How a Computer Works (2015)
2. Inside the P.C
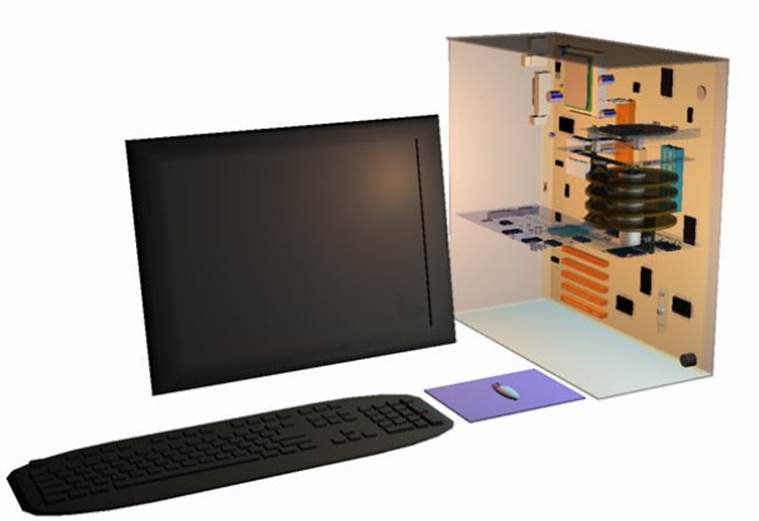

Case

To protect the fragile P.C (personal computer) against damage it is housed in a case. Different case styles are available. A tower case is useful where desktop space is limited as it can go on the floor. The disadvantage here is accessing the CD ROM/DVD drives to change disks. A desktop case as its name implies sits underneath the monitor and allows disks to be easily accessed. The case is plastic or metal.
Peripherals
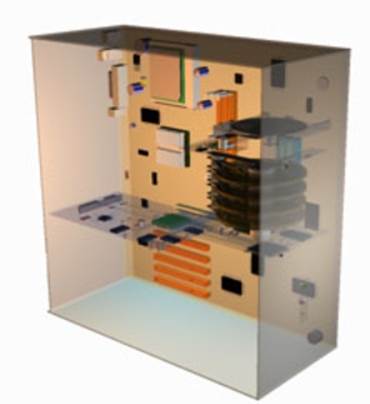
Most peripherals sit inside the case. Others for practical reasons sit outside. Often when buying additional peripherals such as a hard drive a choice is available of internal or external types.
The internal types tend to be less expensive as the casing is less protective.
Outside of the case
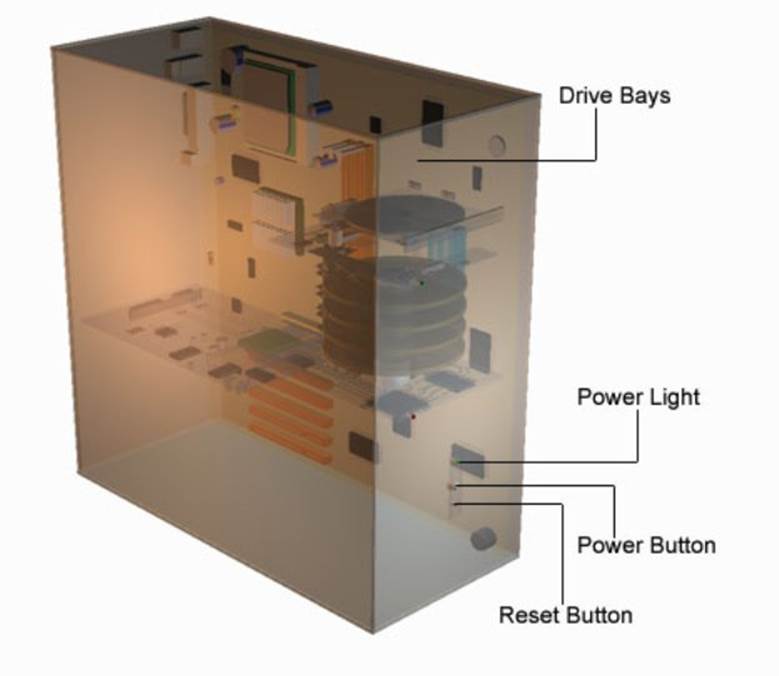
On the outside of the case are the drive slots and power, reset buttons. Small l.e.ds (light emitting diodes) light up when the power is on and the hard drive is being accessed.
Connections
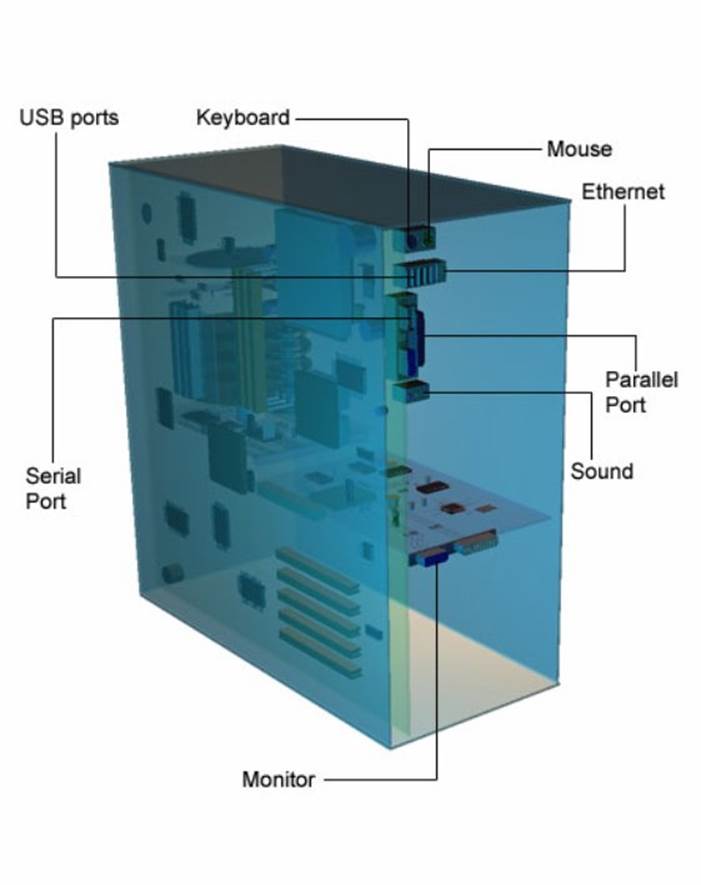
The back of the case contains all the connectors for external peripherals like the mouse, keyboard, monitor and printer.
Motherboard
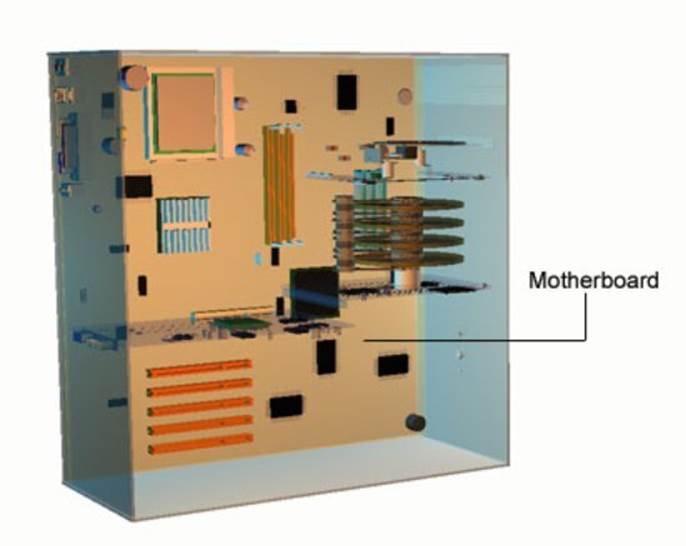
Inside the case a large p.c.b (printed circuit board) called the motherboard sits. The motherboard circuit and microchips control the computers operation.
E-IDE
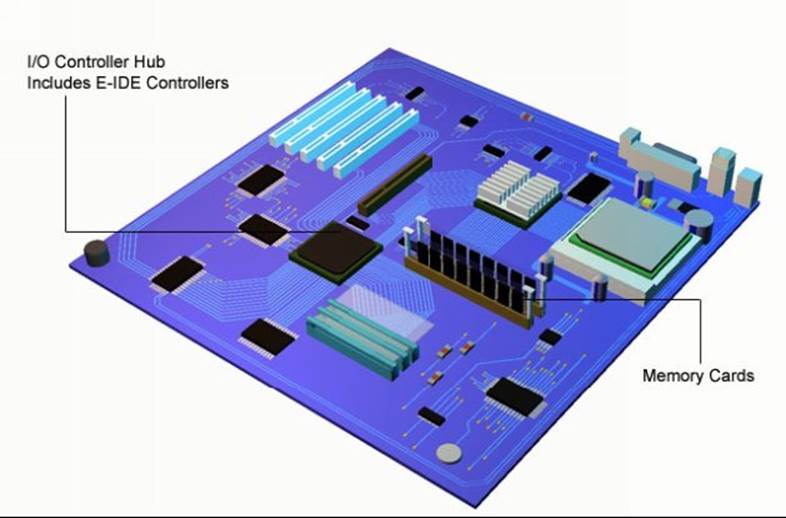
All internal and external peripherals connect to the motherboard. The connectors for these are soldered directly to the motherboard and protrude through the rear of the case.
Memory cards are slotted into special connector strips, this enables, where permissible, memory cards to be changed and upgraded to bigger memory cards.
E-IDE connections are made through ribbon cable to the CD-ROM/DVD and hard disks.
Jumpers
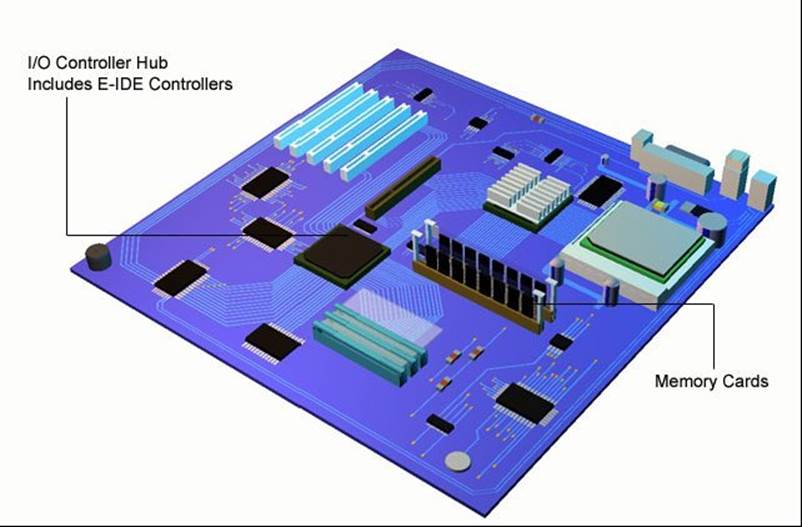
Spare connectors enable additional internal drives to be added. Adding a new drive is just a case of pushing a spare connector onto the drive and changing a jumper setting.
Jumper settings are small metal posts on the motherboard, which a jumper connection connects across.
Blanking Plates
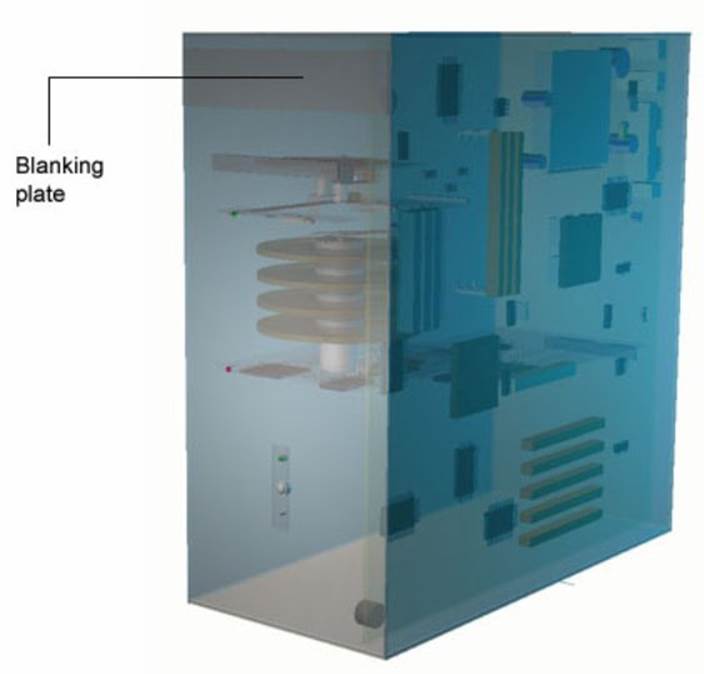
Blanking plates on the front of tower cases are pushed out for the new drive to slot in.
AGP Slot
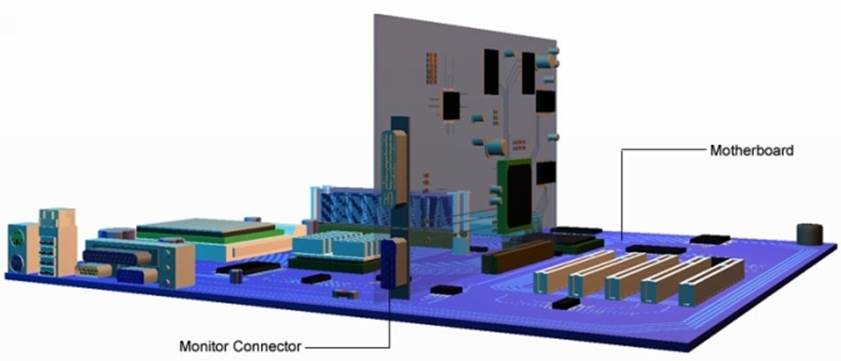
The AGP slot is where the graphics card is connected. This card interfaces the motherboard to the monitor. The monitor connector protrudes through the rear of the case.
PCI Slots
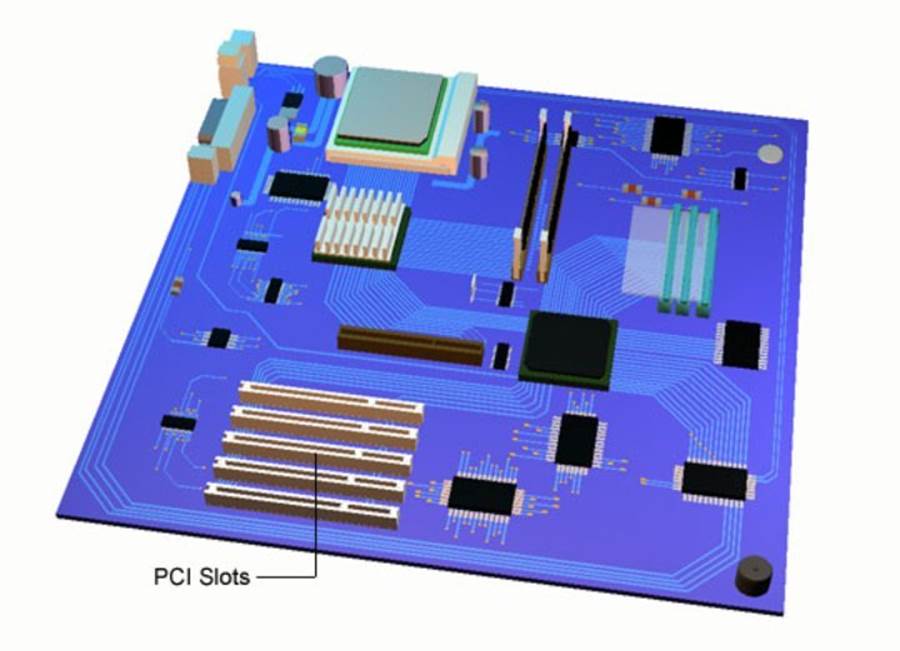
PCI slots enable expansion cards to be fitted. Expansions cards like sound, MIDI, SCSI (small computer systems interface).
The motherboard itself can be replaced for one with a more powerful processor; this saves the cost of buying a new system.

Power Supply: (Not Shown) The mains lead connects to a transformer which steps down the mains voltage to a lower voltage, 5 volts etc. Each internal component and peripheral draws their electricity from the power supply.
Case: The case is made from metal or plastic and protects all the components and peripherals from dirt and damage.
CD-ROM Drive
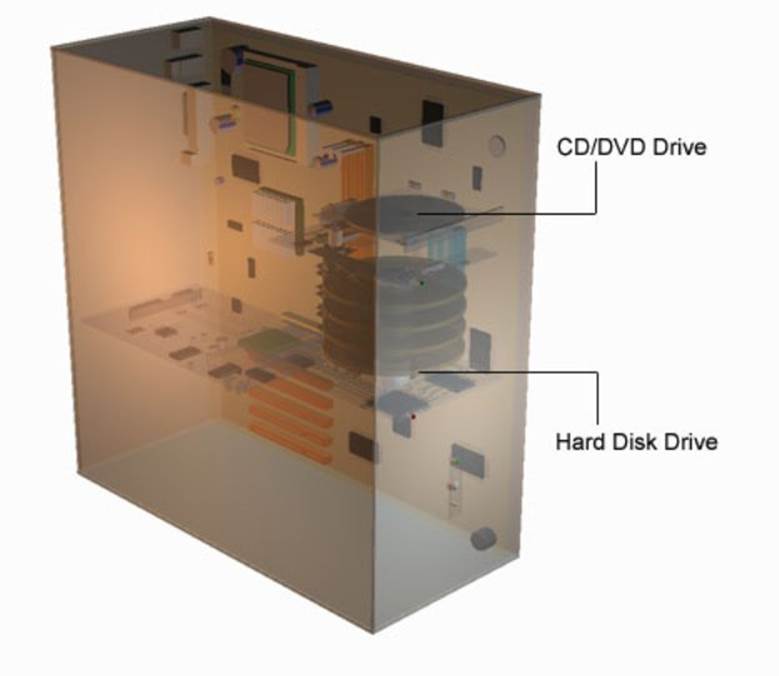
This optical drive uses a laser beam to read data bits from a CD (compact disk). Most software programs are distributed on CD.
Music CD’s can also be played providing a sound card and speakers are in the system.
Most systems include a CD-RW that enables data to be written to CD-R and CD-RW disks.
A DVD drive enables DVD disks to be played in systems that have the necessary video card.
Hard Drive
Hard Drive: The operating system, programs and data files are stored on magnetic platters. The platters spin at high speed and enable data bits to be transferred to the computer at high speed.
E-IDE Controllers
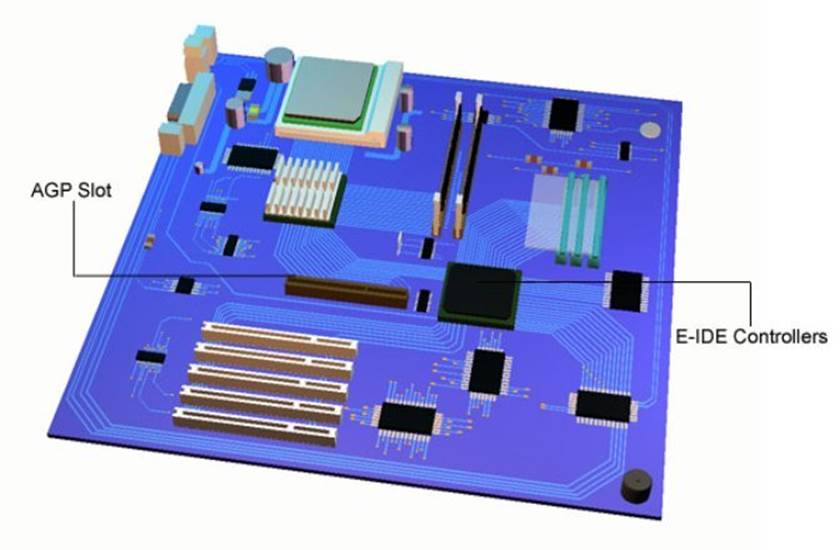
E-IDE Controllers: Built into the motherboard these provide a standard interface for transferring data bits between the drives and computer.
AGP Expansion slot: A 3D graphics card slots into the accelerated graphic port connector to provide high-speed access to the computer’s memory.
Display Adapter
Display Adapter Interfaces the motherboard to the computers monitor. The Display Adapter (Also known as the Graphics Card) contains its own memory and microchips to display information on the monitor.
Expansion Slots

PCI Expansion slot. The PCI (Peripheral component interconnect) expansion slots are designed for Plug and Play expansion cards.
Sound Card
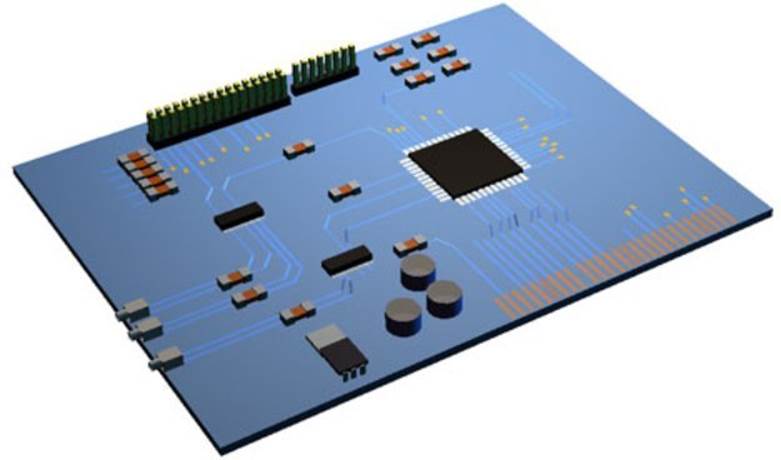
The sound card maybe an expansion card or be built into the motherboard. The sound card provides an analogue to digital converter (ADC) for converting external sounds into digital data bits that can be saved on the hard drive.
The card also includes a digital to analogue converter for playing sound files stored on the hard drive.
A MIDI port is also included on some cards for interfacing the computer to musical instruments.
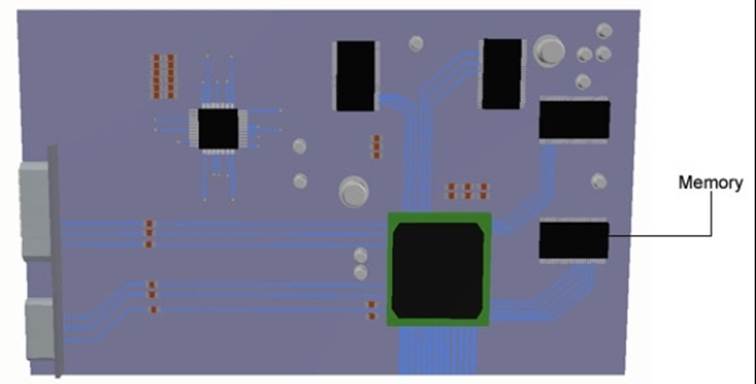
Memory Card
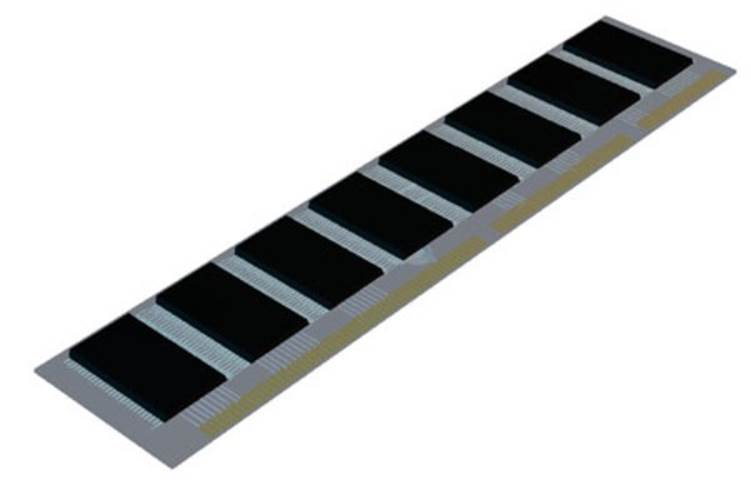
The memory card provides on-board memory for the computer.
The RAM (Random accessible memory) chips are soldered onto a small PCB that slots into a connector on the motherboard.
Clock
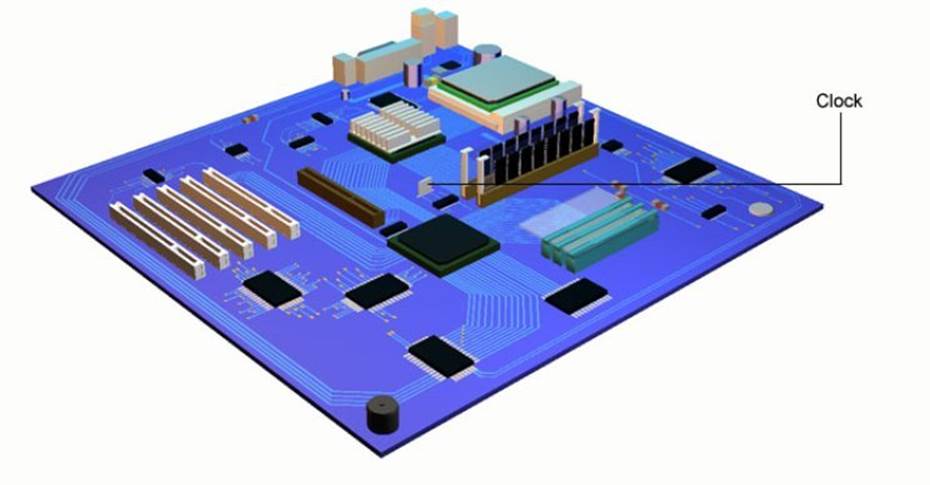
The real time clock is an electrical crystal quartz that sends out a timing signal at a certain frequency that all the microprocessors synchronize with. The clock ensures all data bits are transferred in step at the right time.
BIOS and CPU
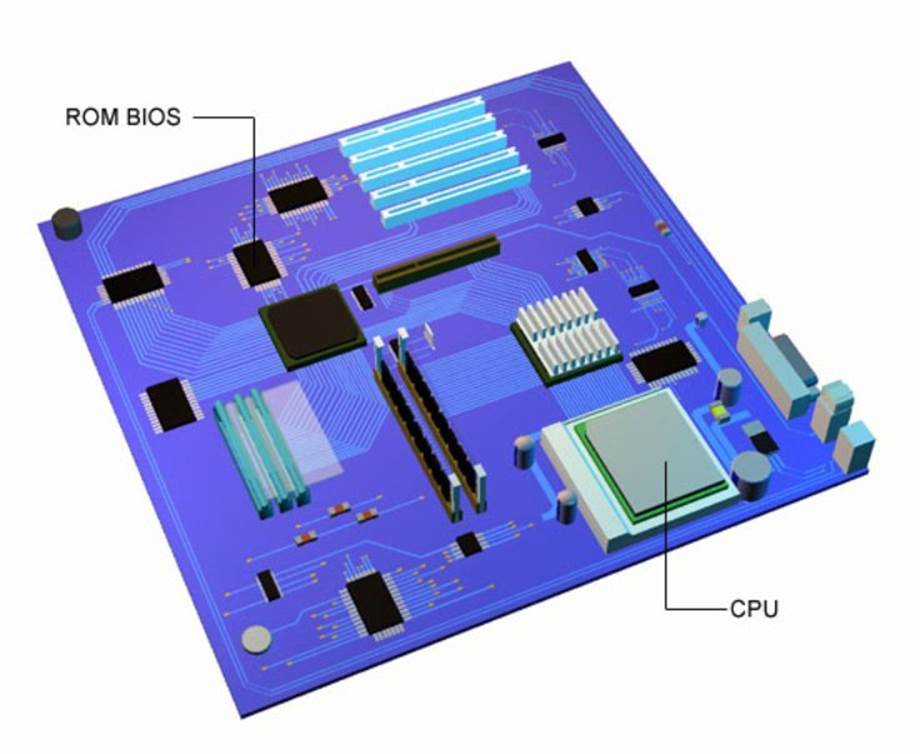
BIOS: The BIOS (basic input/output system) is an intermediary between the operating system and the various connected peripherals.
CPU: The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the brains of the computer. Almost all data bits travel through the CPU as it carries out most of the computers operations.
USB
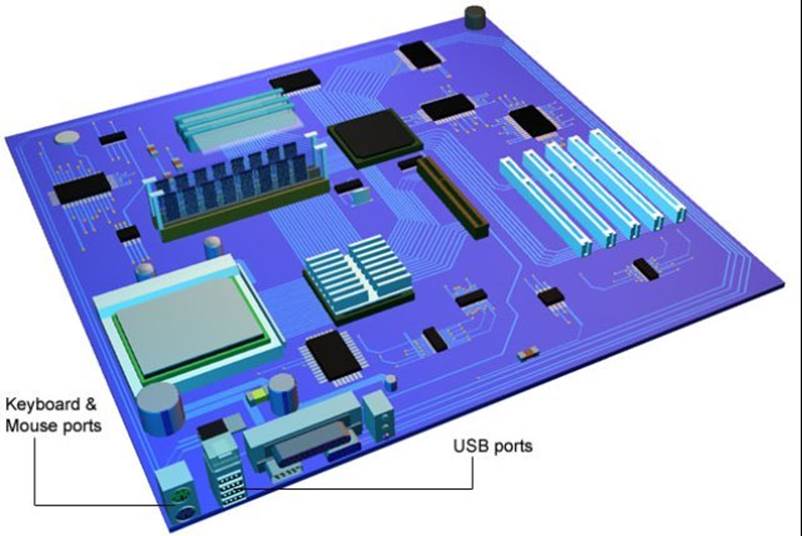
USB Ports: Universal serial bus ports let software programs connect directly to peripherals like the mouse, keyboard, printers and monitors without encountering resource conflicts.
Mouse Port: The mouse connects to this port, also known as a PS2 port.
Keyboard Port: The keyboard connects to this port.
Ports
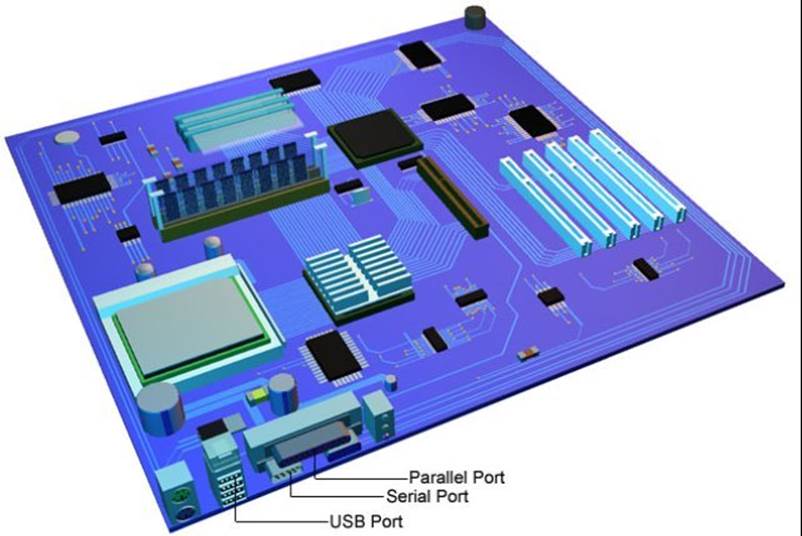
Parallel Port: Most often used to connect a printer.
Serial Port: The modem or certain types of mouse connect to the serial port.
All materials on the site are licensed Creative Commons Attribution-Sharealike 3.0 Unported CC BY-SA 3.0 & GNU Free Documentation License (GFDL)
If you are the copyright holder of any material contained on our site and intend to remove it, please contact our site administrator for approval.
© 2016-2026 All site design rights belong to S.Y.A.