SEO for 2016: The Complete Do-It-Yourself SEO Guide (2015)
Chapter 1. SEO
When people come up to me when I am speaking at shows or other book signing events, they many times ask me "What is SEO?” I quickly reply, "No one uses the telephone book anymore, right?" At this point I usually get a nod "yes". Then I continue, "People use Google, Bing or Yahoo! as their telephone book." Then I go on, "If your company's website is not on the first page of Google, Bing, or Yahoo! for a search for your product or service, you are either losing a lot of business or your business is going to fail. Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the exact science to get your website up on page 1 of a search. If your website is on page two or later for the keywords that define your product or service, you are invisible on the Internet."
Almost every company now has a website but less than 5% know of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) or use as part of their company’s marketing plan. This is a huge mistake the the bottom line. One of the largest Internet statistics organizations in the world is AccuQuality.com. In their August of 2015 Internet Usage Report it reported that those companies who use professional SEO services garner over 72% of all clicks on the Internet. So if SEO is not part of your marketing plan it should be. Those using PPC gained a mere 11.2% of the clicks. Only 2% of the 4 billion business websites out there got traffic from search engines that didn't pay for it with PPC or use SEO. Most of those have good brand names and have been around for many years. Another interesting new statistic this year is that over 35% of all sales online come from mobile devices. This is pretty interesting as it is almost an 18% jump in four years.
NOTE: Statistics from AccuQuality.com report used with signed permission statement.
To do SEO right you now need to also remember to utilize Google and Bing's Webmaster Tools as well as Google Analytics. These tools have all changed and been made extremely useful tools with many monitoring and notification features.
As I said earlier, the Internet is now the telephone book and as a business you have to adapt and not only adapt well, but one up your competitors so your website URL comes up at the top of the list in any keyword search. No longer can you just pay $2,500 a month for a full page ad in a telephone book to stand out. You have to do the equivalent on the Internet. Your website has to stand out in the center of 4 billion other business websites and outshine all the other competitors in your industry to be successful.
My website looks better than my competition! I’m good, right?
Good SEO does not really care about the look and feel of your website for the most part. You want to have a great looking website but you have to incorporate about 150 different coded items that Google and the other search engines look for and the list grows every year. The coding behind the look of your website is actually more important to the search engines than what your visitors see when they come for a visit. That's why some of the ugliest websites make the first page of Google. It really boils down to a task of marketing your website not only to your customers but to the search engines as well.
Search Engine Algorithms
First off, many people do not know what a search engine algorithm is. Another mistake is thinking Google has just one algorithm when it is actually many. Each algorithm has a specific task to perform. An algorithm is basically a program that is made to filter data and provide or changes based on the results.
Sidebar: How do search engines collect information on websites?
Search engines and Google collect information on every website using little programs called bots, crawlers, or spiders. These little programs have visited virtually every website on the Internet to collect information on every one of them. These little programs collect keywords, phrases, links, and other coding located on every website. It then stores this information in huge databases used by the search engines to apply filters called algorithms. A virtual copy of almost every publically available website worldwide can be found in these search engine databases.
To make it easy to understand, imagine that you have a list in an Excel document and it contained 5,000 names and you only wanted to know the names in the list that had the last name of Smith. You could write a small program that found only the name Smith and displayed those entries with only that name. That is a basic algorithm. Now Google's algorithms are much more complex and the amount of data it has to filter is almost unimaginable but each algorithm Google runs has a specific task and changes displayed results differently.
In 2015, Google used many new algorithm changes to shake things up. Each algorithm has a specific purpose or filter. Let’s take a look at some of the Google Algorithms in recent history that really shook things up. Let’s take a look at these major algorithms in the next few sections.
Skynet RankBrain Algorithm
Have you ever seen many of the movies or TV shows where humans try to make robots as smart as people and then the robots try to take over? One of my favorites is the Cylon’s from the TV show Battlestar Galactica. Killer robots.
Well from the reaction of the SEO community you would have thought that the Cylon’s were attacking us when Google announced that they were implementing what they are calling the RankBrain Algorithm in my many of the searches Google performs.
In 2014 Google acquired an artificial intelligence company called Deep Mind and this appears to be its first attempt at using some of that newly acquired technology in to searches.

So Google came up with a machine that they are calling Artificial Intelligence(AI) that they think has the ability to learn and understand colloquial human speech. Google’s new ranking factor is called Skynet RankBrain. In early attempts with AI the machines the machines struggled with being able to figure out the nuances of the human language. The new RankBrain AI is able to use complex long-tail context clues such as the user’s location to understand the searcher’s actual intent to deliver more relevant results.
So how do we optimize for RankBrain?
For those SEO Writers and webmasters out there. Fear not. RankBrain isn’t going to drastically change how you create your content or much how you change what you are doing with design. That is if you are following Google’s Webmaster guidelines and best practices. There are some steps that you can take to ensure that your website content is ready for Google’s AI.
Much of this goes back to the old ways of delivering content to your prospective website visitors:
Find a compelling subject and match a keyword.
Offer a fresh and possibly alternative perspective or a unique angle on your subject matter. Be sure to include a targeted keyword or two in the text you are creating. Make sure the words people would be searching for are in the text. Don’t forget that part of AI is matching complete sentence searches which someone who might be do a Siri or Cortana query from a phone. Normally these are complete sentences.
Include a Q & A at the bottom of the page.
What is the best way to get complete phrases as a keyword for phone searches? Add a list of questions and answers at the bottom of your page. Think of your product or service you are trying to pitch. Then hold your own phone to your mouth and ask your phone to search for it based on what you would look for. Then explain your product or service to a teenager and see what they would search for. You might be surprised by the different results. You can optimize your page for several of those longer tail keywords if you know what they are. Every time you find a new way of querying for your product or service you can simply add a new question and answer in to the bottom of your web page without adding a whole new page.
Do a sanity check though and make sure that consumers are actually using the keywords that you are optimizing for to search for your product or service. You can learn more in the next chapter on how to do this.
Don’t target for lots of visits like most people try to do. Don’t target Keywords that are unlikely to bring visitors to buy your product or services even though they are searched for more than average.
TIP: Standard optimization applies. RankBrain definitely analyses a web page to make sure it follows Google’s guidelines and has good coding. Make sure that after you create that great content that you insert your keyword phrase throughout the content, post them in specific locations such as the URL, title tag, H1, H2, in emphasized text in the body of the post, and in the ALT tags on images. (You will learn about this in the next few chapters.)
Other things to note for RankBrain factors.
There are a few other key notes for RankBrain factors:
1. RankBrain is only one of many algorithms and not used in every search.
2. The RankBrain algorithm uses less “Exact Match Keywords” than many of the other algorithms. It looks for more variations in how the keywords are used on a page. Some algorithms allow you to use one or two exact match keywords in every paragraph and you watch your rankings rise. But RankBrain emphasizes the importance of using several variations of your targeted keywords. Even though it’s a machine AI, the key here is to write for like a human.
3. Later in this book you will learn about semantic markup which actually gives you an easy way of providing the context that RankBrain is looking for. Semantic HTML markup is used to illustrate your targeted subject matter by allowing you to tag the appropriate content or target of a page.
When it’s all said and done, RankBrain is just another advance in semantic search. If you align your website with Google practices your rankings should fall in line and bring in visitors. You will learn more about optimizing your pages for both best practices and the RankBrain algorithm throughout this book.
Panda Algorithm
This is a series of algorithms with the specific purpose of filtering based on content or words that are actually seen on the page. It looks for such on-page factors as such as how much content is on a web page, whether the content is duplicated on the same website or on other websites, and how often the content is updated on the page.
This is the algorithm that runs and really shakes things up. This has been a very active algorithm in the past three years and we have seen over 25 changes to this algorithm since it was announced.
Penguin Update
This algorithm's primary purpose is to look for over-optimization factors on website pages and other factors such as linking. This algorithm is more of a shakeup algorithm. It runs periodically to shake things up and other algorithms that run later actually reverse most of the effects of this algorithm within two to four weeks.
Penalty Algorithms
These are algorithms that are run by Google that penalize websites based on certain criteria. Such criteria as links from porn or hate websites, links from certain identified paid link farms, unnatural link building, negative reviews, negative PR, duplicate content, high bounce rates which can indicate that that visitors were not finding what they were searching for on the website and the visitor left quickly, and many other factors.
Google has many of these and some run just once, some run once a year, and some run all the time.
Domain Name Match
This is an algorithm we began in the summer of 2012 when Google announced the algorithm to scare people from getting or using keyword matching domains. What does this mean? Say you have a roofing company in Miami and people search on Google for "Miami roofing company". To help you in Google's results, you buy the domain name Miami RoofingCompany.com to help you become relevant for that key term. Google uses this algorithm to make that domain name drop in its results for the keyword.
This is really another algorithm that runs to shake things up. Google wants to be the phone book for the Internet. The problem with this algorithm for Google is that when the algorithm runs, many of the domains that are exact matches are well known brand names and Google has really had to turn this algorithm down and it is not very effective.
Manual Intervention
This is something new. It is a process where Google's technical team members can give a manual penalty to a website for just about any reason or take a penalty away. Most are websites that are given penalties are for bad press, bad PR, or using paid linking or link farms.
Hummingbird Algorithm
This algorithm made headlines and so much misleading information was written about this algorithm and what it does. In October of the year it came out, Matt Cutts form Google admitted that it has nothing to do with SEO and works to help with full sentence searches most often used with voice searches.
PDF Algorithm
Believe it or not there is an algorithm that gives PDFs with a keyword relevance enough to make it on to the first page.
NOTE: Each algorithm takes a tremendous amount of processing power and must filter against billions and billions of items in Google's databases. Most only run periodically and some only run a few times a year.
Search Engine Queries
The search query bar is the most familiar part of any search engine. The search query bar is the little box where you type the words related to what you want to find and select a search. In a few moments just like magic, a list of websites shows up on the results screen. Today, the search engines are getting very good at giving you the best results possible. It is rare that you will click on an organic link that is not relevant to your search words or a website that no longer exists. I fit doesn’t give you the right results you need to refine your search words.
Since the Panda Algorithm update was released you also won’t find many websites without recently updated content.
I mentioned organic links in the first paragraph. An organic link is a list of 7 to 10 results on the results page when you type in a search that come up because of the algorithm used by the search engines. Until this year it was standard to see 10 results but Google has been experimenting with pages that have fewer organic results and more paid results.
What’s interesting is that Bing and Google both know where you are based on your IP Address and other geographical indications and cater your organic results to your known location.
NOTE: Google is also getting smarter with personalized results. If you are logged in to Google and you perform the same search multiple times, Google assumes you didn't find the earlier results relevant and gives you a different set of results.
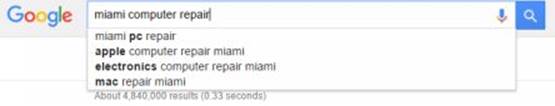
A year ago when I was visiting Miami Florida and sitting in a hotel I looked up the keywords “Miami computer repair”. So as I typed you can see below how Google gave me suggested keywords and the organic result searches. This is important later on when choosing keywords as studies are showing that users chose these suggestions more than 50% of the time as you can see below.

I decided to do the same search today just to see how the suggested keywords changed as you can see in the screenshot below.
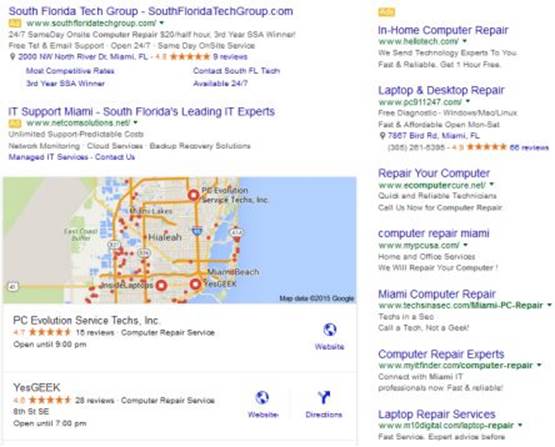
You will also notice from the next screenshot above that I did not specify any address or whether it was for Miami Florida or the city of Miami in any other state. It only gave me results for computer places in Miami Florida where I happen to be at the time. More important than that, I got computer places just around the hotel I was staying at. It knows this information simply from the IP Address my computer is using to access the Internet. It's absolutely amazing how far search engines have come and how fast their advanced algorithms work.
So now I need to tell you a new term you will see throughout this book with the initials SERP or SERPs. When you type in a string of words to get relevant results and then click search, the collection of pages you see with the results are termed search engine results pages (SERPs)in the search engine world. The higher your business or entity is found on search results pages, the more traffic you can expect to generate from searches on those key words.
It has been proven that those in the top 20 get the most clicks, as users typically do not go beyond page 2 of a search. If your website is in the first five results in a search, given that the description you created for your website is enticing to the search, you will get the most clicks for that keyword. Your goal is to get your website at least on page one of the searches that are most relevant to the services or products your business provides. It really is sink or swim.
If you are on page one for a search you get all the business in the world. If you are on page three or more you will be virtually invisible. Sales really are a numbers game. If your product or service makes a sale on an average of 1 out of every 10 visitors to your website, the more visits you get the more sales you will make.
Something very interesting has happened with Google the past few years and the first I heard about this was from AccuQuality.com's Internet Usage Report for 2015. This report lists major trends and usage behavior and something big caught my eye. Being in the first position of Google for most searches will not land you the most clicks anymore. At first I thought this couldn't be true. The results in the past year have been astonishing and user behaviors have really changed and in a significant way. Most clicks for almost all keywords on Google based on their research are coming from positions two through six on the first page of SERPs.
There are many reasons cited in the report but the most common given by users is Google has done a good job at masking where the PPC results are and the first organic results start. Google appears on many video screens as part of the PPC ad group above the page. This is important because many people trust organic results much more than pay-per-click results. Search engine users click on organic results 90% of the time. Almost anyone can pay money for PPC and many of the PPC ads shown on pages have no relation to their searches as the organic results more often do.
Secondly, many people believe the first website in Google's results are either have the most expensive products or services or they are paying Google to be there. This last reason is because the 1st organic result on a SERP is often by itself underneath the PPC results at the top but above the Google Products listings or the Local Places results. It creates some confusion. Google is constantly changing the page layouts as well to make it even more confusing.