phase. A company is not out of an emergency state until it is back in operation at the original primary site or a new site that was constructed to replace the primary site, because the company is always vulnerable while operating in a backup facility. Many logistical issues need to be considered as to when a company must return from the alternate site to the original site. Some of these issues include ensuring the safety of the employees, ensuring proper communications and connectivity methods are working, and properly testing the new environment. Once the coordinator, management, and salvage team sign off on the readiness of the facility, the salvage team should back up data from the alternate site and restore it within the new facility, carefully terminate contingency operations, and securely transport equipment and personnel to the new facility.
![]() B is incorrect because the recovery phase includes the preparation of the offsite facility (if needed), the rebuilding of the network and systems, and the organization of staff to move into a new facility. The recovery process needs to be as organized as possible to get the company up and running as soon as possible. Templates should be developed during the plan development stage that can be used by the different teams during the recovery phase to step them through the necessary phases and to document their findings. The templates keep the teams on task and also quickly tell the team leaders about the progress, obstacles, and potential recovery time.
B is incorrect because the recovery phase includes the preparation of the offsite facility (if needed), the rebuilding of the network and systems, and the organization of staff to move into a new facility. The recovery process needs to be as organized as possible to get the company up and running as soon as possible. Templates should be developed during the plan development stage that can be used by the different teams during the recovery phase to step them through the necessary phases and to document their findings. The templates keep the teams on task and also quickly tell the team leaders about the progress, obstacles, and potential recovery time.
![]() C is incorrect because the project initiation phase is how the actual planning of the business continuity plan begins. It does not occur during the execution of the plan. The project initiation phase involves getting management support, developing the scope of the plan, and securing funding and resources.
C is incorrect because the project initiation phase is how the actual planning of the business continuity plan begins. It does not occur during the execution of the plan. The project initiation phase involves getting management support, developing the scope of the plan, and securing funding and resources.
![]() D is incorrect because the damage assessment takes place at the start of actually carrying out the business continuity procedures. A damage assessment helps determine whether the business continuity plan should be put into action based on activation criteria predefined by the BCP coordinator and team. After the damage assessment, if one or more of the situations outlined in the criteria have taken place, then the team is moved into recovery mode.
D is incorrect because the damage assessment takes place at the start of actually carrying out the business continuity procedures. A damage assessment helps determine whether the business continuity plan should be put into action based on activation criteria predefined by the BCP coordinator and team. After the damage assessment, if one or more of the situations outlined in the criteria have taken place, then the team is moved into recovery mode.
18. Several teams should be involved in carrying out the business continuity plan. Which team is responsible for starting the recovery of the original site?
A. Damage assessment team
B. BCP team
C. Salvage team
D. Restoration team
![]() C. The BCP coordinator should have an understanding of the needs of the company and the types of teams that need to be developed and trained. Employees should be assigned to the specific teams based on their knowledge and skill set. Each team needs to have a designated leader, who will direct the members and their activities. These team leaders will be responsible not only for ensuring that their team’s objectives are met, but also for communicating with each other to make sure each team is working in parallel phases. The salvage team is responsible for starting the recovery of the original site. It is also responsible for backing up data from the alternate site and restoring it within the new facility, carefully terminating contingency operations, and securely transporting equipment and personnel to the new facility.
C. The BCP coordinator should have an understanding of the needs of the company and the types of teams that need to be developed and trained. Employees should be assigned to the specific teams based on their knowledge and skill set. Each team needs to have a designated leader, who will direct the members and their activities. These team leaders will be responsible not only for ensuring that their team’s objectives are met, but also for communicating with each other to make sure each team is working in parallel phases. The salvage team is responsible for starting the recovery of the original site. It is also responsible for backing up data from the alternate site and restoring it within the new facility, carefully terminating contingency operations, and securely transporting equipment and personnel to the new facility.
![]() A is incorrect because the damage assessment team is responsible for determining the scope and severity of the damage caused. Whether or not a disaster is declared and the BCP put into action is based on this information collected and assessed by the damage assessment team.
A is incorrect because the damage assessment team is responsible for determining the scope and severity of the damage caused. Whether or not a disaster is declared and the BCP put into action is based on this information collected and assessed by the damage assessment team.
![]() B is incorrect because the BCP team is responsible for creating and maintaining the business continuity plan. As such, its responsibilities also include identifying regulatory and legal requirements that must be met, identifying all possible vulnerabilities and threats, performing a business impact analysis, and developing procedures and steps in resuming business after a disaster. The BCP team is made up of representatives from a variety of business units and departments, including senior management, the security department, the communications department, and the legal department. This is not the team that starts the physical recovery of the original site.
B is incorrect because the BCP team is responsible for creating and maintaining the business continuity plan. As such, its responsibilities also include identifying regulatory and legal requirements that must be met, identifying all possible vulnerabilities and threats, performing a business impact analysis, and developing procedures and steps in resuming business after a disaster. The BCP team is made up of representatives from a variety of business units and departments, including senior management, the security department, the communications department, and the legal department. This is not the team that starts the physical recovery of the original site.
![]() D is incorrect because the restoration team is responsible for getting the alternate site into a working and functioning environment. Both the restoration team and the salvage team must know how to do many tasks, such as install operating systems, configure workstations and servers, string wire and cabling, set up the network and configure networking services, and install equipment and applications. Both teams must also know how to restore data from backup facilities, and how to do so in a secure manner that ensures that the systems’ and data’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability are not compromised.
D is incorrect because the restoration team is responsible for getting the alternate site into a working and functioning environment. Both the restoration team and the salvage team must know how to do many tasks, such as install operating systems, configure workstations and servers, string wire and cabling, set up the network and configure networking services, and install equipment and applications. Both teams must also know how to restore data from backup facilities, and how to do so in a secure manner that ensures that the systems’ and data’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability are not compromised.
19. ACME Inc. paid a software vendor to develop specialized software, and that vendor has gone out of business. ACME Inc. does not have access to the code and therefore cannot keep it updated. What mechanism should the company have implemented to prevent this from happening?
A. Reciprocal agreement
B. Software escrow
C. Electronic vaulting
D. Business interruption insurance
![]() B. The protection mechanism that ACME Inc. should have implemented is called software escrow. Software escrow means that a third party holds the source code, and backups of the compiled code, manuals, and other supporting materials. A contract between the software vendor, customer, and third party outlines who can do what and when with the source code. This contract usually states that the customer can have access to the source code only if and when the vendor goes out of business, is unable to carry out stated responsibilities, or is in breach of the original contract. If any of these activities takes place, then the customer is protected because it can still gain access to the source code and other materials through the third-party escrow agent.
B. The protection mechanism that ACME Inc. should have implemented is called software escrow. Software escrow means that a third party holds the source code, and backups of the compiled code, manuals, and other supporting materials. A contract between the software vendor, customer, and third party outlines who can do what and when with the source code. This contract usually states that the customer can have access to the source code only if and when the vendor goes out of business, is unable to carry out stated responsibilities, or is in breach of the original contract. If any of these activities takes place, then the customer is protected because it can still gain access to the source code and other materials through the third-party escrow agent.
![]() A is incorrect because a reciprocal agreement is an offsite facility option that involves two companies agreeing to share their facility in case a disaster renders one of the facilities unusable. Reciprocal agreements deal with disaster recovery and not software protection when dealing with the developing vendor.
A is incorrect because a reciprocal agreement is an offsite facility option that involves two companies agreeing to share their facility in case a disaster renders one of the facilities unusable. Reciprocal agreements deal with disaster recovery and not software protection when dealing with the developing vendor.
![]() C is incorrect because electronic vaulting is a type of electronic backup solution. Electronic vaulting makes copies of files as they are modified and periodically transmits them to an offsite backup site. The transmission does not happen in real time but is carried out in batches. So, a company can choose to have all files that have been changed sent to the backup facility every hour, day, week, or month. The information can be stored in an offsite facility and retrieved from that facility in a short period of time. Electronic vaulting has to do with backing up data so that it is available if there is a disruption or disaster.
C is incorrect because electronic vaulting is a type of electronic backup solution. Electronic vaulting makes copies of files as they are modified and periodically transmits them to an offsite backup site. The transmission does not happen in real time but is carried out in batches. So, a company can choose to have all files that have been changed sent to the backup facility every hour, day, week, or month. The information can be stored in an offsite facility and retrieved from that facility in a short period of time. Electronic vaulting has to do with backing up data so that it is available if there is a disruption or disaster.
![]() D is incorrect because a business interruption insurance policy covers specified expenses and lost earnings if a company is out of business for a certain length of time. This insurance is commonly purchased to protect a company in case a disaster takes place and they have to shut down their services for a specific period of time. It does not have anything to do with protection or accessibility of source code.
D is incorrect because a business interruption insurance policy covers specified expenses and lost earnings if a company is out of business for a certain length of time. This insurance is commonly purchased to protect a company in case a disaster takes place and they have to shut down their services for a specific period of time. It does not have anything to do with protection or accessibility of source code.
20. Which of the following incorrectly describes the concept of executive succession planning?
A. Predetermined steps protect the company if a senior executive leaves.
B. Two or more senior staff cannot be exposed to a particular risk at the same time.
C. It documents the assignment of deputy roles.
D. It covers assigning a skeleton crew to resume operations after a disaster.
![]() D. A skeleton crew consists of the employees who carry out the most critical functions following a disaster. They are put to work first during the recovery process. A skeleton crew is not related to the concept of executive succession planning, which addresses the steps that will be taken to fill a senior executive role should that person retire, leave the company, or die. The objective of a skeleton crew is to maintain critical operations, while the objective of executive succession planning is to protect the company by maintaining leadership roles.
D. A skeleton crew consists of the employees who carry out the most critical functions following a disaster. They are put to work first during the recovery process. A skeleton crew is not related to the concept of executive succession planning, which addresses the steps that will be taken to fill a senior executive role should that person retire, leave the company, or die. The objective of a skeleton crew is to maintain critical operations, while the objective of executive succession planning is to protect the company by maintaining leadership roles.
![]() A is incorrect because executive succession planning includes predetermined steps that protect the company if someone in a senior executive position retires, leaves the company, or is killed. The loss of a senior executive could tear a hole in the company’s fabric, creating a leadership vacuum that must be filled quickly with the right individual. The line of succession plan defines who would step in and assume responsibility for this role.
A is incorrect because executive succession planning includes predetermined steps that protect the company if someone in a senior executive position retires, leaves the company, or is killed. The loss of a senior executive could tear a hole in the company’s fabric, creating a leadership vacuum that must be filled quickly with the right individual. The line of succession plan defines who would step in and assume responsibility for this role.
![]() B is incorrect because the concept of two or more senior staff not being exposed to a particular risk at the same time is a policy that some larger organizations establish as part of their executive succession planning efforts. The idea is to protect senior personnel and the organization if a disaster were to strike. For example, an organization may decide that the CEO and president cannot travel on the same plane. If the plane went down and both individuals were killed, then the company could be in danger.
B is incorrect because the concept of two or more senior staff not being exposed to a particular risk at the same time is a policy that some larger organizations establish as part of their executive succession planning efforts. The idea is to protect senior personnel and the organization if a disaster were to strike. For example, an organization may decide that the CEO and president cannot travel on the same plane. If the plane went down and both individuals were killed, then the company could be in danger.
![]() C is incorrect because executive succession planning can include the assignment of deputy roles. An organization may have a deputy CIO, deputy CFO, and deputy CEO ready to take over the necessary tasks if the CIO, CFO, or CEO becomes unavailable. Executive succession planning is the decision to have these deputies step into the CIO, CFO, or CEO roles.
C is incorrect because executive succession planning can include the assignment of deputy roles. An organization may have a deputy CIO, deputy CFO, and deputy CEO ready to take over the necessary tasks if the CIO, CFO, or CEO becomes unavailable. Executive succession planning is the decision to have these deputies step into the CIO, CFO, or CEO roles.
21. What is the missing second step in the graphic that follows?
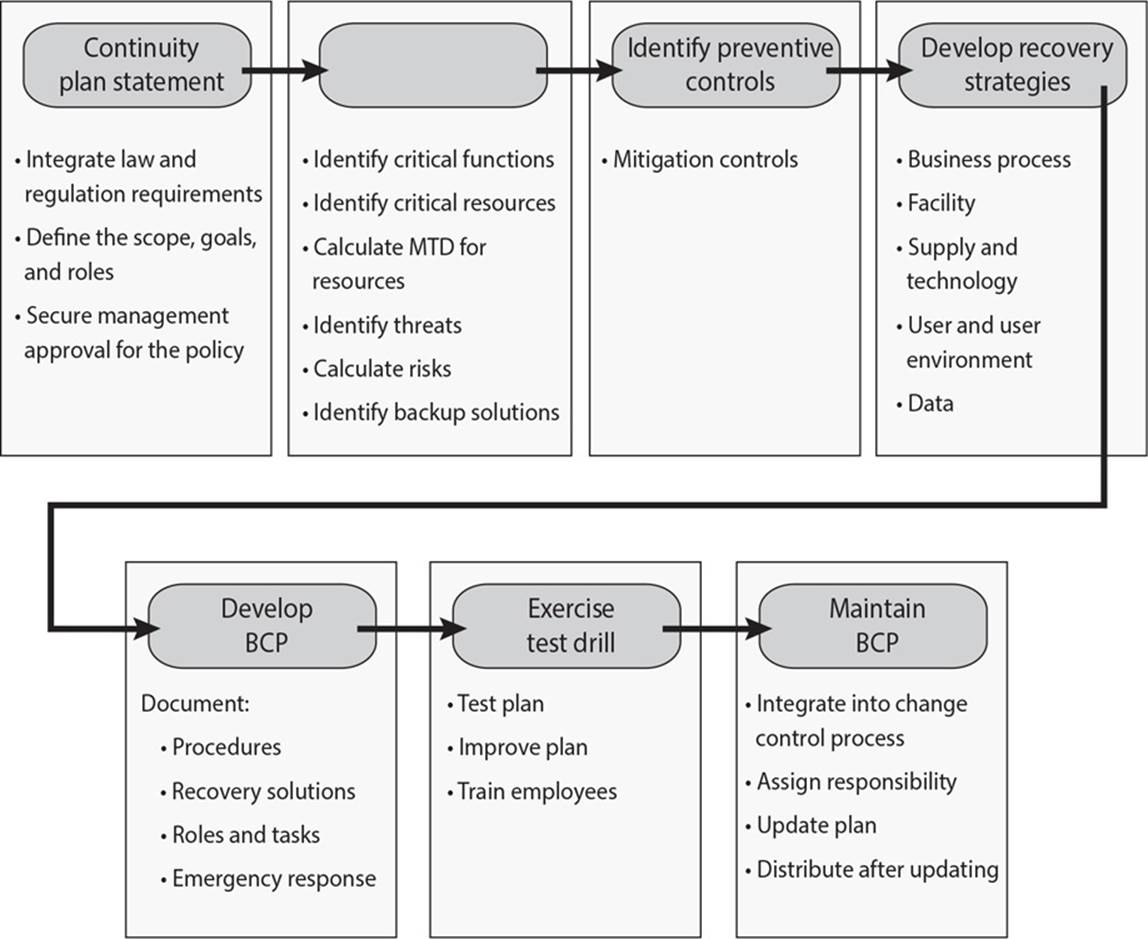
A. Identify continuity coordinator
B. Business impact analysis
C. Identify BCP committee
D. Dependency identification
![]() B. A business impact analysis (BIA) is considered a functional analysis, in which a team collects data through interviews and documentary sources; documents business functions, activities, and transactions; develops a hierarchy of business functions; and finally applies a classification scheme to indicate each individual function’s criticality level. It is one of the most important first steps in the planning development of a business continuity plan (BCP). Qualitative and quantitative data needs to be gathered, analyzed, interpreted, and presented to management. Identifying critical functions and systems allow the organization to prioritize them based on necessity.
B. A business impact analysis (BIA) is considered a functional analysis, in which a team collects data through interviews and documentary sources; documents business functions, activities, and transactions; develops a hierarchy of business functions; and finally applies a classification scheme to indicate each individual function’s criticality level. It is one of the most important first steps in the planning development of a business continuity plan (BCP). Qualitative and quantitative data needs to be gathered, analyzed, interpreted, and presented to management. Identifying critical functions and systems allow the organization to prioritize them based on necessity.
![]() A is incorrect because the business continuity coordinator needs to be put into position before this whole process starts. He will be the leader for the BCP team and will oversee the development, implementation, and testing of the continuity and disaster recovery plans. The coordinator should be identified in the project initiation and oversee all the steps shown in the graphic. It is best if this person has good social skills and is somewhat of a politician because he will need to coordinate a lot of different departments and busy individuals who have their own agendas. This person needs to have direct access to management and have the credibility and authority to carry out leadership tasks.
A is incorrect because the business continuity coordinator needs to be put into position before this whole process starts. He will be the leader for the BCP team and will oversee the development, implementation, and testing of the continuity and disaster recovery plans. The coordinator should be identified in the project initiation and oversee all the steps shown in the graphic. It is best if this person has good social skills and is somewhat of a politician because he will need to coordinate a lot of different departments and busy individuals who have their own agendas. This person needs to have direct access to management and have the credibility and authority to carry out leadership tasks.
![]() C is incorrect because a BCP committee needs to be put together after the coordinator is identified to help carry out all the steps in the graphic. Management and the coordinator should work together to appoint specific, qualified people to be on this committee. The team must be composed of people who are familiar with the different departments within the company, because each department is unique in its functionality and has distinctive risks and threats. The best plan is when all issues and threats are brought to the table and discussed. This cannot be done effectively with a few people who are familiar with only a couple of departments. Representatives from each department must be involved with not only the planning stages but also the testing and implementation stages.
C is incorrect because a BCP committee needs to be put together after the coordinator is identified to help carry out all the steps in the graphic. Management and the coordinator should work together to appoint specific, qualified people to be on this committee. The team must be composed of people who are familiar with the different departments within the company, because each department is unique in its functionality and has distinctive risks and threats. The best plan is when all issues and threats are brought to the table and discussed. This cannot be done effectively with a few people who are familiar with only a couple of departments. Representatives from each department must be involved with not only the planning stages but also the testing and implementation stages.
![]() D is incorrect because dependencies between company critical functions and resources are carried out during the BIA. This is only one of the components in the overall BIA process. Identifying these types of dependencies is critical because it is important to look at a company as a complex animal instead of a static two-dimensional entity. It comprises many types of equipment, people, tasks, departments, communications mechanisms, and interfaces to the outer world. The biggest challenge of true continuity planning is understanding all of these intricacies and their interrelationships. A team may develop plans to back up and restore data, implement redundant data processing equipment, educate employees on how to carry out automated tasks manually, and obtain redundant power supplies. But if all of these components don’t know how to work together in a different environment to get the products out the door, it might all be a waste of time.
D is incorrect because dependencies between company critical functions and resources are carried out during the BIA. This is only one of the components in the overall BIA process. Identifying these types of dependencies is critical because it is important to look at a company as a complex animal instead of a static two-dimensional entity. It comprises many types of equipment, people, tasks, departments, communications mechanisms, and interfaces to the outer world. The biggest challenge of true continuity planning is understanding all of these intricacies and their interrelationships. A team may develop plans to back up and restore data, implement redundant data processing equipment, educate employees on how to carry out automated tasks manually, and obtain redundant power supplies. But if all of these components don’t know how to work together in a different environment to get the products out the door, it might all be a waste of time.
22. Different threats need to be evaluated and ranked based upon their severity of business risk when developing a BCP. Which ranking approach is illustrated in the graphic that follows?

A. Mean time to repair
B. Mean time between failures
C. Maximum critical downtime
D. Maximum tolerable downtime
![]() D. The BIA identifies which of the company’s critical systems are needed for survival and estimates the outage time that can be tolerated by the company as a result of various unfortunate events. The outage time that can be endured by a company is referred to as the maximum tolerable downtime (MTD). This is the timeframe between an unplanned interruption of business operations and the resumption of business at a reduced level of service. During the BIA, the BCP team identifies the maximum tolerable downtime for the critical resources. This was done to understand the business impact that would be caused if the assets were unavailable for one reason or another.
D. The BIA identifies which of the company’s critical systems are needed for survival and estimates the outage time that can be tolerated by the company as a result of various unfortunate events. The outage time that can be endured by a company is referred to as the maximum tolerable downtime (MTD). This is the timeframe between an unplanned interruption of business operations and the resumption of business at a reduced level of service. During the BIA, the BCP team identifies the maximum tolerable downtime for the critical resources. This was done to understand the business impact that would be caused if the assets were unavailable for one reason or another.
![]() A is incorrect because the mean time to repair (MTTR) is the amount of time it will be expected to take to get a device fixed and back into production. For a hard drive in a redundant array, the MTTR is the amount of time between the actual failure and the time when, after noticing the failure, someone has replaced the failed drive and the redundant array has completed rewriting the information on the new drive. This is likely to be measured in hours. For an unplanned reboot, the MTTR is the amount of time between the failure of the system and the point in time when it has rebooted its operating system, checked the state of its disks (hopefully finding nothing that its file systems cannot handle), restarted its applications, allowed its applications to check the consistency of their data (hopefully finding nothing that their journals cannot handle), and once again begun processing transactions. For well-built hardware running high-quality, well-managed operating systems and software, this may be only minutes. For commodity equipment without high-performance journaling file systems and databases, this may be hours, or, worse, days if automated recovery/rollback does not work and a restore of data from tape is required.
A is incorrect because the mean time to repair (MTTR) is the amount of time it will be expected to take to get a device fixed and back into production. For a hard drive in a redundant array, the MTTR is the amount of time between the actual failure and the time when, after noticing the failure, someone has replaced the failed drive and the redundant array has completed rewriting the information on the new drive. This is likely to be measured in hours. For an unplanned reboot, the MTTR is the amount of time between the failure of the system and the point in time when it has rebooted its operating system, checked the state of its disks (hopefully finding nothing that its file systems cannot handle), restarted its applications, allowed its applications to check the consistency of their data (hopefully finding nothing that their journals cannot handle), and once again begun processing transactions. For well-built hardware running high-quality, well-managed operating systems and software, this may be only minutes. For commodity equipment without high-performance journaling file systems and databases, this may be hours, or, worse, days if automated recovery/rollback does not work and a restore of data from tape is required.
![]() B is incorrect because the mean time between failures (MTBF) is the estimated lifespan of a piece of equipment. MTBF is calculated by the vendor of the equipment or a third party. The reason for using this value is to know approximately when a particular device will need to be replaced. Either based on historical data or scientifically estimated by vendors, it is used as a benchmark for reliability by predicting the average time that will pass in the operation of a component or a system until its final death. Organizations trending MTBF over time for the device they use may be able to identify types of devices that are failing above the averages promised by manufacturers and take action such as proactively contacting manufacturers under warranty, or deciding that old devices are reaching the end of their useful life and choosing to replace them en masse before larger-scale failures and operational disruptions occur.
B is incorrect because the mean time between failures (MTBF) is the estimated lifespan of a piece of equipment. MTBF is calculated by the vendor of the equipment or a third party. The reason for using this value is to know approximately when a particular device will need to be replaced. Either based on historical data or scientifically estimated by vendors, it is used as a benchmark for reliability by predicting the average time that will pass in the operation of a component or a system until its final death. Organizations trending MTBF over time for the device they use may be able to identify types of devices that are failing above the averages promised by manufacturers and take action such as proactively contacting manufacturers under warranty, or deciding that old devices are reaching the end of their useful life and choosing to replace them en masse before larger-scale failures and operational disruptions occur.
![]() C is incorrect because maximum critical downtime is not an official term used in BCP and is a distracter answer.
C is incorrect because maximum critical downtime is not an official term used in BCP and is a distracter answer.
23. What type of infrastructural setup is illustrated in the graphic that follows?
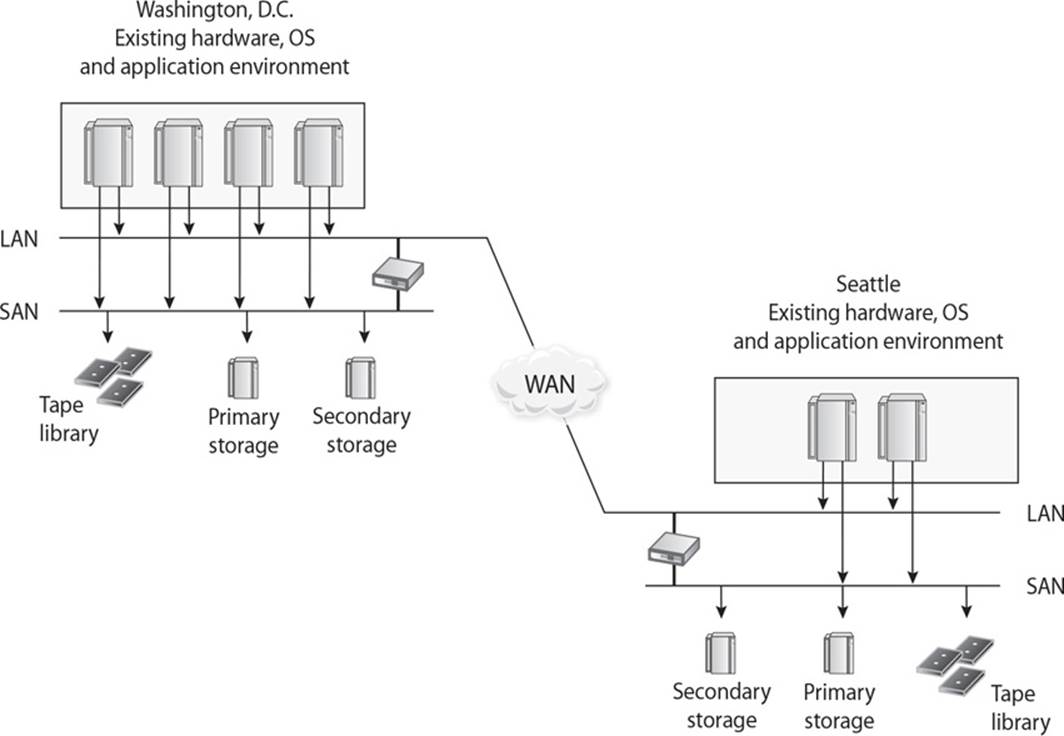
A. Hot site
B. Warm site
C. Cold site
D. Reciprocal agreement
![]() A. A hot site is a facility that is leased or rented and is fully configured and ready to operate within a few hours. The only missing resources from a hot site are usually the data, which will be retrieved from a backup site, and the people who will be processing the data. The equipment and system software must absolutely be compatible with the data being restored from the main site and must not cause any negative interoperability issues. These sites are a good choice for a company that needs to ensure a site will be available for it as soon as possible.
A. A hot site is a facility that is leased or rented and is fully configured and ready to operate within a few hours. The only missing resources from a hot site are usually the data, which will be retrieved from a backup site, and the people who will be processing the data. The equipment and system software must absolutely be compatible with the data being restored from the main site and must not cause any negative interoperability issues. These sites are a good choice for a company that needs to ensure a site will be available for it as soon as possible.
![]() B is incorrect because a warm site is a leased or rented facility that is usually partially configured with some equipment, but not the actual computers. In other words, a warm site is usually a hot site without the expensive equipment. Staging a facility with duplicate hardware and computers configured for immediate operation is extremely expensive, so a warm site provides an alternate facility with some peripheral devices. This is the most widely used model. It may be a better choice for companies that depend upon proprietary and unusual hardware and software, because they will bring their own hardware and software with them to the site after the disaster hits.
B is incorrect because a warm site is a leased or rented facility that is usually partially configured with some equipment, but not the actual computers. In other words, a warm site is usually a hot site without the expensive equipment. Staging a facility with duplicate hardware and computers configured for immediate operation is extremely expensive, so a warm site provides an alternate facility with some peripheral devices. This is the most widely used model. It may be a better choice for companies that depend upon proprietary and unusual hardware and software, because they will bring their own hardware and software with them to the site after the disaster hits.
![]() C is incorrect because a cold site is a leased or rented facility that supplies the basic environment, electrical wiring, air conditioning, plumbing, and flooring, but none of the equipment or additional services. It may take weeks to get the site activated and ready for work. The cold site could have equipment racks and dark fiber (fiber that does not have the circuit engaged) and maybe even desks, but it would require the receipt of equipment from the client, since it does not provide any. The cold site is the least expensive option but takes the most time and effort to actually get up and functioning right after a disaster.
C is incorrect because a cold site is a leased or rented facility that supplies the basic environment, electrical wiring, air conditioning, plumbing, and flooring, but none of the equipment or additional services. It may take weeks to get the site activated and ready for work. The cold site could have equipment racks and dark fiber (fiber that does not have the circuit engaged) and maybe even desks, but it would require the receipt of equipment from the client, since it does not provide any. The cold site is the least expensive option but takes the most time and effort to actually get up and functioning right after a disaster.
![]() D is incorrect because a reciprocal agreement is one in which a company promises another company it can move into its facility and share space if it experiences a disaster and vice versa. Reciprocal agreements are very tricky to implement and are unenforceable. This is a cheaper way to go than the other offsite choices, but it is not always the best choice. Most environments are maxed out pertaining to the use of facility space, resources, and computing capability.
D is incorrect because a reciprocal agreement is one in which a company promises another company it can move into its facility and share space if it experiences a disaster and vice versa. Reciprocal agreements are very tricky to implement and are unenforceable. This is a cheaper way to go than the other offsite choices, but it is not always the best choice. Most environments are maxed out pertaining to the use of facility space, resources, and computing capability.
24. There are several types of redundant technologies that can be put into place. What type of technology is shown in the graphic that follows?
A. Tape vaulting
B. Remote journaling
C. Electronic vaulting
D. Redundant site
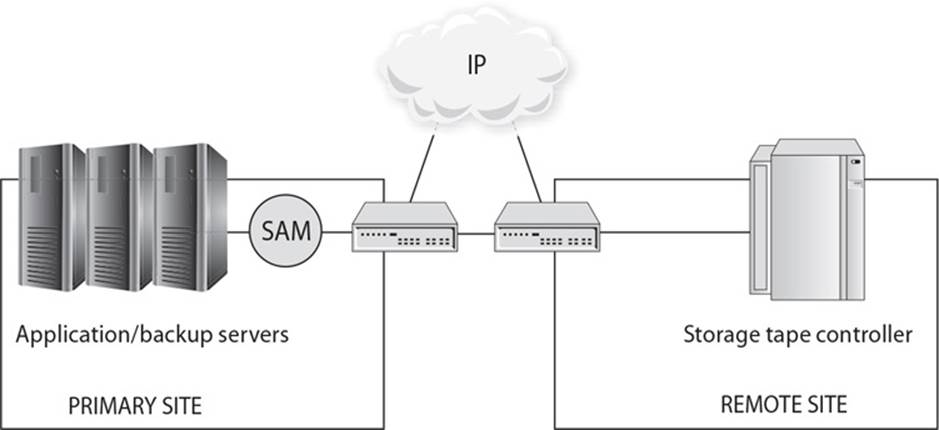
![]() A. Each site should have a full set of the most current and updated information and files, and a commonly used software backup technology is referred to as tape vaulting. Many businesses back up their data to tapes that are then manually transferred to an offsite facility by a courier or an employee. With automatic tape vaulting, the data is sent over a serial line to a backup tape system at the offsite facility. The company that maintains the offsite facility maintains the systems and changes out tapes when necessary. Data can be quickly backed up and retrieved when necessary. This technology reduces the manual steps in the traditional tape backup procedures. Basic vaulting of tape data is sending backup tapes to an offsite location, but a manual process can be error prone. Electronic tape vaulting transmits data over a network to tape devices located at an alternate data center. Electronic tape vaulting improves recovery speed and reduces errors, and backups can be run more frequently.
A. Each site should have a full set of the most current and updated information and files, and a commonly used software backup technology is referred to as tape vaulting. Many businesses back up their data to tapes that are then manually transferred to an offsite facility by a courier or an employee. With automatic tape vaulting, the data is sent over a serial line to a backup tape system at the offsite facility. The company that maintains the offsite facility maintains the systems and changes out tapes when necessary. Data can be quickly backed up and retrieved when necessary. This technology reduces the manual steps in the traditional tape backup procedures. Basic vaulting of tape data is sending backup tapes to an offsite location, but a manual process can be error prone. Electronic tape vaulting transmits data over a network to tape devices located at an alternate data center. Electronic tape vaulting improves recovery speed and reduces errors, and backups can be run more frequently.
![]() B is incorrect because remote journaling is a technology used to transmit data to an offsite facility, but this usually only includes moving the journal or transaction logs to the offsite facility, not the actual files. This graphic specifically shows a tape controller and remote journaling mainly takes place between databases. Remote journaling involves transmitting the journal or transaction log offsite to a backup facility. These logs contain the deltas (changes) that have taken place to the individual files. If and when data are corrupted and need to be restored, the company can retrieve these logs, which are used to rebuild the lost data. Journaling is efficient for database recovery, where only the reapplication of a series of changes to individual records is required to resynchronize the database.
B is incorrect because remote journaling is a technology used to transmit data to an offsite facility, but this usually only includes moving the journal or transaction logs to the offsite facility, not the actual files. This graphic specifically shows a tape controller and remote journaling mainly takes place between databases. Remote journaling involves transmitting the journal or transaction log offsite to a backup facility. These logs contain the deltas (changes) that have taken place to the individual files. If and when data are corrupted and need to be restored, the company can retrieve these logs, which are used to rebuild the lost data. Journaling is efficient for database recovery, where only the reapplication of a series of changes to individual records is required to resynchronize the database.
![]() C is incorrect because electronic vaulting most commonly takes place between databases and makes copies of files as they are modified and periodically transmits them to an offsite backup site. The transmission does not happen in real time but is carried out in batches. So, a company can choose to have all files that have been changed sent to the backup facility every hour, day, week, or month. The information can be stored in an offsite facility and retrieved from that facility in a short period of time. This form of backup takes place in many financial institutions, so when a bank teller accepts a deposit or withdrawal, the change to the customer’s account is made locally to that branch’s database and to the remote site that maintains the backup copies of all customer records.
C is incorrect because electronic vaulting most commonly takes place between databases and makes copies of files as they are modified and periodically transmits them to an offsite backup site. The transmission does not happen in real time but is carried out in batches. So, a company can choose to have all files that have been changed sent to the backup facility every hour, day, week, or month. The information can be stored in an offsite facility and retrieved from that facility in a short period of time. This form of backup takes place in many financial institutions, so when a bank teller accepts a deposit or withdrawal, the change to the customer’s account is made locally to that branch’s database and to the remote site that maintains the backup copies of all customer records.
![]() D is incorrect because while the graphic could be illustrating that the tape controller is located at a redundant site, a redundant site is not actually a technology. Some companies choose to have redundant sites, meaning one site is equipped and configured exactly like the primary site, which serves as a redundant environment. These sites are owned by the company and are mirrors of the original production environment. This is one of the most expensive backup facility options, because a full environment must be maintained even though it usually is not used for regular production activities until after a disaster takes place that triggers the relocation of services to the redundant site.
D is incorrect because while the graphic could be illustrating that the tape controller is located at a redundant site, a redundant site is not actually a technology. Some companies choose to have redundant sites, meaning one site is equipped and configured exactly like the primary site, which serves as a redundant environment. These sites are owned by the company and are mirrors of the original production environment. This is one of the most expensive backup facility options, because a full environment must be maintained even though it usually is not used for regular production activities until after a disaster takes place that triggers the relocation of services to the redundant site.
25. The following is a graphic of a business continuity policy. Which component is missing from this graphic?
A. Damage assessment phase
B. Reconstitution phase
C. Business resumption phase
D. Continuity of operations plan
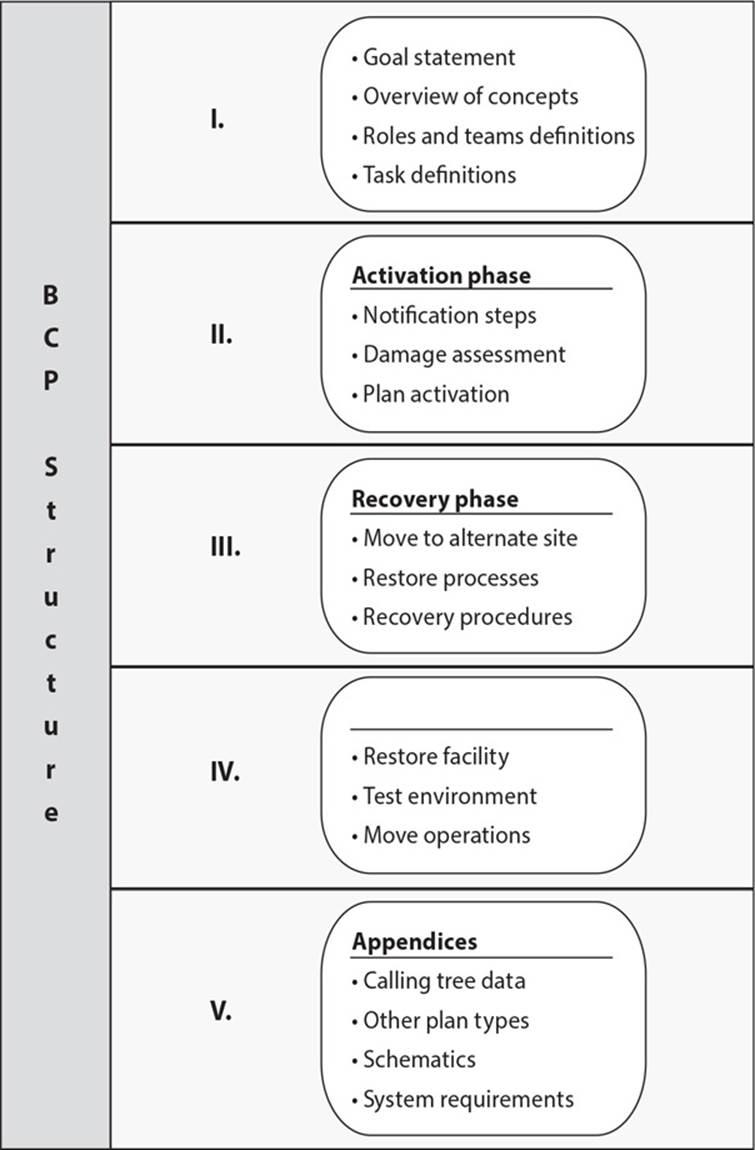
![]() B. After a disaster takes place and a company moves out of its facility, it must move back in after the facility is reconstructed. When it is time for the company to move back into its original site or a new site, the company is ready to enter into the reconstitution phase. A company is not out of an emergency state until it is back in operation at the original primary site or a new site that was constructed to replace the primary site, because the company is always vulnerable while operating in a backup facility. Many logistical issues need to be considered as to when a company must return from the alternate site to the original site. The following lists a few of these issues:
B. After a disaster takes place and a company moves out of its facility, it must move back in after the facility is reconstructed. When it is time for the company to move back into its original site or a new site, the company is ready to enter into the reconstitution phase. A company is not out of an emergency state until it is back in operation at the original primary site or a new site that was constructed to replace the primary site, because the company is always vulnerable while operating in a backup facility. Many logistical issues need to be considered as to when a company must return from the alternate site to the original site. The following lists a few of these issues:
• Ensuring the safety of employees
• Ensuring an adequate environment is provided (power, facility infrastructure, water, HVAC)
• Ensuring that the necessary equipment and supplies are present and in working order
• Ensuring proper communications and connectivity methods are working
• Properly testing the new environment
![]() A is incorrect because a role, or a team, needs to be created to carry out a damage assessment once a disaster has taken place. The assessment procedures should be properly documented and include the following steps:
A is incorrect because a role, or a team, needs to be created to carry out a damage assessment once a disaster has taken place. The assessment procedures should be properly documented and include the following steps:
• Determine the cause of the disaster.
• Determine the potential for further damage.
• Identify the affected business functions and areas.
• Identify the level of functionality for the critical resources.
• Identify the resources that must be replaced immediately.
• Estimate how long it will take to bring critical functions back online.
• If it will take longer than the previously estimated Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) values to restore operations, then a disaster should be declared and the Business Continuity Planning (BCP) should be put into action.
After this information is collected and assessed, it will indicate what teams need to be called to action and whether the BCP actually needs to be activated. The BCP coordinator and team must develop activation criteria. After the damage assessment, if one or more of the situations outlined in the criteria have taken place, then the team is moved into recovery mode.
![]() C is incorrect because a business resumption plan focuses on how to re-create the necessary business processes that need to be reestablished instead of focusing on only IT components (i.e., it is process-oriented instead of procedure-oriented). This plan could be mentioned in the BCP policy, but the policy does not outline the specifics of reestablishing business processes.
C is incorrect because a business resumption plan focuses on how to re-create the necessary business processes that need to be reestablished instead of focusing on only IT components (i.e., it is process-oriented instead of procedure-oriented). This plan could be mentioned in the BCP policy, but the policy does not outline the specifics of reestablishing business processes.
![]() D is incorrect because a continuity of operations plan (COOP) establishes senior management and a headquarters after a disaster. It provides instructions on how to set up a command center so that all activities and communication take place centrally and in a controlled manner. This type of plan also outlines roles and authorities, orders of succession, and individual role tasks that need to be put into place after a disaster takes place. This plan could be mentioned in the BCP policy, but the policy does not outline the specifics of setting up a command center and its components.
D is incorrect because a continuity of operations plan (COOP) establishes senior management and a headquarters after a disaster. It provides instructions on how to set up a command center so that all activities and communication take place centrally and in a controlled manner. This type of plan also outlines roles and authorities, orders of succession, and individual role tasks that need to be put into place after a disaster takes place. This plan could be mentioned in the BCP policy, but the policy does not outline the specifics of setting up a command center and its components.
26. The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) metrics have similar roles, but their values are very different. Which of the following best describes the difference between RTO and MTD metrics?
A. The RTO is a time period that represents the inability to recover, and the MTD represents an allowable amount of downtime.
B. The RTO is an allowable amount of downtime, and the MTD represents a time period that represents the inability to recover.
C. The RTO is a metric used in disruptions, and the MTD is a metric used in disasters.
D. The RTO is a metric pertaining to loss of access to data, and the MTD is a metric pertaining to loss of access to hardware and processing capabilities.
![]() B. The RTO value is smaller than the MTD value, because the MTD value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line. The RTO assumes that there is a period of acceptable downtime. This means that a company can be out of production for a certain period of time (RTO) and still get back on its feet. But if the company cannot get production up and running within the MTD window, the company is sinking too fast to properly recover.
B. The RTO value is smaller than the MTD value, because the MTD value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line. The RTO assumes that there is a period of acceptable downtime. This means that a company can be out of production for a certain period of time (RTO) and still get back on its feet. But if the company cannot get production up and running within the MTD window, the company is sinking too fast to properly recover.
![]() A is incorrect because the MTD is a time period that represents the inability to recover, and the RTO represents an allowable amount of downtime.
A is incorrect because the MTD is a time period that represents the inability to recover, and the RTO represents an allowable amount of downtime.
![]() C is incorrect because the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the earliest time period and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity. The RTO value is smaller than the MTD value, because the MTD value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line.
C is incorrect because the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the earliest time period and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity. The RTO value is smaller than the MTD value, because the MTD value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line.
![]() D is incorrect because the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the earliest time period and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity. The RTO value is smaller than the MTD value, because the MTD value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line. RTO is not a metric pertaining to loss of access to data, and the MTD is not a metric pertaining to loss of access to hardware and processing capabilities.
D is incorrect because the Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the earliest time period and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity. The RTO value is smaller than the MTD value, because the MTD value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line. RTO is not a metric pertaining to loss of access to data, and the MTD is not a metric pertaining to loss of access to hardware and processing capabilities.
27. High availability (HA) is a combination of technologies and processes that work together to ensure that specific critical functions are always up and running at the necessary level. To provide this level of high availability, a company has to have a long list of technologies and processes that provide redundancy, fault tolerance, and failover capabilities. Which of the following best describes these characteristics?
A. Redundancy is the duplication of noncritical components or functions of a system with the intention of decreasing reliability of the system. Fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to discontinue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place. If a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a working system.
B. Redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system. Fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to continue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place. If a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a working system.
C. Redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system. Fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to continue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place. If a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a nonworking system.
D. Redundancy is the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system. Fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to continue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place. If a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a working system.
![]() D. High availability (HA) is a combination of technologies and processes that work together to ensure that specific critical functions are always up and running. The specific thing can be a database, a network, an application, a power supply, etc. To provide this level of high availability, the company has to have a long list of technologies and processes that provide redundancy, fault tolerance, and failover capabilities. Redundancy, fault tolerance, and failover capabilities increase the reliability of a system or network. High reliability allows for high availability.
D. High availability (HA) is a combination of technologies and processes that work together to ensure that specific critical functions are always up and running. The specific thing can be a database, a network, an application, a power supply, etc. To provide this level of high availability, the company has to have a long list of technologies and processes that provide redundancy, fault tolerance, and failover capabilities. Redundancy, fault tolerance, and failover capabilities increase the reliability of a system or network. High reliability allows for high availability.
![]() A is incorrect because redundancy within this type of technology encompasses the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system. Redundancy is commonly built into the network at a routing protocol level. The routing protocols are configured so if one link goes down or gets congested, then traffic is routed over a different network link. Redundant hardware can also be available so if a primary device goes down the backup component can be swapped out and activated.
A is incorrect because redundancy within this type of technology encompasses the duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the intention of increasing reliability of the system. Redundancy is commonly built into the network at a routing protocol level. The routing protocols are configured so if one link goes down or gets congested, then traffic is routed over a different network link. Redundant hardware can also be available so if a primary device goes down the backup component can be swapped out and activated.
![]() B is incorrect because fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to continue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place (a fault). If a database experiences an unexpected glitch, it can roll back to a known good state and continue functioning as though nothing bad happened. If a packet gets lost or corrupted during a TCP session, the TCP protocol will resend the packet so that system-to-system communication is not affected. If a disk within a RAID system gets corrupted, the system uses its parity data to rebuild the corrupted data so that operations are not affected.
B is incorrect because fault tolerance is the capability of a technology to continue to operate as expected even if something unexpected takes place (a fault). If a database experiences an unexpected glitch, it can roll back to a known good state and continue functioning as though nothing bad happened. If a packet gets lost or corrupted during a TCP session, the TCP protocol will resend the packet so that system-to-system communication is not affected. If a disk within a RAID system gets corrupted, the system uses its parity data to rebuild the corrupted data so that operations are not affected.
![]() C is incorrect because if a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a working system.
C is incorrect because if a technology has a failover capability, this means that if there is a failure that cannot be handled through normal means, then processing is “switched over” to a working system.
The following scenario will be used to answer questions 28 and 29.
Sean has been hired as business continuity coordinator. He has been told by his management that he needed to ensure that the company is in compliance with the ISO/IEC standard that pertained to technology readiness for business continuity. He has also been instructed to find a way to transfer the risk of being unable to carry out critical business functions for a period of time because of a disaster.
28. Which of the following is most likely the standard that Sean has been asked to comply with?
A. ISO/IEC 27031
B. ISO/IEC 27005
C. ISO/IEC BS7799
D. ISO/IEC 2899
![]() A is correct. ISO/IEC 27031:2011 is a set of guidelines for information and communications technology readiness for business continuity. It is a component of the overall ISO/IEC 27000 series.
A is correct. ISO/IEC 27031:2011 is a set of guidelines for information and communications technology readiness for business continuity. It is a component of the overall ISO/IEC 27000 series.
![]() B is incorrect because the purpose of ISO/IEC 27005 is to provide guidelines for information security risk management. It supports the general concepts specified in ISO/IEC 27001 and is designed to assist the satisfactory implementation of information security based on a risk management approach. This standard deals with developing a formal risk management approach and not necessarily continuity issues.
B is incorrect because the purpose of ISO/IEC 27005 is to provide guidelines for information security risk management. It supports the general concepts specified in ISO/IEC 27001 and is designed to assist the satisfactory implementation of information security based on a risk management approach. This standard deals with developing a formal risk management approach and not necessarily continuity issues.
![]() C is incorrect because this is a distracter answer. There is no official standard called ISO/IEC BS7799.
C is incorrect because this is a distracter answer. There is no official standard called ISO/IEC BS7799.
![]() D is incorrect because this is a distracter answer. There is no official standard called ISO/IEC 2899.
D is incorrect because this is a distracter answer. There is no official standard called ISO/IEC 2899.
29. Which of the following would be best for Sean to implement as it pertains to his company’s needs?
A. Infrastructure cloud computing
B. Co-location at a multiprocessing center
C. Business interruption insurance
D. Shared partner extranet with integrated redundancy
![]() C. A company could choose to purchase a business interruption insurance policy. With this type of policy, if the company is out of business for a certain length of time, the insurance company will pay for specified expenses and lost earnings. Another policy that can be bought insures accounts receivable. If a company cannot collect on its accounts receivable for one reason or another, this type of coverage covers part or all of the losses and costs.
C. A company could choose to purchase a business interruption insurance policy. With this type of policy, if the company is out of business for a certain length of time, the insurance company will pay for specified expenses and lost earnings. Another policy that can be bought insures accounts receivable. If a company cannot collect on its accounts receivable for one reason or another, this type of coverage covers part or all of the losses and costs.
![]() A is incorrect because infrastructure cloud computing does not have anything to do with transferring risk. It is just a model that allows a company to outsource its infrastructure needs to a service provider.
A is incorrect because infrastructure cloud computing does not have anything to do with transferring risk. It is just a model that allows a company to outsource its infrastructure needs to a service provider.
![]() B is incorrect because a co-location at a multiprocessing center has nothing to do with transferring risk. If a company carries out multiprocessing at a co-location, that provides redundancy and failover services if a disaster is experienced.
B is incorrect because a co-location at a multiprocessing center has nothing to do with transferring risk. If a company carries out multiprocessing at a co-location, that provides redundancy and failover services if a disaster is experienced.
![]() D is incorrect because a shared partner extranet with integrated redundancy does not address transferring risk to another entity. An extranet is just a shared network segment, and integrated redundancy just means that if a failure takes place the company’s functionalities should not be affected.
D is incorrect because a shared partner extranet with integrated redundancy does not address transferring risk to another entity. An extranet is just a shared network segment, and integrated redundancy just means that if a failure takes place the company’s functionalities should not be affected.
The following scenario will be used to answer questions 30, 31, and 32.
Jeff is leading the business continuity group in his company. They have completed a business impact analysis and have determined that if the company’s credit card processing functionality was unavailable for 48 hours the company would most likely experience such a large financial hit that it would have to go out of business. The team has calculated that this functionality needs to be up and running within 28 hours after experiencing a disaster for the company to stay in business. The team has also determined that the restoration steps must be able to restore data that are one hour old or less.
30. In this scenario, which of the following is the recovery time objective value?
A. 48 hours
B. 28 hours
C. 20 hours
D. 1 hour
![]() B. The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the earliest time period and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity. The RTO value is smaller than the Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) value, because the MTD value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line. In this scenario 28 hours is the RTO and 48 hours is the MTD.
B. The Recovery Time Objective (RTO) is the earliest time period and a service level within which a business process must be restored after a disaster to avoid unacceptable consequences associated with a break in business continuity. The RTO value is smaller than the Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) value, because the MTD value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line. In this scenario 28 hours is the RTO and 48 hours is the MTD.
![]() A is incorrect because the RTO value is 28 hours. The RTO assumes that there is a period of acceptable downtime. This means that a company can be out of production for a certain period of time (RTO) and still get back on its feet. But if the company cannot get production up and running within the MTD window, the company is sinking too fast to properly recover.
A is incorrect because the RTO value is 28 hours. The RTO assumes that there is a period of acceptable downtime. This means that a company can be out of production for a certain period of time (RTO) and still get back on its feet. But if the company cannot get production up and running within the MTD window, the company is sinking too fast to properly recover.
![]() C is incorrect because this value does not represent either the RTO or MTD value.
C is incorrect because this value does not represent either the RTO or MTD value.
![]() D is incorrect because this value does not represent either the RTO or MTD value.
D is incorrect because this value does not represent either the RTO or MTD value.
31. In this scenario, which of the following is the Work Recovery Time value?
A. 48 hours
B. 28 hours
C. 20 hours
D. 1 hour
![]() C. The Work Recovery Time (WRT) is the remainder of the overall MTD value after RTO. RTO usually deals with getting the infrastructure and systems back up and running, and WRT deals with restoring data, testing processes, and then making everything “live” for production purposes.
C. The Work Recovery Time (WRT) is the remainder of the overall MTD value after RTO. RTO usually deals with getting the infrastructure and systems back up and running, and WRT deals with restoring data, testing processes, and then making everything “live” for production purposes.
![]() A is incorrect because in this scenario 48 hours is the MTD value.
A is incorrect because in this scenario 48 hours is the MTD value.
![]() B is incorrect because in this scenario 28 hours is the RTO value.
B is incorrect because in this scenario 28 hours is the RTO value.
![]() D is incorrect because this value does not represent the Work Recovery Time.
D is incorrect because this value does not represent the Work Recovery Time.
32. In this scenario, what would the 1-hour time period be referred to as?
A. Recovery Time Period
B. Maximum Tolerable Downtime
C. Recovery Point Objective
D. Recovery Point Time Period
![]() C. The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. This value represents the earliest point in time in which data must be recovered. The higher the business value of data, the more funds or other resources that can be put into place to ensure a smaller amount of data is lost in the event of a disaster.
C. The Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is the acceptable amount of data loss measured in time. This value represents the earliest point in time in which data must be recovered. The higher the business value of data, the more funds or other resources that can be put into place to ensure a smaller amount of data is lost in the event of a disaster.
![]() A is incorrect because this is a distracter answer. There is no official term Recovery Time Period.
A is incorrect because this is a distracter answer. There is no official term Recovery Time Period.
![]() B is incorrect because the Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line.
B is incorrect because the Maximum Tolerable Downtime (MTD) value represents the time after which an inability to recover significant operations will mean severe and perhaps irreparable damage to the organization’s reputation or bottom line.
![]() D is incorrect because this is a distracter answer. There is no official term Recovery Point Time Period.
D is incorrect because this is a distracter answer. There is no official term Recovery Point Time Period.