SEO For 2013 & Beyond: SEO Made Simple For Beginners (2013)
Chapter 6. ADVANCED SEO CONSIDERATIONS
The purpose of SEO shall not remain confined within the narrow alleys of keyword research and on-page techniques only. The need to reach out is real and cannot be overlooked at any cost.
Many experts suggest that search engines follow traffic. If a website or a webpage is being visited by a large number of people coming from different sources other than search results, then the search engines will sit up and take notice of that very quickly.
In other words, spare no effort to break out from the mold of copybook style of SEO, and do everything ethically possible to spread the influence of your website. In this chapter we will discuss some of the steps that enhance the ability of a website to be seen by more visitors.
The emphasis is on envisioning the bigger picture that can rapidly grow your website while helping it mature over time.
Image Optimization
A significant part of the information available on the net consists of images. Starting from logos and headings to charts, graphs, and myriad pictorial illustrations, there is no dearth of images that, like texts, support the information being conveyed to the surfers who scour the net.
Though images are long-standing companions for texts, people barely search for them exclusively for informational needs. They rather look for images which in some instances they can replicate or suitably alter for their requirement. From search engines’ point of view, there is no way telling how good and relevant an image is at the place of its usage except for 3 parameters:
1. Name of the image,
2. Title of the image, and
3. Alt attribute of the image
As can be seen, it is easy to manipulate all the 3 parameters to give the search engines a false idea of keyword relevance even while showing a completely irrelevant image. This is a dangerous game to play for the sake of ‘SEO on the fast lane’ simply because such tricks inevitably bring down the goodwill and the prestige of a website.
As opposed to text optimization for the search engines, there is generally an absence of clear-cut directives for optimizing images. This may be partly because of the accepted views that the search engines cannot yet decipher the actual content of rich media like images, and whatever is available for consideration is nothing but texts associated with them.
However, based on user experience, some important factors with regard to image optimization are explained below:
1. Use descriptive name for the image file that has the keyword phrase in it. For example, if a page is on fashion jewelry, then you can name the jewelry image in the page something like ‘glittering-set-of-fashion-jewelry.jpg’.
2. The image title is said to have no SEO-related importance. Yet in many browsers, the visitors see it while moving the cursor on the image. For that reason it is better not to omit the image title. This too can be made lengthier while using a variation of keyword phrase. For example, it can be ‘Designer jewelry for fashion is a must wear’.
3. Alt attribute is considered the most important from SEO point of view. Here is what Jill Whalen, the SEO expert, has to say6.1:
But the alt attribute text of clickable images seems to be treated very similarly to anchor text in an all-text link.
Note there are 2 issues here. One, the image has to be clickable, and two, the alt attribute text is similar to anchor text in an all-text link. The alt attribute should have the keyword phrase, but once again, use it in a long sentence.
Example of embedding a clickable image with the title and alt attribute is as under:
<a href=””><img src=”glittering-set-of-fashion-jewelry.jpg” title=” Designer jewelry for fashion is a must wear” alt=“Affordable designer fashion jewelry” width=”″ height=”″/></a>
4. It is better to be cautious and not use the keyword phrase in the alt attributes of more than 2 images in a single webpage. Else, it may be considered as spam by search engines.
5. According to some experts6.2 the text near the image in the HTML is also important, and also the image age.
6. An image is considered authoritative based on the page it links to upon clicking, and what other pages, if any, link to it.
7. In eye-tracking experiments6.3 jointly by The Poynter Institute and 2 others, it has been found that larger online images hold the eye longer than smaller images. At least 210 x 230 pixels in size were viewed by more than half of the testers, and clean, clear faces in images attract more eye fixations on homepages.
Researchers routinely conduct various studies to understand how online images are perceived by the visitors, and what, if any, can be done to the images to ensure enriching user experience in a webpage.
Authority of Your Website – Relevant Contents
People love authority. They like command. These are the qualities that give them the satisfaction of being at the right place at the right time. Search engines follow (rather, made to follow through logic-supported algorithms) these human traits rather closely. And why not!
Picture yourself looking for information on royal Bengal tiger for one of your projects. When you search for the term you’ll come across results that show quite a few pages from the tourism sites.
But the ones that rank at the top are from the prestigious content sites like Wikipedia, National Geographic, and the like. You are likely to visit these pages since your need is to collect reliable information for your project.
The search engines give importance to the pages from the websites that command authority on the strength of the contents they contain. This ‘strength’ is not built overnight. It accrues to a website over a length of time when the site goes on adding pages of relevant contents optimized for search engines.
I have extensively dealt on web contents in the earlier chapters. But to summarize again, here are 4 important factors to consider:
1. Build contents for your website having relevance with the main thrust of the site. For example, in a website on web video production, continually have contents that concern with the different aspects of video making.
2. Each content page needs to be optimized for one or two relevant key-phrases. This will work as a signal to the search engine robots as to the importance of that webpage with respect to the chosen key-phrase.
3. Keep on accumulating relevant contents.
4. Ensure that the contents you create, though relevant, are actually helpful to your readers, and not some gibberish only aimed for ranking.
Authority of Your Website – Incoming Links
Perhaps the most sought-after and prized gifts for any website are incoming hyperlinks to it from other websites. This is one asset the need of which never ceases, both for the website concerned and other websites that link to it.
Incoming links are obvious stamps of authority. The famous link analysis algorithm, PageRank, named after Google founder Larry Page, is an indicator of the importance of a webpage as viewed by Google.
Google describes PageRank6.4 as under:
PageRank reflects our view of the importance of web pages by considering more than 500 million variables and 2 billion terms. Pages that we believe are important pages receive a higher PageRank and are more likely to appear at the top of the search results.
PageRank also considers the importance of each page that casts a vote, as votes from some pages are considered to have greater value, thus giving the linked page greater value. We have always taken a pragmatic approach to help improve search quality and create useful products, and our technology uses the collective intelligence of the web to determine a page's importance.
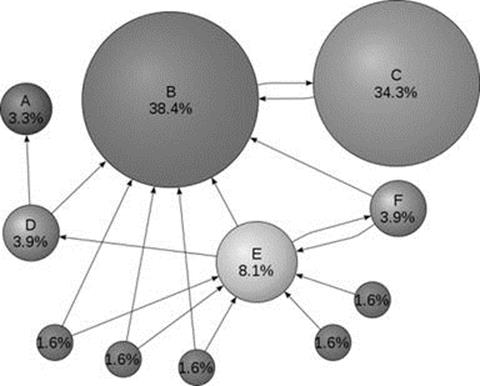
Figure 6.1
From the pictorial illustration6.5 of PageRank above (Figure 6.1) above it is clear that getting incoming links from good quality webpages should be a priority for any website owner. The reality is however quite harsh.
No one gives links on request unless the link-donor decides that doing so will fetch rewards. This aspect needs to be understood clearly.
Large authoritative sites whose links do count a lot will hardly bother to give links to a startup. Those that give when approached may perhaps ask for favors in return that may prove costly for startups.
Small and medium websites often spend good amount of resources to get incoming links from others, which in case of authority websites is akin to chasing the mirage. In the long run, such do-or-die efforts spread the resources so thin that the website itself becomes unviable to run properly.
The best advice therefore will be to first build authority of your website with relevant contents, and only after that there can be moderate attempts toward the goal of getting quality incoming links.
Apart from creating quality contents over a period of time, there can be a 2-pronged approach to build authority of your website through links by:
1. Giving stress on internal linking among the pages of your website with keyword variations as anchor texts. This must be followed to the maximum extent, especially since this is well within the control of the website owner.
2. Reaching out to get links, like writing in top web publications, guest-blogging, and so on (covered in the next chapter).
Speed of Website Pages
Why and how is website speed important? Let us hear from horse’s mouth. This is what Google has to say in the Official Google Webmaster Central Blog6.6:
You may have heard that here at Google we're obsessed with speed, in our products and on the web. As part of that effort, today we're including a new signal in our search ranking algorithms: site speed. Site speed reflects how quickly a website responds to web requests.
2 things become clear from the above.
1. Google is obsessed with site speed, and so
2. Site speed is an important parameter in Google’s search ranking algorithms.
This means how fast or slow your webpage loads in a browser is one determining factor (among others) in the rankings of Google’s search results.
Google’s internal studies6.7 have shown that slowing down the search results page by 100 to 400 milliseconds has a measurable impact on the number of searches per user, which, though seemingly small, has real consequence at the scale of Google web search.
Google goes on to say that it encourages site designers to think twice about adding a feature that hurts performance if the benefit of the feature is unproven.
There is pretty much you, as a website owner, can do to improve the speed of your website. Yahoo Developer Network (YDN) has charted out best practices for speeding up web site6.8. Some among them are as under:
· Minimize HTTP requests
· Use a Content Delivery Network
· Put style sheets at the top
· Put scripts at the bottom
· Make JavaScript and CSS external
· Minify JavaScript and CSS
· Avoid redirects
· Remove duplicate scripts
· Minimize the number of iframes
· Optimize images
How to Know Page Speed
To be cautioned is a good idea, but even better is to be able to have a good measurable data of that. There are quite a few tools that Google and Yahoo suggest using to find out the loading time of the webpages.
A few of them are mentioned below:
1. Yahoo YSlow6.9 analyzes web pages and suggests ways to improve their performance based on a set of rules for high performance web pages. It is a Firefox add-on6.10, and has the Firebug web development tool integrated with it.
2. Similar to YSlow, Page Speed6.11 is the tool for optimizing the performance of webpages. This also is a Firefox/Firebug add-on, and has later been utilized in some third-party products.
3. WebPagetest6.12 is based on the technology of Page Test, but it’s an online tool. You have to enter a website URL, and start testing. A little later you’ll get the page’s performance in both analytical and visual formats.
4. Pingdom Tools6.13 is my favorite. Like WebPagetest, this one too is available online (see Figure 6.2). It is fast and provides good amount of information like total loading time, total objects, number of scripts and images, and so on. The results also give a glimpse of the size and the time taken by each object to load in the page.

Figure 6.2
Age of Website
There is a lot of conjecture about the age of a website playing a prominent role in Google’s algorithms for search ranking. Many people feel older websites are seen favorably by Google, while others say that more than the website, it’s the age of the domain name that is more important.
The truth is not known because Google, to the best of my knowledge, has not commented upon the matter. You may like to think that if at all Google gives preference to older sites then all the new web ventures, howsoever attractive, will always remain at a disadvantage.
This looks unlikely. If however a new website with a new domain gets prominence with lots of incoming links in a short time, then it can raise doubts in Google’s minds. This is something that was some years back referred to as the Sandbox effect6.14.
Having said that, when you are going to start a new website consider the following domain-related steps as enumerated by webconfs.com6.15.
1. Make sure you register your domain name for the longest amount of time possible.
2. Consider registering a domain name even before you are sure you're going to need it.
3. Think about purchasing a domain name that was already pre-owned.
4. Keep track of your domain's age. One of the ways you can determine the age of a domain is with this handy Domain Age Tool6.16.